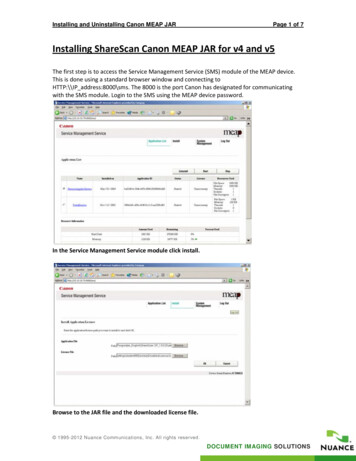
Transcription
All about MEAPThis white paper will help youunderstand MEAP (Mobile EnterpriseApplication Platform) better. It will helpyou decide why and how MEAP fitsinto your mobility strategy. And it willgive you some tips and best practices tomake the best use of your MEAP.
Table of ContentsIntroduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3MEAP – An overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4Is MEAP suited for my enterprise? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4Getting the best out of your MEAP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5Roadmap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5Applications and users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5Security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7Deployment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7Robustness. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7Integration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7Connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7Flexibility. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7Management rights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7Conclusion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
IntroductionMobility is changing the way enterprises do business, and interact with customers and employees. Even as mobility has been a part ofenterprises for several years in some form or the other, it’s getting smarter and more organized now. The faster enterprises can adoptsolutions that work best for them, the quicker they will benefit from all the advantages that mobility brings.A key element in any mobility strategy is the platform that hosts the mobile applications. The selected platform should be able toprovide an optimum mix of mobile software, networks and hardware ensuring that enterprises extend the right data and functionalityto mobile devices; use network and connectivity that is most suited for their needs; and are able to mix and match devices andmodels as per their functionality, cost and flexibility. MEAP or Mobile Enterprise Application Platform is one such platform.This white paper will help you understand MEAP (Mobile Enterprise Application Platform) better. It will help you decide why and howMEAP fits into your mobility strategy. And it will give you some tips and best practices to make the best use of your MEAP.3
A MEAP can helporganizationsachieve theirmobility goal in anorganized, secureand efficient way.MEAP – An overviewMEAP is an application platform middleware that enables and supports the development ofmobile enterprise applications. Based on the principle of ‘write once, deploy to many’, MEAPs areready to hit the ground running. They eliminate the laborious triad of effort, time and money thatis required to develop mobile applications. MEAPs reduce infrastructure and back-end worries.They are fast to develop and deploy and can integrate multiple features. They offer robust backend connectivity, allow code reuse, and are highly secure while being easy to manage.With MEAPs, enterprises can build, deploy and manage mobile applications for any data systemacross devices and wireless networks, and deliver them to any user. MEAPs support both offlineand online capabilities. They run on tablets, smart phones, handhelds and notebooks. A keyadvantage for enterprises is that MEAPs deliver data to mobile users through a unified andorganized interface.While point solutions or mobile development toolkits may offer richer functionalities and superioruser experience, they may not be able to handle new technologies, dictates of market forces orchanges in back end systems. MEAP on the other hand offers a robust platform that can weathermany changes. A MEAP allows an enterprise to focus on delivering mobile applications for theircustomers and employees with the knowledge that their mobile applications can rapidly evolve tonew mobile OS’s and features, as well as new mobile devices and form factors. Even as dissentingvoices argue that MEAPs tend to be rigid, entail vendor lock-in, take several months to deployand require a set of complex integration, they are surprisingly flexible and can be cost effective inthe long run. MEAPs do come at a cost (read vendor lock-in), however their advantages generallyoutweigh the CAPEX investments.Meap benefitsFaster development and deployment across multiple mobile devices and operating systemsMultiple feature integrationRobust securityStrong back-end connectivityEasy application and user managementIs MEAP suited for my enterprise?To know if MEAP is suitable for your organization, you should assess your organization’s strategy,current technology infrastructure, customer needs and business model, against some keyparameters like:MEAP P (Mobile Enterprise Application Platform)4Mobility roadmapMultiple devices, OS,back-end systemsApplication types andtarget userIf your business strategyincludes a shift to mobility andincreased investment in mobileapplications to serve youremployees, suppliers, andcustomers, then an investmentin MEAP is justified.MEAPs are most effective ifyour enterprise deals withmultiple applications, operatingsystems, device types, andbackend systems.MEAP supports both B2Eand B2C applications, andare always a candidate forconsideration if data securityand support for multiplemobile OS is a criticalapplication requirement.
