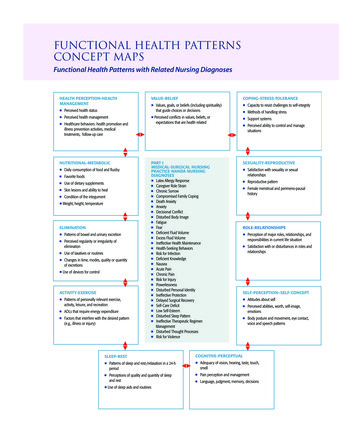
Transcription
Functional Area #5:Structure of the HR Function(Behavioral Competencies: Business Acumen, Critical Evaluation, Consultation)Any student use of these slides is subject to the same License Agreement that governsthe student’s use of the SHRM Learning System materials. SHRM1
HR’s Role in the OrganizationParticipate in developingorganization’s businessstrategyHR’sRoleAlign HR strategy toorganizationalstrategy SHRMSupport otherfunctions in theirstrategic roles2
HR’s Integrated RolesFinance/accountingSales/marketingHRResearch nsystemsAdministrativeOperationalStrategic SHRM3
Changes Influencing anizationalgrowth/retractionIncreased accountability SHRM4
Consultation Competency How have you used your awarenessof internal and external changes toguide the decision making of yourstakeholders (e.g., discussing theimpact of trends in workforce skillswith function leaders)? Which of your knowledge, skills,abilities, or other characteristicshave been useful in consulting withstakeholders?5
Core Business FunctionsExecutive managementis responsible for corefunctions andorganization’s overallperformance.ExecutiveManagementMarketingand SalesInformationTechnology SHRM6
Finance and Accounting Plans, processes, documents, and accounts for financialresources. Applies budgeting approaches.Budget TypeCharacteristicsZero-basedEach unit or goal is ranked, and available funds areallocated with budgets starting at zero.Incremental orline-itemTraditional approach; prior budget is basis for nextbudget.FormulaDifferent units receive varying percentages ofbudget.Activity-basedBased on how much it costs to perform activities;funding based on strategic significance of activities. SHRM7
Marketing and Sales; R&DMarketing and Sales Bring in revenue. Develop intelligenceabout customers,competitors, andmarkets. Position and sellproducts/services. SHRMR&D Generate futurerevenue through newproduct design anddevelopment. Needs to attract,develop, and retaintalent.8
Operations and ITOperations Develops, produces, anddistributes products/services. May be globally dispersedand involve externalpartners. Requires complexlogistics andsophisticated planning. SHRMIT Makes businessintelligence availableacross the enterprise. Manages systems forfuture growth, costefficiencies, and security.9
Role of HR Understands the organizational goals and therole each function plays. Serves as a cross-functional bridge:– Facilitates cross-functional understanding andcollaboration.– Advises core functions on how to align withorganizational strategy.– Identifies and supports need for resources or training.– Locates talent dispersed throughout the globalorganization. SHRM10
Business Acumen Competency How has your knowledge of otherbusiness functions and yourorganization’s business influencedspecific actions by HR (e.g.,understanding the type of expertsneeded by R&D and future trends forthat need)? Which of your knowledge, skills,abilities, or other characteristics havebeen useful in responding to thischallenge? SHRM11
Organizational DesignBusinesslife cycleStrategicorientationOrganizationalDesignSize and scopeNecessary functions SHRMCommunicationDecision making12
Structural Principles Decision-making authority Layers of hierarchy Chain of command Span of control Formalization SHRM13
Organizational StructuresTypeAdvantagesDisadvantagesFunctional Easy to understand Weak customer or product focusSpecializations develop Potentially weak communicationEconomies of scaleamong functionsCommunication within functions Weak grasp of broaderCareer pathsorganizational issuesFewer people Hierarchical structureProduct Economies of scale Regional or local focusProduct team culture More peopleProduct expertise Weak customer focusCross-functional communicationGeographic Proximity to customer Localization Quicker response time Cross-functional communication SHRM Fewer economies of scale More people Potential quality control14
Organizational Structures,ContinuedTypeFront-backMatrix SHRMAdvantages High level of customerfocus Flexibility (units can beadded to meet demandfor new products oremergence of newcustomers)Disadvantages Possible conflict between front andback (for example, explainingdrops in sales by mutualaccusations of poor performance) Necessity for developing new skills(customer/market focus) for allemployees Balance of Complexitystandardization and Unclear lines of authoritylocalization Bureaucratic behavior Availability of best globaltalent15
HR Processes and TeamManagersLeaders Help create and implementorganizational strategy. Create and implementhuman capital strategy. SHRMProcessesSpecialistsGeneralists Collect and analyze data. Ensure compliance. Complete daily HRoperations.16
Critical Evaluation Competency How have you used workforce datato support specific decisions in yourorganization (e.g., identifying trendsin attractive employee rewards)? Which of your knowledge, skills,abilities, or other characteristicshave been useful in working withdata in this way? SHRM17
HR Structural AlternativesHR OrganizationModelFunctional HRAdvantages Risks/DisadvantagesEffective in enterprise with single strategiesConsistency between HQ policyand BU practicesIsolation of headquartersHR from realities in the lineDedicated HR Promotes strategic alignment between headquarters and units Loss of shared knowledgeand experienceDuplications andinefficienciesShared servicesand COE HR Reduces transactional activity in favor of value-creating activityBalances standardization andlocalizationUnderuse of servicecenters SHRM 18
Third-Party ContractorsSuccessful outsourcing/cosourcing dependson: Choosing the right activities to outsource/cosource. Alignment of contractor’s performanceobjectives with strategic requirements. Confirmation of contractor’s reliability,capacity, expertise, and ethical behavior. SHRM19
Ethical Practices Competency How have you applied your EthicalPractices competency in contractingfor HR services or performing duediligence on organizational sourcing(e.g., taking steps to protectemployee data)? Which of your knowledge, skills,abilities, or other characteristicshave been useful in responding tothis challenge? SHRM20
Measuring HR Performance Balanced scorecards HR audits ComplianceBest practicesStrategicFunction-specific HR metrics in key performance areas (e.g.,recruiting, financial management, talentretention and development) SHRM21
HR Strategic AlignmentRecognize HR’s mission to serve the organization and its functions.Position HR as an expert in human resource planning.Fulfill HR mission to create and maintain productive workforce.Understand other functions and build partnerships.Understand industry.Use facts and figures to support recommendations.Measure strategic success. SHRM22
HR Strategic ProcessStep 1:Get the bigpicture. SHRMStep 2:Conduct anHR SWOTanalysis.Step 3:Develop HRmission andvisionstatements.Step 4:Conduct adetailed HRanalysis.Step 5:Determinecriticalpeopleissues.Step 6:Develop HRgoals,metrics,consequences,andsolutions.Step 7:Developimplementation andevaluationplan.23
the student’s use of the SHRM Learning System materials. (Behavioral Competencies: Business Acumen, Critica