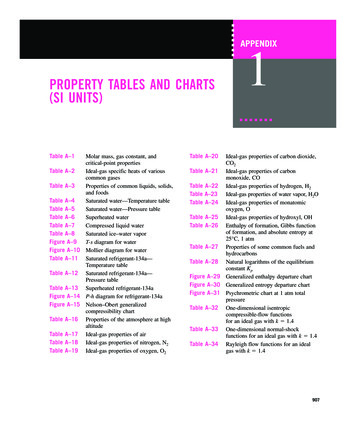
Transcription
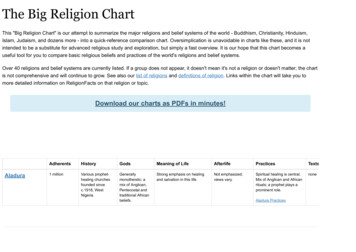
The Big Religion ChartThis "Big Religion Chart" is our attempt to summarize the major religions and belief systems of the world - Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism,Islam, Judaism, and dozens more - into a quick-reference comparison chart. Oversimplication is unavoidable in charts like these, and it is notintended to be a substitute for advanced religious study and exploration, but simply a fast overview. It is our hope that this chart becomes auseful tool for you to compare basic religious beliefs and practices of the world's religions and belief systems.Over 40 religions and belief systems are currently listed. If a group does not appear, it doesn't mean it's not a religion or doesn't matter; the chartis not comprehensive and will continue to grow. See also our list of religions and definitions of religion. Links within the chart will take you tomore detailed information on ReligionFacts on that religion or topic.Download our charts as PDFs in minutes!AladuraAdherentsHistoryGodsMeaning of LifeAfterlifePracticesTexts1 millionVarious prophethealing churchesfounded sincec.1918, WestNigeria.Generallymonotheistic; amix of Anglican,Pentecostal andtraditional Africanbeliefs.Strong emphasis on healingand salvation in this life.Not emphasized;views vary.Spiritual healing is central.Mix of Anglican and Africanrituals; a prophet plays aprominent role.noneAladura Practices
AsatruAdherentsHistoryGodsMeaning of LifeAfterlifePracticesTextsunknownRevival of Norseand Germanicpaganism, 1970sScandinavia andUSA.Polytheistic, Norsegods andgoddesses, Norsecreation myths.Salvation or redemption notemphasized. Fatalistic outlook.Valhalla (heaven) fordeath in battle; Hel(peaceful place) formost; Hifhel (hell) forthe very evil.Sacrifice of food or drink,toast to the gods,shamanism (lessfrequently), celebration ofsolstice holidays. NineNoble Virtues is moralcode.Eddasepics)HavamattribuAsatru GodsHistory of AsatruAsatruAsatru PracticesAtheism7.4 million selfidentifiedatheists; 1.1billion arereligiously"unaffiliated"Appears throughouthistory (includingancient Greekphilosophy), butespecially after theEnlightenment(19th cent).There is no God ordivine beings.Not addressed. But manyatheists believe that sincethere is no afterlife, this onelife is of great importance.Only humans can helpthemselves and each othersolve the world's wain.moderincludeDawkiSaganBaha'i Faith5-7 millionFounded byBahá'u'lláh, 1863,Tehran, Iran.One God, who hasrevealed himselfprogressivelythrough majorworld religions.The soul is eternal andessentially good. Purpose oflife is to develop spiritually anddraw closer to God.Soul separates fromthe body and beginsa journey towards oraway from God.Heaven and hell arestates of being.Daily prayer, avoidance ofintoxicants, scripturereading, hard work,education, work for socialjustice and equality.WritingBahá'uother BleaderHistory of theBaha'i Faithmeaning of life (Bahai)Baha'i Beliefsabout GodBon100,00011th-century TibetAdherents HistoryBaha'iBaha'i Practicesafterlife (Baha'i)NontheisticBuddhism, butmeditation onpeaceful andwrathful deities.Gain enlightenment.Reincarnation untilgain enlightenmentMeditation on mandalasand Tibetan deities,astrology, monastic life.BonpoGodsMeaning of LifeAfterlifePracticesText
