Transcription
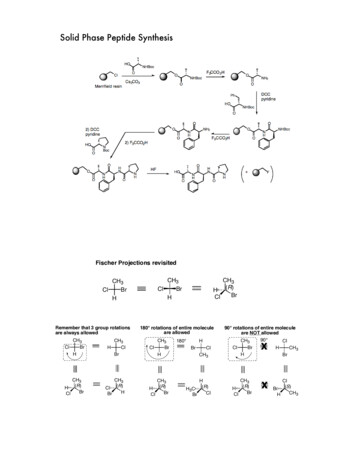
Solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS),strategies, resins and comparison withFmoc-strategy
General scheme of SPPSattach to linkerdeprotect amino functioncouplen times deprotectionand couplingcleave
N-α-protecting groups two mainly used N-α-protecting groupsFmocBoc
Boc-protecting groupBoc tert. Butyloxycarbonylortert. Butoxycarbonyl stable to bases and nucleophiles unaffected by catalytic hydrogenation deprotection with TFA is rapid
Introduction of the Boc-groupDi-tert-butyl-dicarbonate Boc-anhydride (t-boc)2O2-(tert. Butoxycarbonyloxyimino)-2-phenylacetonitril Boc-NOOOOOOOOONN both commercially availablestorage in refrigerator for extended periods(t-boc)2O is more expensivepreparation: „Kates S. A., Albericio F. (ed): Solid-Phase Synthesis, Apractical guide, Marcel Dekker Inc. 2000, p. 105-107“
N-α-Boc protected amino acids already N-α-Boc protected amino acids can simply bebought from firms like „Novabiochem“Oe.g. Boc-Ala-OHONHCOOH
Cleavage of the Boc-groupTFAE1-eliminationCO2 cleavageTFA is volatile and can be easily removed in vacuum!
Resins for Boc SPPS Resins for preparing peptide acids Merrifield (Chloromethylstyrene-divinylbenzene)-was the standard support for the synthesis of peptide acids by Boc SPPSnow only used in the synthesis of small to medium sized peptides, because thebenzylic ester resin linkage is not completely stable towards repetitive treatmentwith TFA, DMFCl BocAS-Cs ,bocKIOHNOR- attachment of the C-terminal residue is achieved by heating the resin in DMF withthe appropiate amino acid cesium salt in the presence of KI- cleavage is affected by treatment of resin with HF or TFMSA, or by hydrogenolysis- alcohols can be released using reducing agents like DIBALH or LiBH4- methyl esters can be produced by transesterification with NaOMe
Resins for Boc SPPS Resins for preparing peptide acids PAM (4-Hydroxymethylphenylacetamidomethyl)-also a standard support for Boc SPPSstabilizing effect of the phenylacetamidomethyl function on the ester linkage reduction of losses during repetitive TFA acidolysisbocOHNORONcoupling:Ha)first addition of the PAM-linker on to the aminomethyl resin and thencoupling of the Boc-protected amino acidb)first coupling of the Boc-protected amino acid to the PAM-linker and thenreaction with the aminomethyl resin followed by end-capping of unreactedaminomethyl groupscleavage:- treatment with HF or TFMSA releases the peptide acid
Resins for Boc SPPS Resins for preparing peptide acids Brominated Wang (Brominated α-Methylphenylacyl resin)OBrR, DMF BocAS-Cs , KIbocOONHOhν (350 nm)bocOHNOHR
Resins for Boc SPPS Resins for preparing peptide amides BHA / MBHA (Benzhydrylamine / 4-Methylbenzhydrylamine)-used for the synthesis of peptide amides by Boc SPPSattachment of the first amino acid with standard methods of amide bondformationcleavage of the carboxamides with HF or TFMSAMBHA is more acid sensitive and the peptide amide can be released with HFor TFMSA under less drastic conditionsNH2NH2
Resins for Boc SPPS Resins for preparing C-terminally modified peptide fragments Brominated PPOA (Brominated [4-Propionylphenoxy]-acetic acid)-versatile resin for the Boc SPPS of peptide acids, esters and hydrazides byphotolytic or nucleophilic cleavageOOBrONH, DMF BocAS-Cs , KIbocOOOHNORONEt3 inmethanol/dioxanehν or NaOH 2
