Transcription
F5 Device Cryptographic ModuleFIPS 140-2 Non-Proprietary Security PolicyHardware Versions:BIG-IP i4000, BIG-IP i5000, BIG-IP i5820-DF, BIG-IP i7000, BIG-IP i7820-DF, BIG-IPi10800, BIG-IP i11800-DS, BIG-IP i15800, BIG-IP 4000, BIG-IP 5250v-F BIG-IP 7000, BIGIP 7200v-F, BIG-IP 10200v-F, BIG-IP 10350v-F, VIPRION B2250, VIPRION B4450Firmware Version:13.1.1 EHFFIPS Security Level 2Document Version 1.0Document Revision: 2019-04-23Prepared by:atsec information security corporation9130 Jollyville Road, Suite 260Austin, TX 78759www.atsec.com 2019 F5 Networks / atsec information security.This document can be reproduced and distributed only whole and intact, including this copyright notice.
F5 Device Cryptographic ModuleFIPS 140-2 Non-Proprietary Security PolicyTable of Contents1.Cryptographic Module Specification . 51.1.Module Description . 51.2.FIPS 140-2 Validation Level . 81.3.Description of modes of operation . 81.4.Cryptographic Module Boundary . 121.4.1.Hardware Block Diagram . 122.Cryptographic Module Ports and Interfaces . 133.Roles, Services and Authentication . 174.3.1.Roles . 173.2.Authentication . 183.3.Services. 19Physical Security . 244.1.5.Operational Environment . 315.1.6.7.Applicability . 31Cryptographic Key Management . 326.1.Key Generation . 326.2.Key Establishment . 336.3.Key Entry / Output . 336.4.Key / CSP Storage . 336.5.Key / CSP Zeroization . 336.6.Random Number Generation . 33Self-Tests . 347.1.8.Tamper Label Placement . 24Power-Up Tests . 347.1.1.Integrity Tests . 347.1.2.Cryptographic algorithm tests . 347.2.On-Demand self-tests . 357.3.Conditional Tests . 35Guidance . 378.1.Delivery and Operation . 378.2.Crypto Officer Guidance . 378.2.1.Installing Tamper Evident Labels . 378.2.2.Install Device . 378.2.3.Password Strength Requirement . 378.2.4.Additional Guidance . 37 2019 F5 Networks / atsec information security.This document can be reproduced and distributed only whole and intact, including this copyright notice.2 of 42
F5 Device Cryptographic Module8.2.5.8.3.9.FIPS 140-2 Non-Proprietary Security PolicyVersion Configuration . 38User Guidance . 38Mitigation of Other Attacks . 39List of FiguresFigure 1 – Hardware Block Diagram . 12Figure 2 – BIG-IP i4000 . 14Figure 3 – BIG-IP i5000/i5820-DF . 14Figure 4 – BIG-IP i7000/i7820-DF . 14Figure 5 – BIG-IP i10800 / i11800-DS . 14Figure 6 – BIG-IP i15800 . 15Figure 7 – BIG-IP 4000. 15Figure 8 – BIG-IP 5250v-F . 15Figure 9 – BIG-IP 7000. 15Figure 10 – BIG-IP 7200v-F . 15Figure 11 – BIG-IP 10200v-F . 16Figure 12 – BIG-IP 10350v-F . 16Figure 13 – VIPRION B2250 . 16Figure 14 – VIPRION B4450 . 16Figure 15 – BIG-IP i4000 (3 of 3 tamper labels) . 25Figure 16 – BIG-IP i5000 (3 of 3 tamper labels) . 25Figure 17 – BIG-IP i5820-DF (4 tamper labels shown) . 25Figure 18 – BIG-IP i7000 (6 of 6 tamper labels shown) . 26Figure 19 – BIG-IP i7820-DF (4 tamper labels shown) . 26Figure 20 – BIG-IP i10800/i11800-DS (6 tamper labels shown) . 27Figure 21 – BIG-IP i10800/i11800-DS (tamper label 5 & 6). 27Figure 22 – BIG-IP i15800 (Front tamper labels 1-3 labels shown) . 27Figure 23 – BIG-IP i15800 (Back tamper labels 4 and 5 labels shown) . 27Figure 24 – BIG-IP 4000 (3 tamper labels shown) . 28Figure 25 – BIG-IP 5250v-F (4 tamper labels shown) . 28Figure 26 – BIG-IP 7000 with faceplate attached (Label 1 is located under faceplate) . 28Figure 27 – BIG-IP 7000 with faceplate removed (1 of 4 tamper labels shown) . 28Figure 28 – BIG-IP 7000 backside (3 of 4 tamper labels shown) . 29Figure 29 – BIG-IP 7200v-F (5 tamper labels shown) . 29Figure 30 – BIG-IP 10200v-F (tamper labels 1-3) . 29Figure 31 – BIG-IP 10200v-F (tamper label 4 shown) . 29Figure 32 – BIG-IP 10350v-F with faceplate attached . 30 2019 F5 Networks / atsec information security.This document can be reproduced and distributed only whole and intact, including this copyright notice.3 of 42