Getting the best out of your MEAPMEAP e is a guide that will help you understand the many aspects of MEAP and how to navigate theMEAP world. It will also give you some tips on what to expect in MEAPs, how to handle certainaspects of MEAP, as well as pitfalls to avoid.RoadmapThere are two fundamental parameters that you should consider at the onset: strategy and cost.Opt for MEAP if your mobility strategy includes multiple enterprise applications that have to bedeployed across the enterprise. Another point to be noted is that the line between applicationsdeveloped natively, or in hybrid environments on through mobile web is tapering, and MEAPmight have what it takes to keep up with these so-called front-runners.Applications and usersMobile applications fall under two buckets: B2E and B2C. Most B2E applications entail standardobjects like user authentication, security, offline data storage, etc., MEAPs here can be used tomobilize business processes, such as field service, and create a unified workflow that interfaces tomultiple backend systems seamlessly.For B2C applications, providing the best user experience is key. Enterprises want their mobileapplications to be polished with the latest user interfaces and mobile device features to makethem attractive to customers. While a MEAP may not be able to support new mobile featuresas quickly as the native SDK, it provides pre-built solutions for securing mobile data and robustbackend integration features. Also, MEAPs provide a rapid application development anddeployment path to new mobile OS’s and devices. These capabilities make MEAP the right choicefor B2C applications. Many enterprises have selected MEAP for their customer-facing mobileapplications because security, integration, and a rapid path to the future are more important thanbeing at the cutting-edge of mobile device features.The following matrix compares MEAPs in B2C and B2E environments:FunctionalityBusiness to Customer (B2C)Development Applications are not verycomplex Business logic is usuallystraightforward Some applications have a richdata set with search functionsand various types of contentMEAP Applicability: High(MEAP helps by developing the sameapplication for multiple platforms)User Interface Branding is very important User experience and usabilityis very important Applications need to be easyto use and intuitiveMEAP Applicability: High(As the same code base is used todevelop multiple platforms, there isconsistency in the user experience.At a widget level the user still getsthe look and feel specific to theunderlying platforms.)Business to Enterprise (B2E) Applications can be verycomplex, with many screensand objects Large amount of data Peripherals are often used toextend device functions inmore complex applicationsMEAP Applicability: Very High Branding is less importantwhen compared to B2C Application training isgenerally given to users Usability is less importantwhen compared to B2CMEAP Applicability: Very High5
The following matrix compares MEAPs within B2C and B2E environments:FunctionalityBusiness to Customer (B2C)Business to Enterprise (B2E)DeploymentInstallation from iTunes Store,Android Market and RIM App Worldare the norm, subject to publiccomment / reviewControlled and private over-theair installs are required from theplatform provider via CorporateBES (blackberry enterprise system)or other systemMEAP Applicability: HighMEAP Applicability: Very HighDevice ManagementNot applicable as companies do notmanage their customers’ devicesMEAP Applicability: Typically, notapplicableUsers, devicesand billing Users and devices are typicallynot pre-registered Total application downloadsdrives billingMEAP Applicability: High(The MEAP server logs eachclient session, this can help inunderstanding usage patterns)User Authentication Some application don’t requireauthentication Some functions requirebackend customer directoryauthenticationSome degree of user, applicationand device management isrequiredMEAP Applicability: Very High Users are pre-registered andmay have multiple devicesthat may be pre-registered orshared among users Known or active users ordevices drives billingMEAP Applicability: High Users are authenticatedagainst corporate directory inmost applicationsMEAP Applicability: Very HighMEAP Applicability: Very High(Authentication is supported byMEAP)Data Security Data is typically related tothe customer or is publiclyavailable Encryption of data andtransport is often required Applications, typically cachesensitive data is removed uponapplication exit Offline mode is not commonMEAP Applicability: Very High(MEAP provides inbuilt encryption)Communications Request / response is typical Push notifications arecommon Messages are generally small(e.g. a stock price, accountbalance) Generally, standard and finiteweb services are usedMEAP Applicability: HighOther Requirements Data and transport encryptionis used often Data is often stored on thedevice and available offline Applications generally do notaccess the web without adegree of policy and securityMEAP Applicability: Very High Request / response and pushof data from host are common Queuing of data is highlydesirable in the mobileplatform Messages can be very large(daily route, parts list, etc.) Generally, standard and finiteweb services are usedMEAP Applicability: Very High In general compliance /regulation is not applicable Compliance / regulationsoften applicable Users and devices are typicallynot tracked but location isused for store locators andother similar functions Status and location tracking ofusers and devices is often usedto verify locations of teammembers and company assetsMEAP Applicability: Medium (owingto location)6 Data is generally corporatesensitiveMEAP Applicability: Very High