Resins for Boc SPPS Resins for preparing C-terminally modified peptide fragments Oxime resin-attachment of the first amino acid with DCCafterwards acetylation of unreacted oxime groupscleavage from the support by various nucleophiles like NaOH, NH3, R1NH2,NaBH4, MeOH, NH2NH2NO2NO2amino acid, DCCHONRHNOON
General aspects of Boc strategy cleavage of the N-α-Boc-protection group with TFA (usually 25-50%(v/v) in DCM) side chain protecting groups must be orthogonal(!), that means: stable against TFA during N-α-Boc deprotection removable at the end of peptide synthesis release of the peptide from the resin by treatment with HF
Side chain protecting groups for Boc strategyArg: Toluolsulfonyl- (Tos) orMesitylen-2-sulfonyl-group (Mts)cleavage: HF/anisole (Tos)thioanisole (Mts)Ser, Thr, Tyr: Benzyl (Bzl)Ocleavage: HFRboc NAsp, Glu: BzlCOOHHOLys: Fmoc or2-Chlorobenzyloxycarbonyl (2ClZ)cleavage: piperidine (Fmoc), TFA (2ClZ)OOClHNCys: Acetamidomethyl (Acm) orMeO4-Methoxybenzyl (MeOBzl)cleavage: Hg2 - or Ag -salts (Acm), HF (MeOBzl)His: Dinitrophenyl-group (DNP)cleavage: thiolesDNPOOHNOHOHNOHHNbocOSOHbocNHboc
Advantages and disadvantages of Boc- and Fmoc-strategyAdvantagesBoc easy to introduce Boc-amino acids are stable at roomtemp. for extended periods (butstorage at 4 C is recommended) deprotection with TFA is rapid successful strategy for many peptidesynthesis applications good coupling resultsDisadvantages temporary and permanent (side chain)protecting groups are both acid labile side chain deprotection during repeatedTFA treatment can occur repeated TFA-mediated N-α-deprotectionover the course of a long synthesis maylead to modification and/or degradation ofsensitive peptide sequences difficulties for fragile peptides that don‘tsurvive the relatively harsh final HFcleavage Boc-strategy requires the use of“dangerous“ HF and expensive laboratoryapparates side reactions are possible:t-Bu reacts with nucleophilic side chainslike trp, tyr, met, his side chain protecting groups / adding ofscavengers (1,2-Ethanedithiole) to thedeprotection reagent
Advantages and disadvantages of Boc- and Fmoc-strategyAdvantagesFmoc orthogonal protection sheme Fmoc-amino acids are easy toprepare in crystalline form in highyield and stable when stored at 4 C milder reaction conditions:milde base (piperidine) for N-αdeprotection, TFA only for the finalresin cleavage and deprotection progress of each deprotectionreaction can be followed by real timespectrophotometric monitoring therelease of the cleaved Fmoc-group at300-320 nmDisadvantages Piperidine: harmful vapor, toxic side reactions: aspartimide formation at AspX residues like Asp-Gly, -Ser,-Thr, -Asn, -Gln linker-bound C-terminal Cysundergoes significantracemisation (ca. 0,5%) witheach cycle of Piperidinetreatment
Literature-Novabiochem 2002/3 tide2.pdf-Kates S. A., Albericio F. (ed): Solid-Phase Synthesis, A practicalguide, Marcel Dekker Inc. 2000
Solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS), strategies, resins and comparison with Fmoc-strategy. General scheme of SPPS attach to linker deprotect amino function couple n times deprotection and coupling . Solid-Phase Synthesis, A practical guide, Marcel Dekker Inc. 2000, p. 105-107" .