Transcription
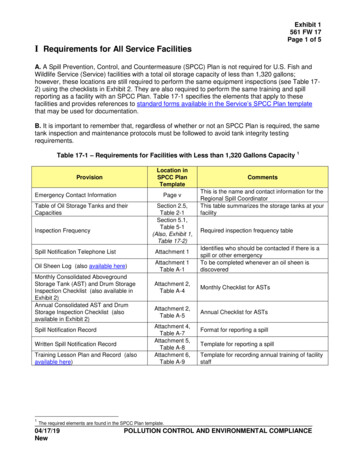
Exhibit 1561 FW 17Page 1 of 5I Requirements for All Service FacilitiesA. A Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure (SPCC) Plan is not required for U.S. Fish andWildlife Service (Service) facilities with a total oil storage capacity of less than 1,320 gallons;however, these locations are still required to perform the same equipment inspections (see Table 172) using the checklists in Exhibit 2. They are also required to perform the same training and spillreporting as a facility with an SPCC Plan. Table 17-1 specifies the elements that apply to thesefacilities and provides references to standard forms available in the Service’s SPCC Plan templatethat may be used for documentation.B. It is important to remember that, regardless of whether or not an SPCC Plan is required, the sametank inspection and maintenance protocols must be followed to avoid tank integrity testingrequirements.Table 17-1 – Requirements for Facilities with Less than 1,320 Gallons Capacity 1Location inSPCC PlanTemplateProvisionEmergency Contact InformationPage vTable of Oil Storage Tanks and theirCapacitiesInspection FrequencySection 2.5,Table 2-1Section 5.1,Table 5-1(Also, Exhibit 1,Table 17-2)Spill Notification Telephone ListAttachment 1Oil Sheen Log (also available here)Attachment 1Table A-1Monthly Consolidated AbovegroundStorage Tank (AST) and Drum StorageInspection Checklist (also available inExhibit 2)Annual Consolidated AST and DrumStorage Inspection Checklist (alsoavailable in Exhibit 2)Spill Notification RecordWritten Spill Notification RecordTraining Lesson Plan and Record (alsoavailable here)1CommentsThis is the name and contact information for theRegional Spill CoordinatorThis table summarizes the storage tanks at yourfacilityRequired inspection frequency tableIdentifies who should be contacted if there is aspill or other emergencyTo be completed whenever an oil sheen isdiscoveredAttachment 2,Table A-4Monthly Checklist for ASTsAttachment 2,Table A-5Annual Checklist for ASTsAttachment 4,Table A-7Attachment 5,Table A-8Attachment 6,Table A-9Format for reporting a spillTemplate for reporting a spillTemplate for recording annual training of facilitystaffThe required elements are found in the SPCC Plan template.04/17/19NewPOLLUTION CONTROL AND ENVIRONMENTAL COMPLIANCE
Exhibit 1561 FW 17Page 2 of 5II SPCC Plan Requirements(Links are provided throughout the exhibit to intranet sites where detailed information is maintained.)A. Who should prepare a Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure (SPCC) Plan?Facilities with oil equipment and a storage capacity of 1,320 gallons or greater must prepare andmaintain an SPCC Plan. The Service has prepared an SPCC Plan template (available by clickinghere) that should be used to prepare all new SPCC Plans, and may be used when revising anexisting, approved SPCC Plan (Exhibit 3 also contains the references to the Service’s SPCC Plantemplate and a link to download the template). For assistance in determining who should prepareyour SPCC Plan, contact your Regional Environmental Compliance Coordinator (RECC).B. What should be included in an SPCC Plan?1. Plan elements and cross-reference to 40 CFR 112. A crosswalk between the SPCC provisionsof 40 CFR 112 and your SPCC Plan must be included so that the location of each requirement in 40CFR 112 can be found. If your existing approved SPCC Plan does not include a crosswalk, then youmust prepare one and insert it into your Plan. A copy of the crosswalk is available here. Insert thecrosswalk after the cover page and before the Table of Contents. It should be the first item withinyour Plan.2. State and local oil storage requirements. Your Plan must address and comply with any state orlocal oil storage requirements. The requirements must be clearly identified in the Table of Contents,and follow the state or local regulations sequence of provisions. Any Plan prepared to state or localrequirements may also need a regulatory crosswalk to those requirements in lieu of, or in addition to,the Federal crosswalk. A section at the bottom of the crosswalk is available for state and local SPCCPlan provisions.3. Service-specific elements of the Plan. Plans must include the following Service-specificelements:(a) SPCC inspection schedule and checklists. The Service’s SPCC Plan template includes a facilityinspection schedule2 (see Table 17-2) and all relevant checklists (see Exhibit 2). Facilities that do nothave an SPCC Plan that was developed using this template should also use the Table 17-2inspection schedule and the inspection checklists provided in Exhibit 2.Table 17-2 – Facility Inspection ScheduleItems to be inspectedAST/Mobile AST/Secondary Containment (with Checklist)Drum and Drum Storage (with Checklist)Oil-Filled Equipment (with Checklist)AST/Mobile