SecurityIn the mobility space, data security takes on a larger dimension because of multiple systems,networks and devices. Such a combination makes the entire system extremely vulnerable. A losthandset, poor password authentication, or breach in security policy can have a cascading effectacross the enterprise.Security has always been high in MEAPs. Features like data encryption, two-factor authenticationor roles-based security are tightly knit into the technology and architecture. Additionally, MEAPallows developers to add-in and customize these security features.SecurityDeploymentDeploymentThe beauty of deploying MEAP is that it is similar to any enterprise software deployment - onpremise behind your firewall or on-demand using as-a-service model. MEAP gives enterprisesthe flexibility to deploy applications depending on needs, strategies or resources. An on-premisedeployment lends more control over the implementation and backend system security, whilean as-a-service model is light on resources for implementation as well as maintenance and canaccelerate mobile application deployment. To drive application adoption for employees, partnersand customers, MEAPs can help set up private, semi-private or even public application storeswhere users can download applications.RobustnessThe core of any successful mobile deployment is the server - the nerve center that handlesmillions of real-time transactions over hundreds of networks worldwide. It bridges the backendsystems and frontend mobile applications and this involves high security, flexibility, scalability, andconfigurability. MEAPs are also known to have flexible connection capabilities to support backendsystems including ERP, CRM, BI, etc., from a broad range of commercial software vendors. MEAPin this case should be on an autonomous and independent server so that no data lies in betweenthe host systems and mobile tyFlexibilityManagement rightsThe biggest challenge for mobile applications is the data and the integration from a variety ofsources both within and without the organization. A sound MEAP should have the wherewithal tointerface with any and all backend systems: custom legacy applications, packaged applications orthird-party web services. More importantly this critical integration should also consider transactionoptimization, encryption and data compression and ensure synchronized data flow from theserver to the mobile device, for both online and offline operations.ConnectivityMobile applications should be above all, smart. The development platform that you adopt shouldenable that intelligence by ensuring sound logic across applications, devices and users. Suchapplications should be able to handle various connections, manage updates or rollbacks, all thewhile ensuring security of the data. It should simultaneously be able to sync with other contenttoo like work files and documents, even if these documents are ad hoc.FlexibilityMEAP enables development capabilities across devices including Android, Symbian, iPhone,Blackberry, Windows Mobile as well as other new entrants in the market. It also supportsa combination of technologies (HTML, CSS and Java). The mobile space is evolving at aphenomenal pace, ensure that the MEAP you select is able to keep up and sustain the changesboth at the device and technology level, as well as support web-based and native applications.Management rightsOften the ongoing management of deployed applications is overlooked. Many times once thedevice is on air, monitoring how the application is being used or whether it needs improvementsis remiss. The MEAP that you select should provide a comprehensive and role-based applicationto manage users, devices, applications and back-end systems. Additionally, this administrationshould be centralized, thus enabling seamless deployment, management and updates.7
ConclusionMobility trends and mobile applications are growing at a rapid pace and the demand for solutionshas spurred vendors to develop innovative and functional platforms. MEAP is one such platformthat helps enterprises increase productivity while reducing cost, and streamlining operations.However, central to the enterprise’s mobility roadmap is a sound strategy and the adoption ofsolutions that will lead it to its goal. A MEAP can help organizations achieve that mobility goal inan organized, secure and efficient way.For more information about solutions for your organization, contact your Dell accountrepresentative or visit dell.com/services.ApplicationsBusiness ProcessConsultingInfrastructureAvailability varies by country. 2011 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.XXX - 2.1 - 201108 - GYSupport
MEAP or Mobile Enterprise Application Platform is one such platform . This white paper will help you understand MEAP (Mobile Enterprise Application Platform) better . It will help you decide why and how MEAP fits into your mobility strategy . And it will give you some tips and best practices to make the best use of your MEAP . 3