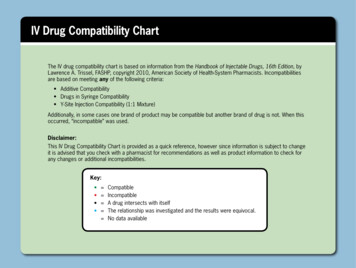
Transcription
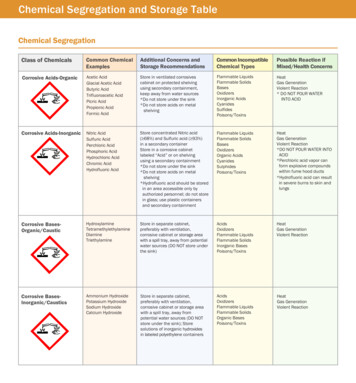
Chemical Segregation and Storage TableChemical SegregationClass of ChemicalsCommon ChemicalExamplesAdditional Concerns andStorage RecommendationsCommon IncompatibleChemical TypesPossible Reaction ifMixed/Health ConcernsCorrosive Acids-OrganicAcetic AcidGlacial Acetic AcidButyric AcidTrifluoroacetic AcidPicric AcidPropionic AcidFormic AcidStore in ventilated corrosivescabinet on protected shelvingusing secondary containment,keep away from water sources*Do not store under the sink*Do not store acids on metalshelvingFlammable LiquidsFlammable SolidsBasesOxidizersInorganic AcidsCyanidesSulfidesPoisons/ToxinsHeatGas GenerationViolent Reaction* DO NOT POUR WATERINTO ACIDCorrosive Acids-InorganicNitric AcidSulfuric AcidPerchloric AcidPhosphoric AcidHydrochloric AcidChromic AcidHydrofluoric AcidStore concentrated Nitric acid( 68%) and Sulfuric acid ( 93%)in a secondary containerStore in a corrosive cabinetlabeled “Acid” or on shelvingusing a secondary containment*Do not store under the sink*Do not store acids on metalshelving*Hydrofluoric acid should be storedin an area accessible only byauthorized personnel; do not storein glass; use plastic containersand secondary containmentFlammable LiquidsFlammable SolidsBasesOxidizersOrganic AcidsCyanidesSulphidesPoisons/ToxinsHeatGas GenerationViolent Reaction*DO NOT POUR WATER INTOACID*Perchloric acid vapor canform explosive compoundswithin fume hood ducts*Hydrofluoric acid can resultin severe burns to skin andlungsCorrosive mineDiamineTriethylamineStore in separate cabinet,preferably with ventilation,corrosive cabinet or storage areawith a spill tray, away from potentialwater sources (DO NOT store underthe sink)AcidsOxidizersFlammable LiquidsFlammable SolidsInorganic BasesPoisons/ToxinsHeatGas GenerationViolent ReactionCorrosive BasesInorganic/CausticsAmmonium HydroxidePotassium HydroxideSodium HydroxideCalcium HydroxideStore in separate cabinet,preferably with ventilation,corrosive cabinet or storage areawith a spill tray, away frompotential water sources (DO NOTstore under the sink); Storesolutions of inorganic hydroxidesin labeled polyethylene containersAcidsOxidizersFlammable LiquidsFlammable SolidsOrganic BasesPoisons/ToxinsHeatGas GenerationViolent Reaction
Chemical SegregationClass of ChemicalsCommon ChemicalExamplesAdditional Concerns andStorage RecommendationsCommon IncompatibleChemicals TypesPossible Reaction ifMixed/Health ConcernsFlammable esiumKeep in a dry, cool area awayfrom oxidizers and corrosivesAcidsBasesOxidizersPoisons/ToxinsFire HazardViolent ReactionFlammable LiquidsEthanol, Ethyl Acetate,Methanol, Acetone,Benzene, Xylene,TolueneDiethyl EtherTetrahydrofuranAcetonitrileGlacial Acetic AcidAcetone liquids withflashpoints 100 FFlammable storage cabinet orrefrigerator rated for flammable/hazardous storage/explosion proof*Peroxide-forming chemicalsmust be dated upon deliveryand opening (two re HazardHeatViolet ReactionPoisons/ToxinsChloroformCyanidesHeavy metal compounds(e.g. Cadmium, Mercury,Osmium, Oxalic Acid,Phenol, Formic Acid),Formamide,Carbon Tetracholride, 2Mercaptoethanol Phenol,Store in a dark, dry, ventilated,cool area in an unbreakablechemically resistant secondarycontainer (polyethylene)* Store volatile toxins withevaporation rate above1.0 - (ether 1.0) in flammablecabinet;Store non-volatile liquid poisons ina refrigerator or cabinet; amountsless than 1 liter can be stored in acabinet above bench level, ONLY ifthe cabinet has sliding doors (notswinging)Flammable e consult Division