Transcription
Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC IntegrationsCustomer Guide to Avaya DMCCSSC Integrations1www.niceincontact.com
Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC IntegrationsCustomer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSCIntegrationsVersion: Avaya DMCC-SSC versions 4.2.1-8.1 are supported. This guide should beused with NICE Uptivity 16.3 or later.Copyright: 2020 NICE inContact, Inc.Contact: Send suggestions or corrections regarding this guide todocumentationrequests@incontact.com.2
Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC IntegrationsTable of ContentsIntroduction . 5Audience . 5Goals . 5Assumptions . 5Need-to-Knows . 5Terminology. 6Customer Responsibilities . 6Avaya DMCC-SSC Integration Overview . 7Known Limitations . 8Avaya Requirements . 8Hardware . 8Software . 8Licensing . 8NICE Uptivity Requirements . 9Hardware . 9Software . 9Licensing . 9Customer Configuration Overview . 10Customer Integration Tasks . 11Verify DMCC License Availability . 11Verify the Switch Configuration in AES . 123
Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC IntegrationsConfigure Softphone Stations on the AES Server . 13Customer Administration Tasks . 14Channel Configuration Settings . 14Appendix: Avaya DMCC Recording Method Comparison. 154
Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC IntegrationsIntroductionAudienceThis document is written for customers and prospective customers interested inusing Uptivity Call Recording in an Avaya DMCC-SSC telephony environment.Readers who will perform procedures in this guide should have a basic level offamiliarity with IP telephony, general networking, the Windows operating system,Avaya telephony, and NICE Uptivity.GoalsThe goal of this document is to provide knowledge, reference, and proceduralinformation necessary to understand a proposed Avaya/NICE Uptivity integrationusing DMCC-SSC, and to configure the Avaya equipment to support the integration.This document is NOT intended as a specific system or network design document. Iffurther clarification is needed, consult with your telephony vendor(s).AssumptionsThis document assumes the reader has access to an Uptivity Sales Engineer,Project Manager, or other resource to assist in applying this information to thereader's environment.Need-to-KnowsTo facilitate ease of use, this document takes advantage of PDF bookmarks.By opening the bookmark pane, readers can easily refer to the portion(s) ofthe guide that are relevant to their needs. For example, the Uptivityapplication administrator can click on the Customer Administration Tasksbookmark to jump directly to that section.To expand and collapse the bookmark pane, click on the bookmark icon on the leftside of the document window.For questions related to Uptivity configuration, consult the Uptivity installationteam.5
Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC IntegrationsThis integration uses Avaya TSAPI. Refer to the Customer Guide to Avaya TSAPIIntegrations for additional limitations, licensing requirements, and customerintegration tasks.TerminologyTo ensure a common frame of reference, this guide uses the following terms inconjunction with this Avaya integration: AES — Application Enablement Services. The AES server in an Avaya contactcenter hosts software that provides CTI events Avaya CMS — Avaya Call Management System. This contact center product isdesigned for businesses with complex contact center operations and high callvolume. Sometimes referred to as Avaya CM. DMCC — Device Media Call Control. This functionality of the Avaya AES andAACC servers provides a means of active recording via VoIP, even for endpointsthat are not IP telephones. GEDI — Graphically-Enhanced DEFINITY Interface. Used by the customer orAvaya vendor to configure the Avaya CMS. MR — Multiple Registration. Avaya functionality that allows the customer toregister up to three devices against a single softphone extension. TSAPI — Telephone Services Application Programming Interface. Avaya TSAPIis the actual software that provides the call control events and metadata toUptivity. S8300, S8500, S8700 — Common models of Avaya PBX equipmentCustomer ResponsibilitiesYou are responsible for supplying the physical connection(s), IP connection(s), orboth to your telephone system and LAN, and for obtaining and loading any licensingrequired by Avaya. You are also responsible for configuring Avaya systemcomponents to support the recording integration. See the Customer IntegrationTasks section for additional information.6
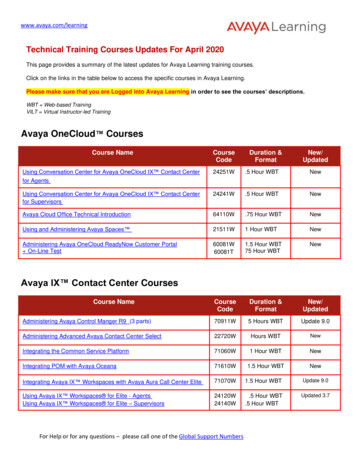
Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC IntegrationsAvaya DMCC-SSC Integration OverviewThe Avaya DMCC-SSC integration uses softphones on the Avaya AES server as theaudio source, and receives call control events and metadata through AES usingTSAPI. NICE Uptivity detects when a station joins a call and makes a request for asingle step conference between Uptivity, the agent's phone, and the correspondingsoftphone on the AES server.General architectural example of the Avaya DMCC-SSC integrationComponentAvaya CM MediaGatewayAvaya AESUptivityRecordingServerFunctionControls audio presented to and from digital phones, IP phones, orboth.Provides DMCC CTI Interface to create and control virtual softphonesfor call recording and to provide call metadata.Receives audio, call control events, and business data. Provides a CTIinterface for recording. May host the Web Portal for playback andadministration.7
Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC IntegrationsKnown Limitations Only devices supporting Physical Device Services can be recorded. This excludesdevices without a speaker-phone (such as CallMaster). This is an Avayalimitation. This integration provides “muxed” (mono) audio and therefore does not supportspeaker separation for reporting or analytics.Avaya RequirementsThis integration requires Avaya TSAPI, which has additional software andlicensing requirements. See the Customer Guide to Avaya TSAPI Integrations.Hardware Avaya S8300, S8500, or S8700 media server Avaya AESSoftware Avaya CM Avaya AESLicensing One (1) DMCC basic license per recording channel: either DMCC DMC on AES orIP API A on CM. One (1) IP station (IP STA) license from the CM per recording channel.A full DMCC license could be used instead, since it includes both the DMCCbasic license and the IP station license. Avaya licensing is subject to change andshould always be verified with your Avaya vendor.8
Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC IntegrationsNICE Uptivity RequirementsHardwareUptivity hardware requirements vary depending on system configurations.Appropriate hardware is identified during the system implementation process. Foradditional information, search online help for keyword site requirements.SoftwareThis guide covers the following: NICE UptivityAdditional third-party software is required for this integration: CACE WinPcap version 4.1.x (available from the WinPCAP organization'swebsite)Licensing One (1) Voice seat license per named agent or One (1) Voice concurrent session license for each simultaneous call that will berecorded. Additional licensing may be required if the system includes optional features (forexample, inContact Screen Recording)9
Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC IntegrationsCustomer Configuration OverviewThe following table provides a high-level overview of the customer configurationsteps in Avaya DMCC-SSC integrations. Links are provided for tasks that arecovered in this guide.Customer Configuration Steps for Avaya DMCC-SSC Integrations123Complete all necessary physical and IP connections between the recording server(s)and the LAN.Obtain any necessary Avaya software and licensing.Complete the tasks and procedures detailed in the Customer Guide to Avaya TSAPIIntegrations.4Verify DMCC License Availability.5Verify the Switch Configuration in AES.6Configure Softphone Stations on the AES Server.10
Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC IntegrationsCustomer Integration TasksThe information in this section is provided for your reference only. Detailed stepsfor the Avaya configuration can be found in Avaya’s documentation, which isavailable on the Avaya website. You should always use the appropriatedocumentation from Avaya to install and configure Avaya components.Verify DMCC License AvailabilityDMCC stations must be licensed to be used for recording audio. Each DMCC stationneeds either a DMCC DMC license on the AES server OR an IP API A license onthe Avaya CM.1. In your web browser, browse to the Web License Manager site for your AESserver (typically http://aes-server/WebLM/, where ‘aes-server’ is the hostnameor IP Address of the AES).2. Log in with an administrative account.3. From the Licensed Products menu section, click Application Enablement.4. On the Licensed Features table, the Device Media and Call Control entrywill list the total and used values for DMCC DMC licenses.The available IP API A license count can be accessed using GEDI. Run GEDI and enter display system-parameters customer.11
Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC IntegrationsIn this image, the limit of available licenses is 18, and there are 0 licenses used.This means that 18 concurrent softphones can be controlled through DMCC, andthus 18 concurrent recordings are possible.After completing this procedure, return to the Customer Configuration Overview.Verify the Switch Configuration in AESIf a switch connection will be used to configure the Uptivity voice board, you mustconfirm that the connection was created, copy the connection name exactly as itappears, and provide that name to the Uptivity installation team.1. Log in to the AES server with an administrative account.2. Navigate to Communication Manager Interface and click SwitchConnection.3. Click Edit H.323 Gatekeeper.4. Enter the gatekeeper’s IP address if necessary.After completing this procedure, return to the Customer Configuration Overview.12
Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC IntegrationsConfigure Softphone Stations on the AES ServerFor each Uptivity recording channel, a corresponding softphone station must becreated and configured on the AES server.To edit the configuration of a station:1. In GEDI, enter: Display station xxxx, where xxxx is the station extension.2. Set Type to a VoIP phone type (for example, 4610).3. Enter the Security Code (numerical passcode) for the extension.4. Set IP Softphone to Y.The "IP Soft" license is used to allow the actual "Avaya IP Softphone" softwareclient to connect and register an extension. Since our DMCC stations do not usethis software, we do not require any additional licenses for the integration.Record the Extension and Security Code used and provide this information to theUptivity installation team.13
Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC IntegrationsCustomer Administration TasksDuring ongoing use of the system, your Uptivity administrator may need toconfigure new channels or reconfigure existing channels. This integration requireschanges to the Voice Boards page in the Uptivity Web Portal when channels areadded or must be reconfigured.For more information on voice boards, search online help for keyword voice boards.Channel Configuration SettingsThis section provides a reference to channel settings that must be configured forthe Avaya DMCC-SSC integration. You should refer to this section whenever youadd new channels to your NICE Uptivity system. To learn how to add channels to avoice board, visit online help.Any other voice board changes should only be done under direct supervision fromSupport. Done incorrectly, voice board modifications can have serious negativeimpact to your system. In addition, altering the hardware configuration of yoursystem may void your warranty.The following settings apply when configuring channels for Avaya DMCC-SSCintegrations:SettingDefinitionValueUsed in deployments where physical devices and channelsAssignhave a one-to-one correspondence, or to allocate specificchannels to specific types of recording. For details, searchAnythingonline help for keyword channel assignment.StationPasswordNameEnter a DMCC station extension.Enter the password for the DMCC station.Enter an optional name for the channel that can be used inchannel scripting.You must restart the CTI Core service after any changes to voice boards,channels, or both.14
Appendix: Avaya DMCC Recording MethodComparisonNICE Uptivity supports three different recording methods using DMCC. Thefollowing table may help you evaluate the pros and cons of each method duringdiscovery, and determine which integration is best for you. This table is based oninformation from inContact’s experience with Uptivity WFO implementations and theAvaya application note Developing Client-Side IP Call Recording Applications UsingAvaya Application Enablement Services. Licensing requirements should always beverified with your Avaya representative.Single Step ConferenceService Observe (SO)(SSC)One Full per concurrentrecording channelORDMCC LicenseOne Basic per concurrentrecording channel AND oneIP Station license perconcurrent recordingchannelMultipleRegistration (MR)One Full per concurrentrecording channelOROne Basic perOne Basic per concurrentconcurrentrecording channel AND one IPrecording channelStation license per concurrentrecording channelOne per recorded device toTSAPI Licensemonitor the device forOne per recorded device. Usedphone events; one perto monitor the device forconcurrent recordingphone events. Joining theOne per recordedchannel to initiate SSC forrecording station to the call isdevicerecording; and one for theperformed via DMCCskill monitored r callFive. CM supports up to sixparticipants including therecording device, leavingfive possible phoneparticipants.Five. CM supports up to sixparticipants including therecording device, leaving fiveSixpossible phone participants.DCP and AvayaH.323. Can registerSupportedextensiontypesrecording devicesAllAllonly at extensionsthat are softphoneenabled on CM'sStation form.
