Transcription
PEPTIDE SYNTHESISDr. Rita P.-Y. ChenInstitute of Biological ChemistryAcademia Sinica1 Solution phase chemistry-Time consuming: isolation and purificationat each step-Low yield: can’t drive reaction to complete-Use excess reagent to improve yield21
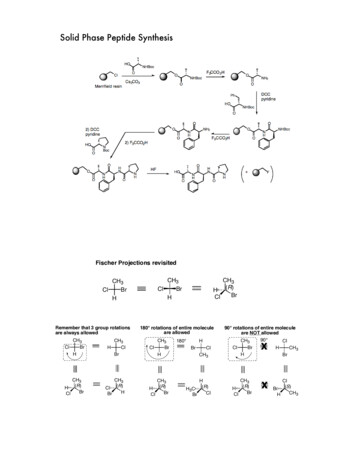
Solid phase peptide synthesis(SPPS)The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1984--for his development of methodologyfor chemical synthesis on a solidmatrixRobert Bruce MerrifieldRockefeller University342
51. Synthesis occurs on the surface of the beadand inside the bead2. Bead swells when solvent is absorbed.Synthesis occurs on multiple surfaces insidethe bead63
Easier!!71. Choose resin!84
Prepare fullyprotected peptide!9105
N-terminal protecting group : X t-Boc 1126
UV301nm13Amino acid activation . YOBt147
152. Choose amino acid!168
17189
Fmoc-cys(mmt)-OH, mmt: methoxytritylCleaved by 1 % TFA in DCM containing 5 % TIS19Development of the photolabile linkerR phosphate, amineCarboxylic acid3’,5’-dimethoxybenzoin (DMB)2-phenyl-5,7-dimethoxybenzofuranSheehan JC, Wilson RM, and Oxford AW (1971) JACS 93, 7222-7228.BrAc-CMB2010
21Fmoc-Lys(mtt)-OHMemtt: methyltritylCleaved by 1 % TFA in DCM containing 5 % TISMePmc(5-member ring: Pbf)2211
3. Choose cleavage reagents!232412
Scavenger!!!! EDT (Ethanedithiol) – scavenger for tbutyl cation, help to remove Trt from Cys EDT, Thioanisole – avoid Met oxidation Phenol – protect Tyr, Trp TIS (Triisopropylsilane) – quench highlystable Trt cation25Side reaction during cleavage . Alkylation for Met, Cys, Trp (by t-Butylcation) Sulfonation for Trp (by Mtr, Pmc): UseTrp(Boc)2613
272814
29ABI 433A Peptide Synthesizer3015
Coupling efficiency and final yieldYield 031Ninhydrin test110 C, 4-6 minA blue to blue-violet color is given by α-amino acidsand constitutes a positive test. Other colors (yellow,orange, red) are negative.3216
Difficult coupling Prolonged coupling time Dry solvent Aggregation – shrinking of resin matrix: usedipolar aprotic solvent (DMF, DMSO, NMP),resin crosslinking 1 % Add chaotropic salt (0.8 M NaClO4, LiCl, 4MKSCN) Use different activation method (PyBOP,HOBt/HBTU, TBTU) Magic mixture: DCM/DMF/NMP (1:1:1) with1 % Triton X100, and 2 M ethylenecarbonateat 55 C for solvent in acylation333417
Batchwise and continuous flow SPPS In batch instruments, reactions and washings are carried out ina shaken, stirred, vortexed, or bubbled reaction vessel.Reagents and solvents are added and removed through a filtervia application of gas pressure or vacuum. In continuous flow mode, a glass column with filters at the topand the bottom contains the resin and acts as a reaction vessel.The system includes a positive displacement pump to enablecontinuous fluid flow. Continuous flow instrumentation wasdesigned for Fmoc/tBu based methods because N protectinggroup removal proceeds under milder conditions (piperidine) Polystyrene (PS) resins, the most traditional support used insolid phase, in conjunction with fluid delivery via a pump,create high pressures that may halt the synthetic process. To overcome this problem, polyethylene glycol (PEG)-PSsupports, which combine a hydrophobic core of PS withhydrophilic PEG chains, have been developed35Antibody against small peptides Antibodies to small peptides have become anessential tool in life science research, withapplications including gene product detection andidentification, protein processing studies, diagnostictests, protein localization, active site determination,protein homology studies and protein purification. Anti-peptide antibodies will always recognize thepeptide.3618
Sequence epitopes in proteins generally consistof 6-12 amino acids and can be classified ascontinuous and discontinuous. Continuous epitopes are composed of a contiguoussequence of amino acids in a protein. Anti-peptideantibodies will bind to these types of epitopes in thenative protein provided the sequence is not buried inthe interior of the protein. Discontinuous epitopes consist of a group of aminoacids that are not contiguous but are brought togetherby folding of the peptide chain or by the juxtapositionof two separate polypeptide chains. Anti-peptideantibodies may or may not recognize this class ofepitope depending on whether the peptide used forantisera generation has secondary structure similar tothe epitope and/or if the protein epitope has enoughcontinuous sequence for the antibody to bind with alower affinity.37 When examining a protein sequence for potential antigenicepitopes, it is important to choose sequences which arehydrophilic, surface-oriented, and