BuddhismAdherentsHistoryGodsMeaning of LifeAfterlifePracticesTexts500 millionBased on teachingsof SiddhartaGautama (theBuddha) in c. 520BC, NE India.Buddhist godsinclude buddhas,bodhisattvas,arhats and deities;such as Tara,Kuan Yin, andAmida Buddha.Escape the cycle of rebirthand attain nirvana (TheravadaBuddhism). Become aboddhisatva then help othersattain enlightenment(Mahayana Buddhism).Rebirth or nirvana.Nirvana is seensimply as thecessation of sufferingby some and as aheavenly paradise byothers.Meditation, mantras,devotion to deities (in somesects), mandalas (Tibetan)TripitaCanonsutrasLotusothersHistory ofBuddhismBuddhist Gods &DeitiesThe Meaning of Life inBuddhismBuddhist PracticesBuddhBuddhism on theAfterlifeCao Dai4-6 millionFounded in 1926,Vietnam by NgoVan Chieu andothers based on aséance.God representedby Divine Eye.Founders ofBuddhism,Taoism, Hinduism,Islam, andChristianityvenerated, andsaints includingVictor Hugo.Goal is peace and harmony ineach person and in the world.Salvation by "cultivating selfand finding God in self."reincarnation untilNirvana/HeavenHierarchy similar to RomanCatholicism. Daily prayer.Meditation. Communicationwith spirit world (nowoutlawed in Vietnam).CaodaChineseReligion394 millionIndigenous folkreligion of China.Dualistic yin andyang; mythologicalbeings and folkdeities.A favorable life and peacefulafterlife, attained throughrituals and honoring ofancestors.judgment, thenparadise orpunishment andreincarnationAncestor worship, prayer,longevity practices,divination, prophecy andastrology, feng shui.noneafterlife (ChineseReligion)Chinese religious ritualsand practicesHeaven is "not alocality, but a divinestate of Mind in whichall the manifestationsof Mind areharmonious andimmortal."Spiritual healing throughprayer and knowledge,Sunday services, dailyBible and Science & Healthreading.History of ChineseReligionChineseTraditionalReligion TheismChristianScience400,000Founded by MaryBaker Eddy in1879,Massachusetts.History of ChristianScienceOne God. NoTrinity (intraditional sense).Matter and evil donot exist."Life, Truth, and Loveunderstood and demonstratedas supreme over all; sin,sickness and deathdestroyed."Christian Science PracticesChristiSciencwith KScriptu
ChristianityAdherentsHistoryGodsMeaning of LifeAfterlifePracticesTexts2.2 billionLife and teachingsof Jesus ofNazareth (born c. 4BCE), a Jew fromPalestine underRoman ruleOne God, who is aTrinity of Father,Son and HolySpirit; angels;demons; saintsAll have sinned and arethereby separated from God.Salvation is through faith inChrist and, for some,sacraments and good works.Resurrection of bodyand soul; eternalheaven or hell (mostdenominations);temporary purgatory(Catholicism)Prayer, Bible study,baptism, Eucharist(Communion), church onSundays, numerousholidays.Bible ( NewChristianityAdherentsChristian HistoryConfucianismGod & SpiritualBeings inChristianityChristiChristian PracticesChristianity on theAfterlifeAdherents HistoryGodsMeaning of LifeAfterlifePracticesText5-6 millionnot addressedTo fulfill one's role in societywith propriety, honor, andloyalty.not addressednoneAnalecConfucian PracticesConfucnot addressednot addressedNone prescribed, althoughsome deists practicedprayer.ThomaPaine'ReasotextsBased on theteachings ofConfucius (551–479 BCE, China)History ofConfucianismDeismunknownEspeciallypopularized in the18th-cent.Enlightenmentunder Kant,Voltaire, Paine,Jefferson, andothersOne Creator Godwho isuninterested in theworld. Reason isbasis for allknowledge.