F5 Device Cryptographic ModuleFIPS 140-2 Non-Proprietary Security PolicyFigure 33 – BIG-IP 10350v-F with faceplate removed (1 of 4 tamper labels shown) . 30Figure 34 – BIG-IP 10350v-F backside (3 of 4 tamper labels shown) . 30Figure 35 – VIPRION B2250 in chassis (1 of 6 tamper labels shown) . 30Figure 36 – VIPRION B2250 top view (5 of 6 tamper labels shown) . 30Figure 37 – VIPRION B4450 in chassis . 31Figure 38 – VIPRION B4450 front (1 of 5 tamper labels shown) . 31Figure 39 – VIPRION B4450 top-view (4 of 5 tamper labels shown). 31List of TablesTable 1 – Tested Modules . 7Table 2 – Security Levels . 8Table 3 – FIPS Approved and Allowed Algorithms . 10Table 3a – FIPS Non-Approved but Allowed Algorithms . 10Table 4 – Non-FIPS Approved Algorithms/Modes . 11Table 5 - Ports and Interfaces . 13Table 6 – FIPS 140-2 Roles . 18Table 7 – Authentication of Roles . 18Table 8 – Non-Authenticated Services . 19Table 9 – Management Services in FIPS mode of operation . 21Table 10 – Crypto Services in FIPS mode of operation . 22Table 11 – Services in non-FIPS mode of operation . 23Table 12 – Inspection of Tamper Evident Labels . 24Table 12a – Number of Tamper Labels per Module . 24Table 13 – Life cycle of CSPs . 32Table 14 – Self-Tests . 35Table 15 – Conditional Tests . 36Copyrights and TrademarksF5 and BIG-IP are registered trademarks of F5 Networks.Intel and Xeon are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. 2019 F5 Networks / atsec information security.This document can be reproduced and distributed only whole and intact, including this copyright notice.4 of 42
F5 Device Cryptographic ModuleFIPS 140-2 Non-Proprietary Security PolicyIntroductionThis document is the non-proprietary FIPS 140-2 Security Policy of F5 Device Cryptographic Modulewith firmware version 13.1.1 EHF and hardware version listed in table 1. It contains the security rulesunder which the module must operate and describes how this module meets the requirements asspecified in FIPS PUB 140-2 (Federal Information Processing Standards Publication 140-2) for aSecurity Level 2 module.1. Cryptographic Module SpecificationThe following section describes the cryptographic module and how it conforms to the FIPS 140-2specification in each of the required areas.1.1. Module DescriptionThe F5 Device Cryptographic Module (hereafter referred to as “the module”) is a smart evolution ofApplication Delivery Controller (ADC) technology. Solutions built on this platform are load balancers.They’re full proxies that give visibility into, and the power to control—inspect and encrypt or decrypt—all the traffic that passes through your network.Underlying all BIG-IP hardware and software is F5’s proprietary operating system, TMOS, whichprovides unified intelligence, flexibility, and programmability. With its application control planearchitecture, TMOS gives you control over the acceleration, security, and availability services yourapplications require. TMOS establishes a virtual, unified pool of highly scalable, resilient, and reusableservices that can dynamically adapt to the changing conditions in data centers and virtual and cloudinfrastructures. The module has been tested on the multichip standalone devices listed in Table 1below with the firmware version 13.1.1 EHF. 2019 F5 Networks / atsec information security.This document can be reproduced and distributed only whole and intact, including this copyright notice.5 of 42
