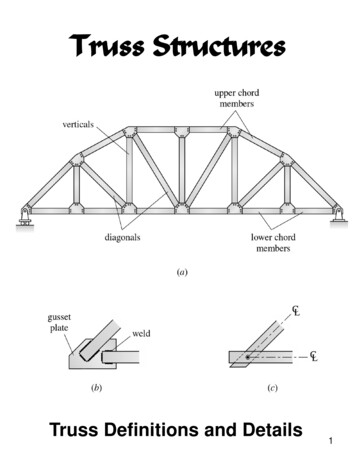
Transcription
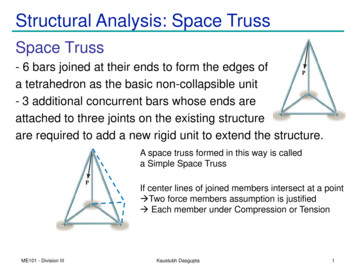
Structural Analysis: Space TrussSpace Truss- 6 bars joined at their ends to form the edges ofa tetrahedron as the basic non-collapsible unit- 3 additional concurrent bars whose ends areattached to three joints on the existing structureare required to add a new rigid unit to extend the structure.A space truss formed in this way is calleda Simple Space TrussIf center lines of joined members intersect at a point Two force members assumption is justified Each member under Compression or TensionME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta1
Space Truss Analysis: Method of Joints Method of Joints– All the member forces are required– Scalar equation (force) at each joint Fx 0, Fy 0, Fz 0– Solution of simultaneous equationsME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta2
Space Truss Analysis: Method of Sections Method of Sections– A few member forces are required– Vector equations (force and moment) F 0, M 0– Scalar equations 6 nos.:: Fx, Fy, Fz and Mx, My, Mz– Section should not pass through more than 6members More number of unknown forces
Space Truss: ExampleDetermine the forces acting in membersof the space truss.Solution:Start at joint A: Draw free body diagramExpress each force in vector notationME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta4
Space Truss: ExampleRearranging the terms and equating the coefficients of i, j, and k unitvector to zero will give:Next Joint B may be analysed.ME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta5
Space Truss: ExampleJoint B: Draw the Free Body DiagramScalar equations of equilibrium may be used at joint BUsing Scalar equations of equilibrium at joints D and C will give:ME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta6
Recapitulation :: Support ReactionME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta7
Recapitulation :: Support ReactionME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta8
Recapitulation :: Free Body DiagramME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta9
Recapitulation :: Free Body DiagramME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta10
Recapitulation :: Method of SectionsMethod of Sections Find out the reactions from equilibrium of whole trussTo find force in member BE:Cut an imaginary section (dotted line)Each side of the truss section should remain in equilibriumME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta11
Example: Method of Sections Calculate the force in member DJDirection of JK :: Moment @ CDirection of CJ :: Moment @ AME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta12
Example: Method of SectionsME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta13
Frames and MachinesA structure is called a Frame or Machineif at least one of its individual membersis a multi-force member member with 3 or more forces acting on it, or member with 2 or more forces and1 or more couple actingFrames: generally stationary and are used to support loadsMachines: contain moving parts and are designed to transmitand alter the effect of forces actingMulti-force members: the forces in these members in generalwill not be along the directions of the members methods used in simple truss analysis cannot be usedME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta14
Frames and MachinesInterconnected Rigid Bodies with Multi-force Members Rigid Non-collapsible–structure constitutes a rigid unit by itselfwhen removed from its supports–first find all forces external to the structure treated as a single rigid body–then dismember the structure & consider equilibrium of each part Non-rigid Collapsible–structure is not a rigid unit by itself but depends on its external supportsfor rigidity–calculation of external support reactionscannot be completed until the structure isdismembered and individual parts areanalysed.ME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta15
Frames and MachinesFree Body Diagrams: Forces of Interactions force components must be consistently represented inopposite directions on the separate FBDs (Ex: Pin at A). apply action-and-reaction principle (Ex: Ball & Socket at A). Vector notation: use plus sign for an action and a minus signfor the corresponding reactionPin Connection at AME101 - Division IIIBall & Socket at AKaustubh Dasgupta16
Frames and MachinesExample: Free Body DiagramsDraw FBD of(a) Each member(b) Pin at B, and(c) Whole systemME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta17
Example on Frames and MachinesCompute the horizontal and vertical components of all forcesacting on each of the members (neglect self weight)ME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta18
Frames and MachinesExample Solution:3 supporting members form arigid non-collapsible assemblyFrame Statically Determinate ExternallyDraw FBD of the entire frame3 Equilibrium equations are availablePay attention to sense of ReactionsME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta19
Frames and MachinesExample Solution: Dismember the frameand draw separate FBDs of each member- show loads and reactions on each memberdue to connecting members (interaction forces)Begin with FBD of PulleyThen draw FBD of Members BF, CE, and ADME101 - Division IIIKaustubh DasguptaAx 4.32 kNAy 3.92 kND 4.32 kN20
Frames and MachinesExample Solution:FBDsAx 4.32 kNAy 3.92 kND 4.32 kNCE is a two-force memberDirection of the line joining the two pointsof force application determines the directionof the forces acting on a two-force member.Shape of the member is not important.ME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta21
Frames and MachinesExample Solution:Find unknown forces from equilibriumMember BFMember CE[ Fx 0]Cx Ex 13.08 kNChecks:ME101 - Division IIIKaustubh Dasgupta22
Structural Analysis: Space Truss Space Truss - 6 bars joined at their ends to form the edges of a tetrahedron as the basic non-collapsible unit - 3 additional concurrent bars whose ends are attached to three joints on the existing structure are required to add a new rigid unit to extend the structure.