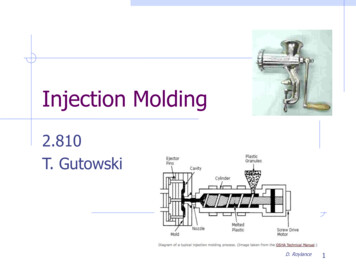
Transcription
Rubber Molding Material Selection Guide
Rubber Molding Material Selection GuideThe two biggest decisions in any rubber molding project are selecting the final design and choosing theappropriate material to achieve the desired functionality of the component. We trust your engineering teamhas been working hard on the design side. The team at Allstates Rubber & Tool Corp. can be a valuableasset in helping with the second part of the equation. As there is a wide range of rubber molding materialsto choose from, we have tried to give you an overview of the most commonly requested products and theircorresponding strengths and weaknesses. This guide should help you narrow down your material optionsby excluding those base polymers that are not suitable. This will provide a good starting point for pricingand performance discussions of compounds around the most applicable polymers. If you have very specificmaterial needs, please contact us directly to aid in the custom formulation of your desired properties.*Note: All “Trade Names” are designated with a registered trademark symbol and referenced to the owner of that registered trademark. We have done our best to cite the proper owner of each “Trade Name”. If you see a discrepancy, please alert us immediatelyand we will be happy to adjust the references appropriately.8201 W. 183rd Street, Unit M, Tinley Park, IL 60487 Phone 800-283-5583 Email mburke@allstatesrubber.comRubber Molding Material Selection Guide // pg. 2
LegendNitrileExcellentChemical Name:Acrylonitrile-butadieneCommon Names:Buna-NASTM D1418, Rubber Nomenclature:NBRASTM D2000 / SAE J200, Automotive Classification:BF, BG, BK, CHISO/DIN 1629, Rubber Nomenclature:NBRMIL-STD-417, Classification of Elastomeric Materials:SBVery GoodGoodFairPoorTemperature Range F-40F to 250FTemperature Range C-40C to 121CDurometer Range (Shore A)20-95Tensile Strength (PSI)200-3000Maximum Elongation (%)600Economical PriceTear ResistanceMetal AdhesionCompression SetReboundAbrasion ResistanceSolvent ResistanceMaterial Overview:Nitrile is the workhorse of the rubber molding world. Asthe most popular material, it has good resistance to water,hydraulic fluid, oil and solvents. Buna-N also has strongabrasion and tear resistance with good compression setproperties. It is the first option that most projects reviewas a mold material as it has an affordable price point.Advantages:Keeping costs down while delivering a strong product withresistance to oils and fuels. Strong mechanical propertiesand wear resistance. It retains its elastomeric propertiesOil/Grease ResistanceWeather/Sunlight ResistanceOzone ResistanceElectrical ResistancePermeability to GasesWater ResistanceHeat ResistanceFlame ResistanceLow Temperature Resistancewell in cold temperatures.Generally Resistant to:Oils, Fuels, Fats, Greases, Hydraulic Fluids, Chemicals, andSolvents.“Nitrile is great for seals, o-rings,Susceptible to weather, and sunlight/ozone aging. It isalso not a good choice when dealing with an applicationany time you have oils or fuels nearan application. It will not swell likeother elastomers and retains goodsealing properties.”’sMikeTiwith flame.and gaskets. It is a great choicepsDisadvantages:8201 W. 183rd Street, Unit M, Tinley Park, IL 60487 Phone 800-283-5583 Email mburke@allstatesrubber.comRubber Molding Material Selection Guide // pg. 3
LegendEPDMExcellentChemical Name:Ethylene-propyleneCommon Names:EPDM, EP, EPT, EPRASTM D1418, Rubber Nomenclature:EPDMASTM D2000 / SAE J200, Automotive Classification:BA, CA, DAISO/DIN 1629, Rubber Nomenclature:EPDMMIL-STD-417, Classification of Elastomeric Materials:RSVery GoodGoodFairPoorTemperature Range F-60F to 300FTemperature Range C-51C to 149CDurometer Range (Shore A)30-90Tensile Strength (PSI)500-3000Maximum Elongation (%)600Economical PriceTear ResistanceMetal AdhesionCompression SetReboundAbrasion ResistanceSolvent ResistanceMaterial Overview:EPDM is another commonly specified material for rubbermolded products. It is frequently used in steam systems,seals for vehicles doors and engine compartments, andbrake lines due to its resistance to glycol based brake fluid.It is an natural choice for automotive applications due toits large temperature range. Smooth flow makes it easy toextrude without imperfections.Advantages:Economical price and excellent for outdoor use withexposure to the elements. Its wide temperature rangeOil/Grease ResistanceWeather/Sunlight ResistanceOzone ResistanceElectrical ResistancePermeability to GasesWater ResistanceHeat ResistanceFlame ResistanceLow Temperature Resistancemakes it a great choice for applications ranging from coldweather to high temperature steam.also very good for cold weather applications.Disadvantages:Not for use with aromatic or aliphatic hydrocarbons,breaks down in petroleum based oils and fuels.“I find EPDM to be highly usefulin energy, military, transportationand automotive projects as theexposure to varying temperaturesand weather climates will notimpact the function of the part.Great both in customer moldedparts and extrusions.”psSuperb against weather, ozone, water, and heat aging. It is’sMikeTiGenerally Resistant to:8201 W. 183rd Street, Unit M, Tinley Park, IL 60487 Phone 800-283-5583 Email mburke@allstatesrubber.comRubber Molding Material Selection Guide // pg. 4