F5 Device Cryptographic ModuleHardware1FIPS 140-2 Non-Proprietary Security PolicyProcessor 1OperatingSystemSpecificationsBIG-IP i4000Intel Xeon D-1518TMOS13.1.1 EHF18114x USBx 1GbE; 4 x 10GbE network portsx Console portx 1GbE management portx LEDsBIG-IP i5000Intel Xeon E5-1630TMOS13.1.1 EHF18114x USB portx 1GbE; 4 x 40GbE network portsx Console portx GbE management portx LEDsBIG-IP i5820-DFIntel Xeon E5-1630TMOS13.1.1 EHF18114x USB portx 10GbE; 4 x 40GbE network portsx Console portx 1GbE management portx LEDsBIG-IP i7000Intel Xeon E5-1650TMOS13.1.1 EHF18114x USB portx 1GbE; 6 x 10GbE network portsx Console portx 1GbE management portx LEDsBIG-IP i7820-DFIntel Xeon E5-1650TMOS13.1.1 EHF18114x USB portx 10GbE; 4 x 40GbE network portsx Console portx 1GbE management portx LEDsBIG-IP i10800Intel Xeon E5-1660TMOS13.1.1 EHF18114x USB portx 10GbE; 6 x 40GbE network portsx Console portx 1GbE management portx LEDsBIG-IP i11800-DSIntel Xeon E5-2695TMOS13.1.1 EHF18114x USB portx 10GbE; 6 x 40GbE network portsx Console portx 1GbE management portx LEDsBIG-IP i15800Intel Xeon E5-2680TMOS13.1.1 EHF18114x USB portx 40GbE; 4 x 100GbE network portsx Console portx 1GbE management portx LEDsBIG-IP 4000Intel Xeon E3-1125CTMOS13.1.1 EHF18114x USB portx 1GbE; 2 x 10GbE network portsx Console portx GbE management portx LEDsBIG-IP 5250v-FIntel Xeon E3-1230TMOS13.1.1 EHF24114x USB portx 1GbE; 8 x 10GbE network portsx Console portx GbE management portx LEDsThe modules make use of AES-NI instruction provided by the underlying processor. 2019 F5 Networks / atsec information security.This document can be reproduced and distributed only whole and intact, including this copyright notice.6 of 42
F5 Device Cryptographic ModuleHardwareFIPS 140-2 Non-Proprietary Security PolicyProcessor 1OperatingSystemSpecificationsBIG-IP 7000Intel Xeon E3-1275TMOS13.1.1 EHF18114x USB portx 1GbE; 2 x 10GbE network portsx Console portx GbE management portx LEDsBIG-IP 7200v-FIntel Xeon E3-1275TMOS13.1.1 EHF24114x USB portx 1GbE; 8 x 10GbE network portsx Console portx GbE management portx LEDsBIG-IP 10200v-FIntel Xeon E5-1650TMOS13.1.1 EHF1 x USB port16 x 10GbE; 2 x 40GbE network ports1 x Console port1 x GbE management port4 x LEDsBIG-IP 10350v-FIntel Xeon E5-2658TMOS13.1.1 EHF1 x USB port16 x 10GbE; 2 x 40GbE network ports1 x Console port1 x GbE management port4 x LEDsVIPRION B2250Intel Xeon E5-2658TMOS13.1.1 EHF14114x USB portx 40 GbE network portsx Console portx GbE management portx LEDsVIPRION B4450Intel Xeon E5-2658ATMOS13.1.1 EHF14114x USB portx 40 GbE; 2 x 100 GbE network portsx Console portx GbE management portx LEDsTable 1 – Tested Modules 2019 F5 Networks / atsec information security.This document can be reproduced and distributed only whole and intact, including this copyright notice.7 of 42
F5 Device Cryptographic ModuleFIPS 140-2 Non-Proprietary Security Policy1.2. FIPS 140-2 Validation LevelFor the purpose of the FIPS 140-2 validation, the F5 Device Cryptographic Module is defined as amulti-chip standalone hardware cryptographic module validated at overall security level 2. The tablebelow shows the security level claimed for each of the eleven sections that comprise the FIPS 140-2standard:FIPS 140-2 SectionSecurityLevel1Cryptographic Module Specification22Cryptographic Module Ports and Interfaces23Roles, Services and Authentication24Finite State Model25Physical Security26Operational Environment7Cryptographic Key Management28EMI/EMC29Self-Tests210Design Assurance211Mitigation of Other AttacksOverall LevelN/AN/A2Table 2 – Security Levels1.3. Description of modes of operationThe module must be installed in the FIPS validated configuration as stated in Section 8 – Guidance. Inthe operational mode the module supports two modes of operation: in "FIPS mode" (the FIPS Approved mode of operation) only approved or allowed securityfunctions with sufficient security strength can be used. in "non-FIPS mode" (the non-Approved mode of operation) only non-approved security functionscan be used.The module enters operational mode after power-up tests succeed. Once the module is operational,the mode of operation is implicitly assumed depending on the security function invoked and thesecurity strength of the cryptographic keys. Critical Security Parameters (CSPs) used or stored inFIPS mode are not used in non-FIPS mode, and vice versa. 2019 F5 Networks / atsec information security.This document can be reproduced and distributed only whole and intact, including this copyright notice.8 of 42
