Transcription
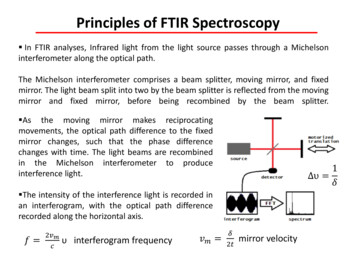
Principles of FTIR Spectroscopy In FTIR analyses, Infrared light from the light source passes through a Michelsoninterferometer along the optical path.The Michelson interferometer comprises a beam splitter, moving mirror, and fixedmirror. The light beam split into two by the beam splitter is reflected from the movingmirror and fixed mirror, before being recombined by the beam splitter. As the moving mirror makes reciprocatingmovements, the optical path difference to the fixedmirror changes, such that the phase differencechanges with time. The light beams are recombinedin the Michelson interferometer to produceinterference light.1 υ 𝛿 The intensity of the interference light is recorded inan interferogram, with the optical path differencerecorded along the horizontal axis.𝑓 2𝑣𝑚𝑐υ interferogram frequency𝑣𝑚 𝛿2𝑡mirror velocity
Principles of Diffuse Reflectance MethodMeasurement of chemicals adhering to a surface - PowdersK is the absorption coefficient, and S is the scatteringcoefficient. In practice, the comparative reflectancer with respect to a standard powder such as KBr orKCl, of which K is near zero (0) in the actualmeasurement rangeSpectrum of solid caffeineShimadzu website
High Sensitivity Reflection MeasurementA reflection method is required to measure substances adhered to or appliedto a material that does not permit light transmission, such as a metal sheet.Path lengthThin FilmOnly the parallel polarized light affects theabsorption by the sample so using apolarizer for measurements increases theapparent peak size. Information on thesample orientation can also be acquired, asonly functional groups with a perpendiculardipole moment with respect to the metalsheet are measured. However, suchincreases in sensitivity are available onlywith a metal substrate.Shimadzu website
High Sensitivity Reflection MeasurementA reflection method is required to measure substances adhered to or appliedto a material that does not permit light transmission, such as a metal sheet.sp3 C-H stretching modesSpectrum of a 25 Å-thick organic film on a Au surface.Shimadzu website
Attenuated Total ReflectanceEnables samples to be examined directly in the solid or liquid statewithout further preparation.Diamond, Si, Ge (high refractive index)Penetration depth 0.5-2 μmShimadzu website
Fluorescence and FTIR MicroscopyDetectorUseful for generating spatial maps of “vibrational modes”. For example,tissue analysis, polymer homogeneity, pharmaceutical quality, forensics.Jasco website
mirror. The light beam split into two by the beam splitter is reflected from the moving mirror and fixed mirror, before being recombined by the beam splitter. As the moving mirror makes reciprocating movements, the optical path difference to the fixed mirror changes, such that the phase difference changes with time. The light beams are recombined