LegendSiliconeExcellentChemical Name:PolysiloxaneCommon Names:Silicone, VMQ, PVMQASTM D1418, Rubber Nomenclature:VMQASTM D2000 / SAE J200, Automotive Classification:FC, FE, GEISO/DIN 1629, Rubber Nomenclature:VMQMIL-STD-417, Classification of Elastomeric Materials:TAVery GoodGoodFairPoorTemperature Range F-100F to 450FTemperature Range C-73C to 232CDurometer Range (Shore A)30-90Tensile Strength (PSI)200-1500Maximum Elongation (%)700Economical PriceTear ResistanceMetal AdhesionCompression SetReboundAbrasion ResistanceSolvent ResistanceMaterial Overview:Silicone should be used as the material for a rubbermolded part when temperature resistance is the mostimportant factor in component performance. The addedadvantage of flexibility and weather resistance allow foradditional deployment considerations. Typical use casesinclude medical devices and food applications. As a semiorganic elastomer, VMQ can be easily torn and is not anOil/Grease ResistanceWeather/Sunlight ResistanceOzone ResistanceElectrical ResistancePermeability to GasesWater Resistanceoption for high wear applications.Heat ResistanceAdvantages:Flame ResistanceLarge functional temperature range, highly flexible,Low Temperature Resistanceexcellent electrical resistance and conductivity properties.Silicone stays flexible to seal in extreme cold.Generally Resistant to:High and low temperatures, weather, ozone, and electrical.Disadvantages:Not for use in high abrasion applications andof choice for the medical industry;or to battle extreme temperatures.”pscomponents with possible tear failures.“Silicone is frequently the materialTi’sMike8201 W. 183rd Street, Unit M, Tinley Park, IL 60487 Phone 800-283-5583 Email mburke@allstatesrubber.comRubber Molding Material Selection Guide // pg. 5
LegendNeopreneExcellentChemical Name:PolychloropeneCommon Names:NeopreneASTM D1418, Rubber Nomenclature:CRASTM D2000 / SAE J200, Automotive Classification:BC, BEISO/DIN 1629, Rubber Nomenclature:SCMIL-STD-417, Classification of Elastomeric Materials:CRVery GoodGoodFairPoorTemperature Range F-50F to 250FTemperature Range C-46C to 121CDurometer Range (Shore A)20-95Tensile Strength (PSI)500-3000Maximum Elongation (%)600Economical PriceTear ResistanceMetal AdhesionCompression SetReboundAbrasion ResistanceSolvent ResistanceMaterial Overview:Neoprene is a strong all-purpose material applicable formany uses rubber molding uses. Frequently it is used inmass transit and transportation as it meets, or exceeds, theFlame-Smoke-Toxicity requirements of ASTM C1166 (flamepropagation), ASTM E162 (flammability), and SMP800C(toxic gas). Additionally, the transportation industryfrequently uses neoprene for constant velocity joint (CVJ)boots, hose covers, vibration mounts, shock absorbers, andwindow seals and gaskets.Oil/Grease ResistanceWeather/Sunlight ResistanceOzone ResistanceElectrical ResistancePermeability to GasesWater ResistanceHeat ResistanceFlame ResistanceAdvantages:Excellent abrasion resistanceand high tensile strength.Low Temperature ResistanceNeoprene is resistant to ozone and weather aging.Additionally, it can be batched to be flame retardant. Itsstrong internal molecular bonding makes neoprene a greatAbrasion, weather, lubricating oils, and flame.custom rubber molded shockabsorbers and motor mounts forDisadvantages:the transportation, agricultural,acids, solvents, and oxygenated hydrocarbons. Also it ismolecular bonding allows it to takeShould not be specified for exposure to strong oxidizingand military industries. Its tightnot good in cold temperature applicationscomponents witha pounding without breaking down.”possible tear failures.psGenerally Resistant to:“We frequently use neoprene in’sMikeTichoice for metal insert bonding.8201 W. 183rd Street, Unit M, Tinley Park, IL 60487 Phone 800-283-5583 Email mburke@allstatesrubber.comRubber Molding Material Selection Guide // pg. 6