F5 Device Cryptographic ModuleFIPS 140-2 Non-Proprietary Security PolicyIn the FIPS Approved Mode, the cryptographic module will provide the following CAVP certifiedcryptographic yption andDecryptionAES-CBCAES-GCMKeys/CSPsCertificate Number(s)128/192/256-bit AES keyC2, C33, C34, C35,C36, C37, C40, C41,C42, C43, C44, C45,C46, C47, C48, C49128/256-bit AES keyC52, C53, C54, C55,C57, C58, C62, C63,C64, C65, C67, C68,C69, C70, C71, C75SP800-90A CTR DRBGRandom NumberGenerationEntropy input string, Vand Key valuesC2, C33, C34, C35,C36, C37, C40, C41,C42, C43, C44, C45,C46, C47, C48, C49,C52, C53, C54, C55,C57, C58, C62, C63,C64, C65, C67, C68,C69, C70, C71, C75FIPS 186-4 RSA KeyPair GenerationRSA Key GenerationRSA public and privatekey pair with 2048/3072bit modulus sizeC2, C33, C34, C35,C36, C37, C40, C41,C42, C43, C44, C45,C46, C47, C48, C49PKCS#1 v1.5 RSASignature Generationand SignatureVerification with SHA256 and SHA-384RSA SignatureGeneration andVerificationRSA private key with2048/3072-bit modulusFIPS 186-4 ECC KeyPair Generation(Appendix B.4.2)ECDSA Key PairGenerationECDSA/ECDHpublic/private key pairfor P-256 and P-384curvesC2, C33, C34, C35,C36, C37, C40, C41,C42, C43, C44, C45,C46, C47, C48, C49,C52, C53, C54, C55,C57, C58, C62, C63,C64, C65, C67, C68,C69, C70, C71, C75FIPS 186-4 ECDSASignature Generationand SignatureVerificationECDSA SignatureGeneration andVerificationECDSA private key(P-256, P- 384 curves)SHA-1SHA-256SHA-384Message DigestN/AHMAC-SHA-1HMAC-SHA-256HMAC-SHA-384Message AuthenticationHMAC key( 112-bit) 2019 F5 Networks / atsec information security.This document can be reproduced and distributed only whole and intact, including this copyright notice.9 of 42
F5 Device Cryptographic ModuleFIPS 140-2 Non-Proprietary Security PolicySP800-56A ECC exceptKDF (Section 5.7.1.2ECC CDH Primitive)Key Agreement Scheme(KAS)private Key with P-256and P-384 curvesKey DerivationSP800-135 KeyDerivation in SSHSession encryption anddata authentication keys2TLS 1.0/1.1/1.2 withSHA-256 and SHA-384C2, C33, C34, C35,C36, C37, C40, C41,C42, C43, C44, C45,C46, C47, C48, C49C2, C33, C34, C35,C36, C37, C40, C41,C42, C43, C44, C45,C46, C47, C48, C49,C52, C53, C54, C55,C57, C58, C62, C63,C64, C65, C67, C68,C69, C70, C71, C75Table 3 – FIPS Approved and Allowed AlgorithmsAlgorithmUsageKeys/CSPsCertificate Number(s)EC Diffie-HellmanKey Agreementprivate key with P-256and P-384 curvesNon-Approved butAllowedRSA PKCSKey WrappingRSA key pair with2048/3072-bit modulussizeNon-Approved butAllowedNDRNGN/AseedNon-Approved butAllowedTable 3a – FIPS Non-Approved but Allowed AlgorithmsAlgorithmAESUsageSymmetric Encryption andDecryptionDESRC4Triple-DESusing OFB, CFB, CTR, XTS andKW modesn/aRSAAsymmetric Encryption andDecryptionusing modulus sizes less than2048-bits or greater than 3072bitsRSAAsymmetric Key GenerationFIPS 186-4 less than 2048-bitmodulus size or greater than3072-bitsDSA2Notesusing any key sizeNo parts of the TLS protocol except the KDF has been reviewed or tested by the CAVP and CMVP. 2019 F5 Networks / atsec information security.This document can be reproduced and distributed only whole and intact, including this copyright notice.10 of 42
F5 Device Cryptographic ModuleFIPS 140-2 Non-Proprietary Security PolicyECDSAECDHusing public/private key pair forcurves other than P-256 and P384RSADigital Signature Generation andVerificationPKCS#1 v1.5 using key sizesother than 2048 and 3072 bitsPKCS#1 v1.5 using SHA-1, SHA224 and SHA-512using X9.31 standardusing Probabilistic SignatureScheme (PSS)DSAusing any key size and SHAvariantECDSAFIPS 186-4 using curves otherthan P-256 and P-384FIPS 186-4 using curves P-256and P-384 with SHA-1, SHA-224and SHA-512SHA-224SHA-512MD5Message S-CMACMessage AuthenticationN/ADiffie-HellmanKey Agreement Scheme (KAS)N/AECDHusing curves other than P-256and P-384TLS KDFKey Derivation functionUsing SHA-1/SHA-224/SHA-512SSH KDFSNMP KDFusing any SHA variantIKEv1 and IKEv2 KDFTable 4 – Non-FIPS Approved Algorithms/Modes 2019 F5 Networks / atsec information security.This document can be reproduced and distributed only whole and intact, including this copyright notice.11 of 42