ofEnvironmental Protection(DEP) for assistance*Hydrofluoric Acid shouldbe stored in an areaaccessible only byauthorized personnel; donot store in glass; useplastic containers andsecondary containmentGeneration of Toxic andFlammable GasCombustionHeatFire HazardExplosion HazardViolent Reaction Chloroformexplosively reacts withchemically-reactive metals(e.g., Aluminum orMagnesium powder, Sodium,and Lithium), StrongOxidizers, Strong Caustics(e.g., Alkalis), anddecomposes in sunlightStore in a secure location awayfrom other chemicals; store in anarea away from friction or shockPlease consult the SDSand the DEPExplosion HazardViolent ReactionHeatShockFriction*Hydrofluoric Acid Hydrofluoric Acid is ahighly acute poisonAcrylamideEthidium BromideSodium AzideExplosivesPicric AcidAmmonium NitrateNitro UreaTrinitroanilineBenzoyl PeroxideTrinitrobenzeneTrinitrobenzoic AcidTrinitrotolueneUrea NitrateTrinitrophenolDiazoisbutylnitrile
Chemical SegregationClass of ChemicalsCommon ChemicalExamplesAdditional Concerns andStorage RecommendationsCommon IncompatibleChemicals TypesPossible Reaction ifMixed/Health ConcernsOxidizersPeroxides, Nitrates,PerchloratesPermanganatesSodium HypochloriteEthyl Acetate, Iodine,Benzoyl PeroxidePotassium DichromateChlorates, Bromates,and Superoxides,Ammonium Persulfate,Ferric chlorideStore in secondary containmentseparately from combustibles andflammable materialsCombustiblesFlammablesOrganic MaterialsReducing AgentsFire HazardGas GenerationToxic GasPeroxide FormersAcrylonitrileIsopropyl Alcohol Ethers(e.g. Diethyl ether,Isopropyl Ether), Acetalsand Ketals, especiallyCyclic Ethers and thosewith primary and/orsecondary Alkyl groupsAldehydes(e.g. Acetaldehyde,Benzaldehyde)Vinyl and Vinylidenecompounds,Dienes TetrahydrofuranDioxaneButylated Hydroxytoluene(BHT)Isopropyl EtherStore in airtight bottles, away fromlight and heat in a dark, cool dryarea; avoid using containers withloose-fitting lids and ground glassstoppers; crystallization, discoloration,and formation or deposition of layersare signs a peroxide former mayhave become shock sensitive; donot use or move such containers:contact DEP; all bottles of peroxideforming chemicals must have thereceived date marked on thecontainer; when the bottle is firstopened, the container must bemarked with the date openedAlways consult the SafetyData Sheet (SDS) and theDivision of EnvironmentalProtection (DEP)Explosion HazardViolent ReactionShock SensitiveCombustion(Exothermic Reaction)Sodium MetalsLithium MetalsPotassium MetalsSodium BorohydrideAlkali Metal HydridesStore in a dry, cool area away frompotential spray from fire sprinklersand other water sources (DO NOTstore under the sink)Aqueous solutionsOxidizersPlease consult the SafetyData Sheet (SDS) and theDivision of EnvironmentalProtection (DEP)Water ReactiveLabel this area for water-reactivestorageIf an old or expired containerof a peroxide-forming chemicalor reactive is found, do notmove it. Contact the DEP at301-496-4710 for assistancein disposing of the containerHeatViolent Reaction
Chemical SegregationClass of ChemicalsCommon ChemicalExamplesAdditional Concerns andStorage RecommendationsCommon IncompatibleChemicals TypesFlammable enSilaneEthaneArsineGermaneHandle flammable compressed gases Oxidizersin a chemical fume hoodToxic Compressed GasesPossible Reaction ifMixed/Health ConcernsFire Hazard ExplosionHazardStore in well-ventilated areas; storeaway from oxidizers, open flames,sparks, and other sources of heatignition; post NO SMOKING signsaround storage area(s) or entrance(s)to storage room(s); flammable gasesstored outdoors