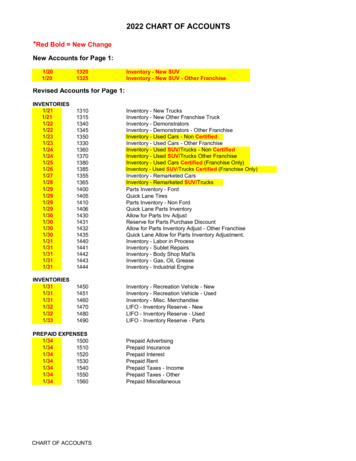
Transcription
Types of Retail FormatsBy: Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIMReference :RM- Swapna Pradhan, RM-Levy and Weitz
The changing structure of retailing Alldynamicdevelopmentsinretailing(department stores, and hypermarkets) areresponses to a changing environment Changing customer demand, new technologies,intense competition, and social change createnew opportunities The Internet and web technologies have itselfcreated a myriad of opportunities for web basedbusiness model of retailing This has created competition for the retailer inorder to maintain and grow its share of marketand compete within its band of retailers2Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
3Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Role of Business ModelProduct /services1. Trends in marketpositioninglocationPricing policy2. Competition3. The OrganizationalcapabilitiesSize and look– store designcommunication4Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Retailer Characteristics affecting businessmodel Every retailer satisfies the needs of specific marketsegment (Mass/ Exclusive/ Speciality) Retailers offer merchandise assortment and variety Retailers adopt a specific pricing strategy(discount/ competitive/ premium) Each retailer develops its own promotional mix On the basis of product mix, a retailer decideschannel of distribution and thus location of store Level of customer service (self-service/ AssortedServices / Full service)5Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Variety and Assortment Variety represents the number of merchandisecategories a retailer offers (Width of product line) Assortment is the number of different items in amerchandise category (depth of the merchandise) Each different item of merchandise is called asStock Keeping Unit (SKU) (Length )6Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Men FormalShirtsMen CasualTrousersWomen Ethnic WomenWear KurtiWestern TopsArrowLee CooperBibaANDLouise PhillipLevisRangmanchChemistryJohn MillerBareWVariety – 4 product linesAssortment – a type of Arrow shirt – 4 colour X 4 sizes 16SKU – 11 different items of merchandise Bigbazaar, Pantaloons, Shopper’s Stop all have formal shirtsection. Bigbazaar has many other categories (more variety) Under shirt section, Shopper’s Stop has more number ofbrands, patterns, sizes etc. than Bigbazaar thus (moreSKUs) Arrow has more assortment as compared than shopper’sstop. (more depth)7Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Classification of retailformatsNon-storeretailingStore basedretailingForms Convenience StoreIndependent RetailerSupermarketChain RetailerDirect SellingHypermarketFranchiseMail OrderSpecialty StoresLeasedTele MarketingDepartmental StoreConsumer cooperativeOff-price RetailersAutomatedVendingCar RentalsOtherservicesFactory OutletsCatalogue ShowroomSwapna Pradhan Page 70 onwards8Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Classification on the basis ofOwnership9Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Classification on the basis of Ownership Independent RetailerA Chain Retailer / Corporate Chain RetailerFranchisingLeased DepartmentConsumer Cooperative10Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Independent Retailer Owns and operates only one retail outletEither propriety/ joint-family/ partnershipLocal baniya/ kirana stores/ apparel stores ve – Good rapport with customers, flexible andthus can react quickly to market changes andcustomer needs-ve – no economies of scale and thus lowbargaining power with suppliers11Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
A Chain Retailer/ Corporate Retail Chain When two or more outlets are under a commonownership, it is called a retail chain.These stores have similar merchandise offered tocustomers along with similarities in ambience,advertising and promotionsE.g. Arrow, Global Desi, Van Heusen,departmental stores like Pantaloons, Westside,Planet M, Foodbazaar ve- bargaining power, cost effectiveness inadvertising and sales promotion-ve – no consideration to local preferences andinability to manage each store, heavy investment12Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Franchising A franchise is a contractual agreementbetween the franchiser and the franchisee,allowing franchisee to conduct a businessunder an established name as per a particularbusiness format in return for a fee orcompensation.Types 13A product or trade mark franchise - e.g. Archie’sA business format franchise – e.g. McDonaldProf. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
14Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Franchise AgreementFranchisee Get a right to usebrand nameAgrees to operate theoutlet in accordancewith proceduresprescribedPays a lump sum royalty on all sales15Franchiser Provides assistance inlocating and buildingthe store, developingthe products andservices sold, trainingmanagers andadvertising supportProf. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Leased Departments Shop-in-shopsWhen a section of a department in a retailstore is leased or rented to an outside party, itis termed as a leased departmentOnly display a fraction of the merchandisesoldAim to make products availableE.g. CCD in Shopper’s Stop16Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Consumer Co-operative Aim to provide essential commodities atreasonable pricesE.g. Apna Bazaar etc.17Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Classification on the basis of theMerchandise OfferedFood RetailersGeneral Retailers Target Market1.2.18Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Convenience Stores Relatively small, located near residential areas,open for long hours, limited line of convenienceproducts like egg, bread, groceriesProvide limited variety and assortment ofmerchandise at convenient locations with speedycheck-outsSize range from 3000-8000 sq.ftTargeted at customers who want to make quickpurchasesNear petrol pumps local baniya19Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Supermarkets Large, low cost, low margin, high-volume, selfservice operations, designed to meet needs forfood, groceries and other non-food related items.Area -400 sqm – 2500 sqm (4305 sqft-26910 sqft)Internationally – 8000-20000 sqftAt least 70% of the merchandise comprising offoodstuff and everyday commoditiesCarry approximately 30000 SKUs with limitedassortmentE.g. Kroger, Safeway, ALDI, Tesco in USE.g. Foodworld, Foodbazaar, Reliance Fresh inIndia20Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Variations in Supermarket Over the years, variations in this businessmodel have emergedSuperstore A variation in supermarketLarger than conventional supermarket with atleast 25000 items and more non-food suchgeneral merchandise, health and beauty etc.Combination store 21Is a superstore and full-line pharmacy withgeneral merchandise and health & beauty careitems accounting for at least 15 % of salesProf. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Hypermarket Combination of a department store a supermarket Invention by Carrefour in Paris 1963 A retail store with a sale area of over 2500 sq.m with atleast 35% selling space devoted to non-grocery products Typical area – 80,000-220,000 sqft Offers variety of food and non-food products likeclothes, jewelry, books CDS, electrical , computers etc Stock SKUs 40000-60000 Cheapest prices, one-stop shopping, a destination offer E.g. Wal-Mart Supercenters, Target (SuperTarget), TescoExtra Stores E.g. Bigbazaar, HyperCity etc.22Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Department Stores Aristide Boucicaut, the son of a successful hat maker founded thefirst department store Bon Marche’ in Saint-Germain, Paris in theyear 1838. Large-scale retail outlet, often multi-leveled, with multiple productcategories, Pleasing ambience, attentive service Carry broad variety and deep assortment, offer customer serviceand organize their store into distinct departments. Selling fashionclothing, accessories, cosmetics, household items Around 7000sqm internationally ( 70,000 sqft) Avg. Indian store 20000-40000 sq.ft. with avg. 50,000-1,00,000SKU’s E.g. Marks & Spencers, Sears, J. C. Penny E.g. Shopper’s Stop, Lifestyle etc.23Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Shoppers’ Stop The company owns 172stores in 25 cities with4.81 million sq.ft spaceacross eight store formats Over 3.3 millioncustomers are a part ofthe First Citizen LoyaltyProgramme24Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Speciality Stores A store specializing in a particular type ofmerchandise or a single product of durable goodslike home furniture, consumer electronics,apparel, jewellery etc. Very specific market segment High level of service and product informationmade available to consumers Narrow product lines (variety), deep assortments Internationally area under 8000 sq.ft E.g. Gap, Ikea E.g. Fabindia, Tanishq, Croma25Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Off Price retailers The merchandise is sold at less than retail pricesGenerally retailers buy manufacturer’s unpopular orunsold inventory at a cheaper rate and sell it at deepdiscounts. Merchandise may being odd sizes,unpopular colours or with minor defectsIt might be manufacturer owned / speciality owned /department storeOutlets are seen as a means of increasing businessE.g. Levi’s Factory outlet, Pantaloon’s Factory Outlet26Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Catalogue showrooms Usually specialise in hard goods such ashousewares, jewellery and consumer electronics,paintsCustomer goes through catalogue and decideswhat does he/she wants to buyE.g. Argos is US27Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Drug Store Is a speciality store that concentrate on healthand personal grooming merchandisePharmaceuticals often represent over 50% ofthe sales28Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Big Box Retailers Over the years, the landscapes of cities andtowns across the world changed thus evolvedlarger formats .that are termed as BIG BOXRETAILERSBig box retailers are large, industrial-stylebuildings or stores with 20,000-2,00,000 sq.ft.Sub-groups 29Discount department storesCategory killersOutlet storesWarehouse clubsProf. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Discount department store 80000sqft to 1,30,000 sqftWide variety including automative parts , homefurnishing, apparel , beauty products etc. 30Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Category killers It is a specialty retailer which offers a very largeselection of product category and economical prices.They focus on single category and stock deepE.g. Toys R Us stock 10000 toy items as compared3,000 in department storeThey buy and sell at cheap rates thus dominate thecategoryInternationally 20,000-1,20,000 sq.ft.31Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Outlet stores 20,000 -80000 sqft,Typically discount stores of major department storesE.g. Nordstrom Rack or J. C. Penny outlets32Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Warehouse clubs 104,000-1,70,000 sq.ft.Offers variety of goods @wholesale priceLimited products (5,000 or less)E.g. Costco Wholesale, Sam’s Club33Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Other Formats1.2.3.4.5.34Super warehouse store – hybrid warehouse /superstore with 50000 - plus items and fullrange of service departments, featuring highquality perishables and reduced pricesLimited assortment store – low price outlet withminimal service and fewer than 2000 items.Numerous private labelSupercenter- large food drug combination andmass merchandiser 1,70000 sq ft (40% groceryitems @loss leader prices)Wholesale clubDollar storeProf. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Airport Retailing Airports in many cities of the western works serveas mini shopping plazas for travellersIt is different from mall retailing with hugemargins / sales per sq. Footmuch smaller than even convenience storeslogistics issue of getting goods to airport iscomplexE.g. Duty Free Shops35Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Non-Store Retailing36Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Direct Selling Involves making a personal contact with theend consumer at home or at the place of work Highly interactive form of retailing Party plan or Multi-level network E.g. Amway, Herbalife, Tupperware37Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Direct Response marketing Catalogue retailing / mail order Appropriate for speciality products- targetedcatalogues to appeal to narrow target marketsTelevision retailingHere existing and prospective customers watch aTV programme demonstrating a product and thenplace an order for the same by telephone, e-mailor Internet(For example: Asian Sky Shop, TSN, TVC, TSNM) E-tailing / Electronic Shopping38Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Information kiosks Have emerged in the western markets as a newtype of electronic retailingThese kiosks , comprising of computer terminalshoused inside and a touch screen on outside toprovide customers with product and companyinformation and may actually aid the customersmaking a purchase39Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Automated Vending / Kiosks A form of non-store retailing where products orservices are placed in a machine and are dispensedto customers when they deposit cash or use plasticmoney (credit or debit card)Most impersonal form of retailingVending machines offer consumers greaterconvenience 24 hours a day, and have replacedmany services formally requiring a human interfacePopular in soft-drinks, candies etc. along with bankATMS40Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
The Cash and Carry Customers do their own order picking, pay in cashand carry the merchandise away.It’s a wholesale format that aids small retailersand businessmen.It offers a wide assortment of goods, food andnon-food items – thus provides one stop shoppingand allows customers to save timeLonger working hours and seven day workingenable customers do the shopping at a convenienttimeE.g. Metro AG and Shoprite41Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Services Retail42Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Services Retail Instead of products, they sell services to the end consumersAirlines, Banks, Repair, Child care, Pre-school, Education,Financial Services, Fitness, Healthcare, Hotels, QuickService Restaurants etc.43Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
India Specific Retail Models44Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
India Specific The Public Distribution SystemITC e-choupalHariyali Kisan BazaarGodrej Adhar45Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM
Classification of retailformatsNon-storeretailingStore basedretailingForms ofOwnershipMerchandiseOfferedBanksConvenience StoreIndependent RetailerSupermarketChain RetailerDirect SellingHypermarketFranchiseMail OrderSpecialty StoresLeasedTele MarketingDepartmental StoreConsumer cooperativeOff-price RetailersAutomatedVendingFactory OutletsCatalogue Showroom46ServiceRetailingProf. Deepa Rohit, LLIMCar RentalsOtherservicesAirportRetailingCash and CarryIndia SpecificformatSwapna Pradhan Page 70 onwards
advertising and sales promotion . Party plan or Multi-level network E.g. Amway, Herbalife, Tupperware. Direct Response marketing 38 Prof. Deepa Rohit, LLIM