F5 Device Cryptographic ModuleFIPS 140-2 Non-Proprietary Security Policy1.4. Cryptographic Module BoundaryThe cryptographic boundary of the module is defined by the exterior surface of the appliance (reddotted line). The block diagram below shows the module, its interfaces with the operationalenvironment and the delimitation of its logical boundary.1.4.1.Hardware Block DiagramThe block diagram below depicts the flow of status output (SO), control input (CI), data input (DI) anddata output (DO). Description of the ports and interfaces can be found in Table 5 – Ports andInterfaces below.- (RAM)StorageInterface(SSD)CentralProcessingUnit (CPU)DisplayInterface(LCD, LED, USB)NetworkInterface(Ethernet, Fiber)- DO- SO- DI- DO- SO- CIFigure 1 – Hardware Block Diagram 2019 F5 Networks / atsec information security.This document can be reproduced and distributed only whole and intact, including this copyright notice.12 of 42
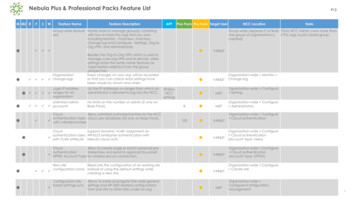
F5 Device Cryptographic ModuleFIPS 140-2 Non-Proprietary Security Policy2. Cryptographic Module Ports and InterfacesFor the purpose of the FIPS 140-2 validation, the physical ports are interpreted to be the physicalports of the hardware platform on which it runs.The logical interfaces are the commands through which users of the module request services. Thefollowing table summarizes the four physical interfaces with details of the FIPS 140-2 logicalinterfaces they correspond to:Logical InterfacePhysical InterfaceDescriptionData InputNetwork InterfaceDepending on module, the network interface consistsSFP, SFP , and/or QSFP ports (Ethernet and/or FiberOptic) which allow transfer speeds from 1Gbps to up to40Gbps.Data OutputNetwork InterfaceDisplay InterfaceDepending on module, the network interface consistsSFP, SFP , and/or QSFP ports (Ethernet and/or FiberOptic) which allow transfer speeds from 1Gbps to up to40Gbps. In addition, Status logs may be output to USBfound in the interface.Control InputDisplay InterfaceNetwork InterfaceThe control input found in the display interface includesthe power button and reset button. The control input foundin the network interface includes the API which controlsystem state (e.g. reset system, power-off system).Status OutputDisplay InterfaceDepending on model, the display interface can consist of aLCD display, LEDs, and/or output to STDOUT whichprovides system status information.Power InputPower InterfaceRemovable PSU (x2)Table 5 - Ports and Interfaces 2019 F5 Networks / atsec information security.This document can be reproduced and distributed only whole and intact, including this copyright notice.13 of 42
F5 Device Cryptographic ModuleFIPS 140-2 Non-Proprietary Security PolicyThe images below show the various modules that were tested. Please use the images to familiarizeyourself with the devices.Figure 2 – BIG-IP i4000Figure 3 – BIG-IP i5000/i5820-DFFigure 4 – BIG-IP i7000/i7820-DFFigure 5 – BIG-IP i10800 / i11800-DS 2019 F5 Networks / atsec information security.This document can be reproduced and distributed only whole and intact, including this copyright notice.14 of 42
F5 Device Cryptographic ModuleFIPS 140-2 Non-Proprietary Security PolicyFigure 6 – BIG-IP i15800Figure 7 – BIG-IP 4000Figure 8 – BIG-IP 5250v-FFigure 9 – BIG-IP 7000Figure 10 – BIG-IP 7200v-F 2019 F5 Networks / atsec information security.This document can be reproduced and distributed only whole and intact, including this copyright notice.15 of 42
F5 Device Cryptographic ModuleFIPS 140-2 Non-Proprietary Security PolicyFigure 11 – BIG-IP 1020
Hardware Versions: Firmware Version: 13.1.1 EHF - NIST . Crypto -