where ambienttemperatures exceed 125 deg F(51.7 deg C) shall be protectedfrom direct sunlightUse a spark proof wrench to attachregulators and make other connections;install a flame/flash arrestor at theregulator outlet flow valveOxidizing CompressedGasesOxygenChlorineFluorineNitrogen oxidesGas mixtures containingOxygen higher thanatmosphericconcentrationsStore oxidizers separately fromflammable gas containers orcombustible materials; minimumseparation requirement from thesematerials is 20 ft or a 5 ft noncombustible barrier with a fire resistancerating of at least 30 minutesFlammable Compressed GasesToxic Compressed GasesFire HazardExplosion HazardFlammable Compressed GasesOxidizing Compressed GasesRelease of Toxic GasHydrogen Sulfide is a colorless,flammable, extremely hazardousgas with a “rotten egg” smell;Prolonged exposure may causenausea, tearing of the eyes,headaches or loss of sleep,airway problems (bronchialconstriction) in some asthmapatients; possible fatigue, lossof appetite, headache,irritability, poor memory,dizziness and slightconjunctivitisClean equipment used for oxygenand nitrous oxide with oxygencompatible materials free from oils,greases, and other contaminantsFluorine shall be handled in speciallypassivated containers and associatedequipmentToxic CompressedGasesCarbon MonoxideHydrogen ChlorideHydrogen SulfideNitrogen DioxideHandle toxic compressed gases ina chemical fume hoodIndoor storage or use of toxiccompressed gases shall be providedwith a gas cabinet, exhaustedenclosure, or gas roomRefer to the SDS information foradditional guidance on the storageand compatibility requirementsContact DOHS to determine if a failsafe valve and/or continuousmonitoring for toxic gas may berequired during use
Chemical SegregationClass of ChemicalsCommon ChemicalExamplesAdditional Concerns andStorage RecommendationsCommon IncompatibleChemicals TypesPossible Reaction ifMixed/Health ConcernsStrong Reducing AgentsAcetyl ChlorideThionyl ChlorideMaleic AnhydrideFerrous SulfideStore in cool, dry, well-ventilatedlocationWater reactiveSegregate from all other chemicalsPlease consult the specificSDS and DEPPlease consult the specificSDS and thylene ChlorideBeta-PropiolactoneCarbon TetrachlorideLabel all containers as "CancerSuspect Agents" or the equivalent.Store according to the hazardousnature of the chemical, usingappropriate security when necessaryPlease consult the specificSDS and DEPPlease consult the specificSDS and DEPTeratogensLead CompoundsMercury CompoundsBenzeneAnilineLabel all containers as "SuspectReproductive Hazard" or“Reproductive Effecter”Aniline incompatible withNitric Acid and hHdrogenPeroxidePlease consult the specificSDS and DEPPlease consult the specificSDS and DEPSodium BicarbonateSodium ChlorideAgarSalt bufferMost non-reactive saltsStore on shelves, or laboratorybenches or shelving preferablybehind glass doors and below eyelevel with like chemicalsPlease consult theSDS and DEPPlease consult the specificSDS and DEPGeneral Stock ChemicalsStore according to the hazardousnature of the chemical, usingappropriate security when necessaryAdapted from Prudent Practices in the Laboratory: Handling and Disposal of Chemicals, National Research Council, 1995, University of Texas/HealthScience at Houston and Boston University Environmental Health & Safety.
Examples Storage Recommendations Chemicals Types Mixed/Health Concerns . Flammable Compressed . Methane Handle flammable compressed gases . Gases . Acetylene in a chemical fume hood Oxidizers Fire Hazard Explosion Toxic Compressed Gases Hazard Butane Propane Store in well-ventilate