AST/Secondary Containment (with Checklist)Approved or permitted floor drains, sumps, and oil/waterseparatorsAST integrity test 3AST post-repair2FrequencyMonthly(all equipment items inspected monthly areon one checklist)Annually(both items inspected annually are on onechecklist)Within every 10 yearsWith each repairThe inspection schedule is based on the inspection checklists in the Steel Tank Institute’s Standard SP-001.340 CFR 112 requires a tank integrity test every 10 years if we fail to conduct the inspections listed in 561 FW 17, Exhibit 1, Table 17-2. If we follow theinspection schedule rigorously, we do not have to conduct the tank integrity test for all STI Category 1 tanks. See 561 FW 17, Exhibit 1, II B.3(c),“Failure to Inspect.”04/17/19NewPOLLUTION CONTROL AND ENVIRONMENTAL COMPLIANCE
Exhibit 1561 FW 17Page 3 of 5(b) Records of inspections. Records of inspections should be signed by the responsible Serviceemployee and retained permanently.(c) Failure to inspect. If we fail to inspect our ASTs according to the schedule in Table 17-2, 40 CFR112(8)(c) specifies tank integrity testing as the only alternative to demonstrate tank integrity, and wemay then be required to perform tank testing per Section D, below. (See Footnote 2.)C. What are the AST tank categories? The Steel Tank Institute (STI) Standard SP001, 6th Edition,January 2018 or as amended, describes three categories of ASTs. Each category is defined byhaving spill control or Continuous Release Detection Mechanism (CRDM) or both.1. Definitions.(a) Continuous Release Detection Mechanism (CRDM). A means of detecting a release of liquidthrough inherent design. CRDM is passive because it does not require sensors or power to operate.Liquid releases are visually detected by facility operators. The system must be designed inaccordance with good engineering practice. Several acceptable and commonly used CRDM systemsare: Release Prevention Barrier (RPB). A liquid containment barrier that is installed under the AST.Its purpose is to divert leaks toward the perimeter of the AST where they can be easilydetected, as well as to prevent liquid from contaminating the environment. RPBs are composedof materials compatible with the liquid stored in the AST and meet appropriate engineeringstandards. Examples are steel (as in steel double-bottom tanks), concrete, elastomeric liners,or other suitable materials, provided the above criteria are met; Double-wall AST or double-bottom AST; Elevated AST, with or without release prevention barrier; Steel diked AST, open or closed top; and Concrete Exterior AST (CE-AST) with an integral secondary containment and interstitialmonitoring opening.(b) Spill Control. A means of preventing a release of liquid to the environment. Spill control methodsinclude: Remote impounding; Secondary containment system; Secondary containment dike/berm; Open top steel diked AST; Closed top steel diked AST with overfill prevention; Double-wall AST with overfill prevention; and CE-AST with overfill prevention.2. Applicability to Service Facilities. Table 17-3, AST Integrity Testing and Inspection Schedules,describes how integrity testing is applied to each of the three tank categories.(a) Most Service installations qualify as STI Category 1 because they have both spill control andCDRM (e.g., are double-walled, elevated, and have over fill protection; some also have concreteshells).(b) If a tank does not meet the Category 1 characteristics (e.g., are single-walled without secondarycontainment or are sitting directly on the ground) then the periodic integrity testing and other04/17/19POLLUTION CONTROL AND ENVIRONMENTAL COMPLIANCENew
Exhibit 1561 FW 17Page 4 of 5requirements in Categories 2 and 3 apply, and cannot be avoided by regular inspections. Important:The monthly inspections required in Table 17-2 must be followed for all STI categories toprevent leaks and equipment failure.D. What are the AST integrity testing and inspection schedules? If an integrity test is required,STI Standard SP001 describes the periodic tank integrity testing methods for use on ASTs. Thefollowing sections describe the requirements for conducting integrity testing.1. Shop-fabricated ASTs. Table 17-3 summarizes the inspection and integrity testing requirementsfor shop-fabricated tanks. Requirements depend on whether the tank has spill control methodsand/or CRDM (see the definitions in Section C.1. above). The table is intended to address mostService shop-fabricated tanks, but may not be all-inclusive.Table 17-3 – AST Integrity Testing and Inspection SchedulesTank SizeHas Spill Control andCRDM(STI Category 1)0-1100Periodic inspectiononly.Periodic inspection only.1101 –5,000Periodic inspectiononly. Periodic inspection; and Formal external inspectionand integrity test every 10years.5,001 30,000 Periodic inspection,and