AdherentsHistoryGodsMeaning of LifeAfterlifePracticesTextsDruze500,000Founded by AlDarazi in 11thcentury, Cairo,Egypt. Roots in theIsma'iliyya sect ofShia Islam.UniversalIntelligence (al-Aqlal-Kulli) or DivineEssence (akin toNeoplatonism), ofwhich al-Hakim isbelieved to be anincarnation.Live a good life for a favorablereincarnation. Await the reappearance of al-Hakim (aFatimid caliph whodisappeared in 1021), who willusher in a Golden Age for truebelievers.Reincarnation.Heaven is a spiritualexistence when onehas escapedreincarnation. Hell isdistance from God inlifetime after lifetime.Modest lifestyles, fastingbefore Eid al-Adha. Beliefsand practices are hidden forprotection from persecution.Special group of initiatescalled uqqal.Al-Naq(CopySecretAwwalthe FirEckankar50,000-500,000Founded by PaulTwitchell in LasVegas, 1965The Divine Spirit,called "ECK.""Each of us is Soul, a spark ofGod sent to this world to gainspiritual experience." Salvationis liberation and Godrealization.Reincarnation. TheSoul is eternal bynature and on aspiritual journey.Liberation possible ina single lifetime.Spiritual Exercises of ECK:mantras, meditation, anddreams. These enable Soultravel and spiritual growth.ShariySugmaby HarHistory of EckankarEpicureanismFalun Gongn/aBased on theteachings ofEpicurus, c. 300BCE, Athens.Eckankar practicesEckantextsPolytheism, butthe gods take nonotice of humans.Pursue the highest pleasures(friendship and tranquility) andavoid pain.No afterlife. The souldissolves when thebody dies.noneLettersPrincipof EpicAdherents HistoryGodsMeaning of LifeAfterlifePracticesText3 million (acc.to officialsources); 100million (acc. toFalun Gongsources)Countless godsand spiritualbeings. Demonicaliens.Good health and spritualtranscendence, achieved bypracticing Falun Gong.Not addressedFive exercises tostrengthen the Falun.Cultivation of truthfulness,benevolence andforbearance. Meat eatingdiscouraged.Zhuanother wMasteLi Hongzhi in 1992in ChinaHistory of FalunGongFalunFalun Gong PracticesGnosticismancient formextinct; smallmodern revivalgroupsVarious teachersincludingValentinus, 1st-2ndcents. ADThe supreme Godis unknowable; thecreator god is eviland matter is evil.Humans can return to thespiritual world through secretknowledge of the universe.Return to the spiritualworld.Asceticism, celibacyGnostincludiGospeattribuapostle
Greek ReligionAdherentsHistoryGodsMeaning of LifeAfterlifePracticesTextsancient formextinct; variousmodern revivalsIndigenous religionof the ancientGreeks, c. 500BCE to 400 CE.Olympic pantheon(Zeus, etc.) mixedwith easterndeities like Isis andCybele.Human life is subject to thewhim of the gods and to Fate;these can be partiallycontrolled through sacrificeand divination.Beliefs varied fromno afterlife toshadowy existence inthe underworld to aparadise-like afterlife(mainly in mysteryreligions).Animal sacrifice, harvestofferings, festivals, games,processions, dance, plays,in honor of the gods. Secretinitiations and rituals inmystery religions.Epic pHomeAncient GreekGodsGreek religious practicesHare a, 1966,USA (with roots in15th-century Hindumovement)Krishna is theSupreme God.Salvation from this Age of Kaliis by a return to Godhead,accomplished throughKrishna-Consciousness.Reincarnation untilunite with theGodhead.Chanting, dancing,evangelism, vegetarianism,temple worship, monasticstyle livingThe BAs It IsHinduism1 billionIndigenous religionof India asdeveloped topresent day.Earliest forms(Vedic religion)date to 1500 BCEor earlier; majordevelopments 1st9th centuries CE.One SupremeReality (Brahman)manifested inmany gods andgoddessesHumans are in bondage toignorance and illusion, but areable to escape. Purpose is togain release from rebirth, or atleast a better rebirth.Reincarnation untilgain enlightenment.Yoga, meditation, worship(puja), devotion to a god orgoddess, pilgrimage to holycities, live according toone's dharma (purpose/role).VedasUpanisBhagaRamayHindu Gods &Goddessesmeaning of life (Hinduism)GodsMeaning of LifeHinduHindu Rituals & PracticesHindu HistoryAdherents HistoryAfterlifePracticesText