Natural RubberChemical Name:PolyisopreneCommon Names:Natural RubberASTM D1418, Rubber Nomenclature:NRASTM D2000 / SAE J200, Automotive Classification:AAISO/DIN 1629, Rubber Nomenclature:NRMIL-STD-417, Classification of Elastomeric Materials:RNLegendExcellentVery GoodGoodFairPoorTemperature Range F-60F to 175FTemperature Range C-51C to 79CDurometer Range (Shore A)20-100Tensile Strength (PSI)500-3500Maximum Elongation (%)700Economical PriceTear ResistanceMetal AdhesionCompression SetReboundAbrasion ResistanceSolvent ResistanceMaterial Overview:Natural rubber is the “granddaddy” of all rubber moldingmaterials. Originally created from the milky latex of therubber tree (hevea brasiliensis), it can now be producedsynthetically. With its strong resilience, abrasion, and surfacefriction properties it is ideal for vibration isolators, mountingpads, diaphragms, seals and o-rings. Unfortunately, naturalrubber has very poor resistance to UV rays, ozone, andpetroleum based products. Special care should be taken toavoid prolonged interaction with these conditions.Oil/Grease ResistanceWeather/Sunlight ResistanceOzone ResistanceElectrical ResistancePermeability to GasesWater ResistanceHeat ResistanceFlame ResistanceAdvantages:The strong dynamic properties of natural rubber makeLow Temperature Resistanceit ideal for use cases requiring high tensile strength, lowcompression set, strong rebound, with tear, and abrasionresistance. Natural rubber is commonly specified whenadherence to a metal component is critical.Generally Resistant to:Abrasion, tear, alcohols, water, and electrical conductivity.Disadvantages:by the FDA for seals used on foodand beverage containers!”psHighly susceptible to petroleum based products, sunlight and’sMikeTiozone.“Natural rubber has been approved8201 W. 183rd Street, Unit M, Tinley Park, IL 60487 Phone 800-283-5583 Email mburke@allstatesrubber.comRubber Molding Material Selection Guide // pg. 7
LegendSBRExcellentChemical Name:Styrene butadieneCommon Names:SBR, GRSASTM D1418, Rubber Nomenclature:SBRASTM D2000 / SAE J200, Automotive Classification:AA, BAISO/DIN 1629, Rubber Nomenclature:SBRMIL-STD-417, Classification of Elastomeric Materials:RSVery GoodGoodFairPoorTemperature Range F-50F to 225FTemperature Range C-46C to 107CDurometer Range (Shore A)30-100Tensile Strength (PSI)500-3000Maximum Elongation (%)600Economical PriceTear ResistanceMetal AdhesionCompression SetReboundAbrasion ResistanceSolvent ResistanceMaterial Overview:SBR is a cost effective polymer for your basic rubbermolding needs. This material can be found in pneumatictires, diaphragms, seals and gaskets. It is our material ofchoice for off-the-shelf rubber parts. This is an excellentmaterial to use for water based applications. Care shouldbe taken when specifying SBR as prolonged exposure tomost petroleum based fluids and solvents will cause theOil/Grease ResistanceWeather/Sunlight ResistanceOzone ResistanceElectrical ResistancePermeability to GasesWater Resistancemolded part to break down.Heat ResistanceAdvantages:Flame ResistanceVery durable material that is resistant to emulsifying inLow Temperature Resistancedamp conditions. Good abrasion resistance. Also, goodfor bonding to inserts.Generally Resistant to:Abrasion, water, wet or dry organic acids.Disadvantages:“You can use SBR as a lower costacids, and most hydrocarbons.many cases as they share many ofalternative to natural rubber inthe same properties!”psPoor resistance to oils, greases, fats, solvents, strongTi’sMike8201 W. 183rd Street, Unit M, Tinley Park, IL 60487 Phone 800-283-5583 Email mburke@allstatesrubber.comRubber Molding Material Selection Guide // pg. 8
LegendFluorocarbonExcellentChemical Name:FluorocarbonCommon Names:Viton , Fluorel ASTM D1418, Rubber Nomenclature:FKMASTM D2000 / SAE J200, Automotive Classification:HKISO/DIN 1629, Rubber Nomenclature:FPMMIL-STD-417, Classification of Elastomeric Materials:TBVery GoodGoodFairPoorTemperature Range F-25F to 400FTemperature Range C-32C to 204CDurometer Range (Shore A)50-95Tensile Strength (PSI)1450Maximum Elongation (%)300Economical PriceTear ResistanceMetal AdhesionCompression SetReboundAbrasion ResistanceSolvent ResistanceMaterial Overview:Viton is known as “the universal o-ring”. This fluorocarboncombines the widest range of chemical resistance withthe most advantageous high temperature properties. Asthe leading material requested for hoses, o-rings, gaskets,and fuel system seals it is relied upon heavily to extendthe lifespan of a rubber molded component far beyond thecapabilities of other materials. Viton can perform reliablywith prolonged exposure to gasoline, as well as the corrosiveenvironment of down-hole drilling operations. Aircraft engineOil/Grease Resis
8201 W. 183rd Street, Unit M, Tinley Park, IL 60487 Phone 800-283-5583 Email mburke@allstatesrubber.com Rubber Molding Material Selection Guide // pg. 3 M i k e ’ s T i p s “Nitrile is great for seals, o-rings, and gaskets. It is a great choice any time you have oils or fuels near an application. It will not swell like other elastomers and retains good sealing properties .