Appendix: Avaya DMCC Recording Method ComparisonSingle Step ConferenceService Observe (SO)(SSC)Four in a two-partyMaximum recordingcall (six minus thedevices in a callnumber of activeTwo for CommunicationManager 4.0 and higherOne for earlier releases.participants).MultipleRegistration (MR)Six (one perparticipant).Available inAES 3.0 and higherAES 3.0 and higherAES 4.1 and higherAES/CM releasesCM 3.0 and higherCM 3.0 and higherCM 5.0 and higherAdditional mediaprocessorsconsumedAdditional TDMtime slotsconsumed(assuming a singleport network)One per recordingdeviceActive Paticipation:One per recordingdeviceSilent Participation: 0One per recording deviceOne per recordingdeviceListen/Talk FAC : One perrecording device0Listen Only FAC: 0No. Avaya AESAllows recordingnotificationwarning to beplayed toparticipantssupports this featurewith SSC but Uptivityruns as a SilentYesParticipant,Nopreventing it fromsending thenotification.Restricted via CORs on bothstation and agent levels.Benefit: Security. Agent mustClass ofRestrictions (CORs)neededN/Abe logged into the CM to berecorded. Drawback:N/ARequires additionaladministration for phones andagents.16Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC Integrations
Appendix: Avaya DMCC Recording Method ComparisonSingle StepConferenceService Observe (SO)Multiple Registration(MR)(SSC)Yes. Depending onconfiguration andprovisioning, eachregistration can bethrough separatehardware and networkpaths, or overlapped,SupportsYes, but at cost ofYes, two forto achieve varyinghighly-available activeCommunication Managerlevels of highavailable callparty slots in4.0 and higheravailability. Supportsrecordingcalls.registration of a secondrecording device at atarget extension,providing a back-upshould one recordingfail. Additionalhardware or licensingmay be required.SO requires a featureaccess code and targetnumber to be dialed; therecan be a slight delayPotential(hundreds of milliseconds)delayafter the call has startedstarting callN/Abefore the recordingor recordingdevice joins the call. Sincestart failurethe SO session requiresN/Adialing, there can be asmall chance of failure ifthe CM does not interpretthe dial string correctly.Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC Integrations17
Appendix: Avaya DMCC Recording Method ComparisonNot recommended iftarget devices are notregistered with the CMon a regular basis (thatis, daily).RegularMR does not notifyregistrationsecondary stationsof targetN/AN/Awhen the primary isrecordingunregistered; thus,devicessecondary stationsinitiate retry events forregistration that mayeventually lead toresource issues on theAES.Single StepService ObserveMultipleConference (SSC)(SO)Registration (MR)Trunk-to-Trunk callsRecordsTrunk-toTrunkTransferstransferred over a VDNcan be recorded bymonitoring the VDN forN/AN/Acall IDs andconferencing a DMCCstation into the calls.RecordsAvaya one-X AttendantNoYes with lallocation18Yes with UptivityNoNoVoice BoardReloading license.Customer Guide to Avaya DMCC-SSC Integrations
audio source, and receives call control events and metadata through AES using TSAPI. NICE Uptivity detects when a station joins a call and makes a request for a single step conference between Uptivity, the agent's phone, and the corresponding softphone on the AES server. General architectural example of the Avaya DMCC-SSC integration