IslamAdherentsHistoryGodsMeaning of LifeAfterlifePracticesTexts1.6 billionBased on teachingsof the ProphetMuhammad;founded 622 CE inMecca, SaudiArabia.One God (Allah inArabic); the sameGod revealed(imperfectly) in theJewish andChristian BiblesSubmit (islam) to the will ofGod to gain Paradise afterdeath.eternal Paradise oreternal HellFive Pillars: Faith, Prayer,Alms, Pilgrimage, Fasting.Mosque services onFridays. Ablutions beforeprayer. No alcohol or pork.Holidays related to thepilgrimage and fast ofRamadan.Qur'antext); H(traditiIslamic Beliefs Aboutthe AfterlifeHistory of IslamIslamicMuslim rituals and practicesJainism4 millionFounded byMahavira, c. 550BCE, eastern IndiaHistory of JainismPolytheism andpantheism. Theuniverse is eternal;many gods exist.Gods, humansand all livingthings areclassified in acomplex hierarchy.Gain liberation from cycle ofrebirth, by avoiding all badkarma, especially by causingno harm to any sentient being.Reincarnation untilliberation.afterlife (Jainism)meaning of life (Jainism)Monasticism under the FiveGreat Vows (Non-Violence,Truth, Celibacy, NonStealing, NonPossessiveness); worshipat temples and at home.Meditation and mantras.The teMahavcollectJain practicesJain theismJehovah'sWitnesses6.5 millionFounded byCharles TazeRussell, 1879,PittsburghHistory of theJehovah'sWitnessesOne God:Jehovah. NoTrinity. Christ isthe first creation ofGod; the HolySpirit is a force.Salvation is through faith inChrist and obeying Jehovah'slaws. The End of the World issoon.Heaven for 144,000chosen Witnesses,eternity on new earthfor other Witnesses.All others annihilated.No hell.No blood transfusions, nocelebration of holidays, nouse of crosses or religiousimages. Baptism, Sundayservice at Kingdom Hall,strong emphasis onevangelism.Jehovah's WitnessesPracticesNew WTranslScriptuJehovaWitnesTexts
JudaismAdherentsHistoryGodsMeaning of LifeAfterlifePracticesTexts14 millionThe religion ofAbraham (c. 1800BCE) and theHebrews,especially after thedestruction of theSecond Temple in70 CE.One God: Yahweh(YHVH)Obey God's commandments,live ethically. Focus is more onthis life than the next.Not emphasized;views vary: noafterlife, shadowyexistence, World toCome (similar toheaven), Gehenna(similar to hell),reincarnationCircumcision at birth,bar/bat mitzvah atadulthood, observingSabbath, wearing tallit andtefilin, prayer servicesHebre(TanakAdherents ofJudaismGod in JudaismHistory of JudaismMayanReligionSeveral millionMaya practice aCatholicismthat retainsmany elementsof traditionalMayan religion.Began c.250 CE(rise of the Mayancivilization)Adherents HistoryJewishJewish Rituals andPracticesThe Afterlife inJudaismMany gods,including Itzamná,Kukulcán, BolonTzacab, and ChacAppease and nourish thegods; determine luckiest datesfor various activities.The soul journeysthrough dark andthreateningunderworld; butsacrificial victims andwomen who die inchildbirth go toheaven.Astronomy, divination,human sacrifice, elaborateburial for royalty, worship instone ; Tthe B
Download our charts as PDFs in minutes! Adherents History Gods Meaning of Life Afterlife Practices Texts Aladura 1 million Various prophet-healing churches founded since c.1918, West Nigeria. Generally monotheistic; a mix of Anglican, Pentecostal and traditional African beliefs. Strong emphasis on healing and salvation in this life. Not emphasized; views vary. Spiritual healing is central. Mix .