Formal externalinspection every 20years.30,001 –50,000 Periodic inspection,and Formal externalinspection every 20years.04/17/19NewHas Spill Control, but notCRDM(STI Category 2) Periodic inspection, Formal external inspectionevery 10 years, and Formal internal inspectionevery 20 years.OR Periodic inspection, Formal external inspectionevery 5 years, and Integrity test every 10years. Periodic inspection, Formal external inspectionand integrity test every 5years, and Formal internal inspectionevery 15 years.Without Spill Control and CRDM(STI Category 3) Periodic inspection, and Formal external inspection andintegrity test every 10 years. Periodic inspection, Formal external inspection andintegrity test every 5 years, and Formal internal inspection every 10years.OR Periodic inspection, Integrity test every 2 years, and Formal external inspection every 5years. Periodic inspection, Formal external inspection andintegrity test every 5 years, and Formal internal inspection every 10years.OR Periodic inspection, Integrity test every year, and Formal external inspection every 5years. Periodic inspection, Formal external inspection andintegrity test every 5 years, and Formal internal inspection every 10years.POLLUTION CONTROL AND ENVIRONMENTAL COMPLIANCE
Exhibit 1561 FW 17Page 5 of 5Has Spill Control andCRDM(STI Category 1)Tank SizePortablecontainersPeriodic inspectiononly.Has Spill Control, but notCRDM(STI Category 2)Periodic inspection only.Without Spill Control and CRDM(STI Category 3)Have the container Department ofTransportation (DOT)-Certified: Plastic container – every 7 years Steel container – every 12 years Stainless steel container – every 17years2. Field-erected ASTs. STI Standard SP001 requires that field-erected ASTs (meaning they areconstructed on site and are generally large tanks) have a periodic integrity test conducted. See yourRegional Environmental Compliance Coordinator (RECC) for the SP001 integrity testing schedule.3. Integrity Testing for All Service ASTs. All Service ASTs that do not meet the Category 1standards must follow the tank integrity testing schedules listed in STI Standard SP001, Categories 2and 3, regardless of whether they have spill control and CDRM.E. Training.1. The Facility Manager must provide annual training for all personnel using oil equipment.2. Training videos prepared by the Service are available that address the inspection of ASTs. Thesevideos are intended to train Service personnel about the components of the ASTs they will encounterand follow the inspection checklists step by step. The videos comply with the Americans withDisabilities Act (ADA), Section 508. The videos without captioning are available here and those withcaptioning are available here.3. The instructor or his/her designee must sign records of training of facility personnel and retainthem at the facility permanently. A training lesson plan checklist is provided as “SPCC TrainingLesson Plan and Log” in Attachment 6 of the SPCC Plan template, and on the Division ofEngineering (DEN) website.F. Amending the SPCC Plan and the 5-Year Plan Review. Existing SPCC Plans must be reviewedevery 5 years to ensure that they accurately describe the physical layout of the facility (see section17.16 of 561 FW 17). If an existing SPCC Plan is current and contains all the elements required by40 CFR 112 and described in the crosswalk, it is not necessary to convert that Plan to a new one thatuses the Service’s SPCC Plan template. Updating to the new format is an option; it is not required.1. Plan Amendment Statement and Review Log. Whenever changes are made to the facility,including routine maintenance and replacement with equivalent equipment, the Facility Managermust ensure the changes are recorded in the “SPCC Plan Amendment Statement and Review Log”form. A copy of this log is provided in the SPCC Plan template, Page viii.2. 5-Year Review Log. Within 90 days before each 5-year anniversary of the SPCC Plan preparationdate, the Facility Manager must perform a complete review of the Plan. If the he/she determines thePlan is current and it accurately reflects the oil equipment as well as all other buildings andinfrastructure (such as roads, fences, gates, etc.), then he/she completes the 5-Year Review andEvaluation of SPCC Plan Review form and inserts it into the SPCC Plan. A copy of the “5-YearReview and Evaluation of SPCC Plan Review” form is provided in the SPCC Plan template, Page ix.04/17/19NewPOLLUTION CONTROL AND ENVIRONMENTAL COMPLIANCE
Table of Oil Storage Tanks and their Capacities Section 2.5, Table 2-1 This table summarizes the storage tanks at your facility Inspection Frequency Section 5.1, Table 5-1 (Also, Exhibit 1, Table 17-2) Required inspection frequency table Spill Notification Telephone List Attachment 1 Identifies who should be contacted if there is a