flexible. Antibodies bind toepitopes on the surface of proteins.Algorithms for predicting protein characteristics such ashydrophilicity/hydrophobicity and secondary structureregions such as alpha-helix, beta-sheet and beta-turn aidselection of a potentially exposed, immunogenic internalsequence for antibody generation. Many commercialsoftware packages such as MacVectorTM, DNAStarTM, andPC-GeneTM incorporate these algorithms.length of the peptide: long peptides (20-40 amino acids inlength) increases the number of possible epitopes. Peptideslonger than 20 residues in length are often more difficult tosynthesize with high purity because there is greater potentialfor side reactions, and they are likely to contain deletionsequences. On the other hand, short peptides ( 10 aminoacids) may generate antibodies that are so specific in theirrecognition that they cannot recognize the native protein ordo so with low affinity. The typical length for generating antipeptide antibodies is in the range of 10-20 residues.3819
Coupling the synthetic peptide tocarrier protein Conjugation to a carrier protein is important because peptidesare small molecules, that alone do not tend to be immunogenic,thus possibly eliciting a weak immune response. The carrier protein contains many epitopes that stimulate Thelper cells, which help induce the B-cell response. It isimportant to ensure the peptide is presented to the immunesystem in a manner similar to the way it would be presented bythe native protein. Internal sequences can be coupled at either end. Anotherconsideration for internal sequences is to acetylate or amidatethe unconjugated end as the sequence in the native proteinmolecule would not contain a charged terminus.39Carrier proteins Many different carrier proteins can be used for coupling tosynthetic peptides. The most commonly selected carriers arekeyhole limpet hemacyanin (KLH) and bovine serum albumin(BSA). The higher immunogenicity of KLH often makes it the preferredchoice. Another advantage of choosing KLH over BSA is thatBSA is used as a blocking agent in many experimental assays.Because antisera raised against peptides conjugated to BSAwill also contain antibodies to BSA, false positives may result. Although KLH is large and immunogenic, it may precipitateduring cross-linking, making it difficult to handle in some cases. Ovalbumin (OVA) is another useful carrier protein. It is a goodchoice as a second carrier protein when verifying whetherantibodies are specific for the peptide alone and not the carrier.4020
Coupling methods The most common coupling methods rely on thepresence of free amino(α-amino or Lys), sulfhydryl(Cys), or carboxylic acid groups (Asp, Glu or αcarboxyl). Coupling methods should be used that linkthe peptide to the carrier protein via the carboxy- oramino-terminal residue. The sequence chosen shouldnot have multiple residues that may react with thechosen chemistry. If multiple reactive sites are present,try to shorten the peptide or choose the sequence sothey are all localized at either the amino or the carboxylterminus of the peptide. For internal sequences the endfurthest from the predicted epitope is normally favoredas this avoids potential masking problems.41Activateprotein orpeptideGlutaldehyde canreact with C, Y, Htoo4221
Multiple Antigen Peptidesystem (MAPs) The MAP system represents a unique approach to antipeptide antibody generation. The system is based on a small immunogenically inertbranched lysine core onto which multipe peptides aresynthesized in parallel.Fmoc-Lys(fmoc)-OH43 The result after synthesis is a three-dimensionalmolecule, which has a high molar ratio of peptideantigen to core molecule and therefore does notrequire the use of a carrier protein to induce anantibody response. The result is a highly immunogenic MAP, whichexhibits significantly higher titers when compared toits monomeric counterpart attached to a carrierprotein. It should be noted that there are some synthesisconcerns when making a MAP complex. Sterichindrance becomes a problem during the synthesis oflong peptides, resulting in some arms of thedendrimer being deletion products. The highmolecular weight of the complex does not lend itselfto good quality control measures (mass spec and/oranalytical HPLC).4422
Solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1984--for his development of methodology for chemical synthesis on a solid matrix Robert Bruce Merrifield Rockefeller University 4. 3 5 6 1. Synthesis occurs on the surface of the bead and inside the bead 2. Bead swells when solvent is absorbed.