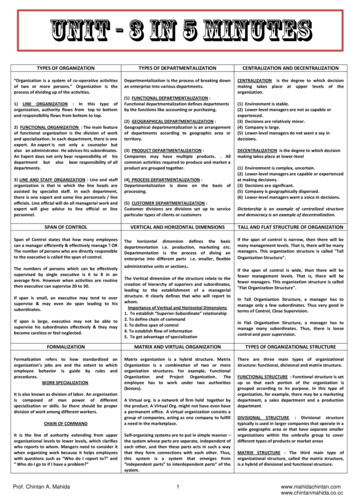
Transcription
If a conflict arises between a Clinical Payment and Coding Policy (“CPCP”) and any plandocument under which a member is entitled to Covered Services, the plan document willgovern. If a conflict arises between a CPCP and any provider contract pursuant to which aprovider participates in and/or provides Covered Services to eligible member(s) and/or plans,the provider contract will govern. “Plan documents” include, but are not limited to, Certificatesof Health Care Benefits, benefit booklets, Summary Plan Descriptions and other coveragedocuments. BCBSTX may use reasonable discretion interpreting and applying this policy toservices being delivered in a particular case. BCBSTX has full and final discretionary authority fortheir interpretation and application to the extent provided under any applicable plandocuments.Providers are responsible for submission of accurate documentation of services performed.Providers are expected to submit claims for services rendered using valid code combinationsfrom Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) approved code sets. Claimsshould be coded appropriately according to industry standard coding guidelines including, butnot limited to: Uniform Billing (UB) Editor, American Medical Association (AMA), CurrentProcedural Terminology (CPT ), CPT Assistant, Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System(HCPCS), ICD-10 CM and PCS, National Drug Codes (NDC), Diagnosis Related Group (DRG)guidelines, Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) National Correct Coding Initiative(NCCI) Policy Manual, CCI table edits and other CMS guidelines.Claims are subject to the code edit protocols for services/procedures billed. Claim submissionsare subject to claim review including but not limited to, any terms of benefit coverage, providercontract language, medical policies, clinical payment and coding policies as well as codingsoftware logic. Upon request, the provider is urged to submit any additional documentation.Hernia RepairPolicy Number: CPCP012Version: 7.0Clinical Payment and Coding Policy Committee Approval Date: May 29, 2020Plan Effective Date: Sept. 15, 2020 (Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Texas Only)Description:A hernia can occur when an internal organ or another part of the body protrudes through thewall of the cavity that it is normally enclosed in. When muscles become weak, tissue can bulgethrough a hole and can cause a visible lump with associated pain.Health care providers (i.e., facilities, physicians and other qualified health care professionals) areexpected to exercise independent medical judgment in providing care to patients. This policy isnot intended to impact care decisions or medical practice.Hernia types listed below is not an all-encompassing coding list and does not guarantee acovered service or reimbursement.1A Division of Health Care Service Corporation, a Mutual Legal Reserve Company, an Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association
Hernia TypeTypes of HerniaDescriptionDiagnosisCause &SymptomsCodesDiaphragmaticHernia Bochdalek HerniaBack and side of thediaphragm. Theintestines, liver,stomach and/orspleen moveupward into thechest cavity.For infants, abirth defect inwhich there isan abnormalopening in thediaphragm.For infants:Ultrasound offetus beforeborn; Afterbirth-physicalexam, X-ray,ultrasound,CT scan, MRI,arterial bloodgas testCommon causes:CongenitalDiaphragmaticHernia (CDH)from abnormaldevelopment ofabdomen informing fetus, orinjuries to 9561,39599,44238For adults:Ultrasound,X-ray, CTscan, MRI(Imagingstudies).Symptoms mayinclude:Difficultybreathing, rapidheart rate(tachycardia),Cyanosis, cavedabdomen,abdominal pain,indigestion orabnormal chestdevelopment.Physicalexam,ultrasound,CT scan.Common causes:Aging, injury,heavy lifting,persistentcoughing,difficulty withbowelmovements orurination thatcauses theabdominal wallto weaken orseparate. Morgagni HerniaFront side of thediaphragm. Theintestines and/orliver move upwardinto the chest cavity.EpigastricHernia IncarceratedHernia- hernia thatis trapped in theabdominal wall. StrangulatedHernia- Anincarcerated herniathat becomesstrangulated cuttingthe blood flow.Symptoms of thisinclude nausea, highfever, sharp painsand swelling.In rareinstances therecan be lateonset ordiagnosis ofdiaphragmatichernias thatmay be relatedto a trauma orother cause.Small in size, 5cm to 6 cm.Typically abovethe umbilicus inthe upperabdomen.49570,49572,49652,49653Symptoms caninclude: Bulge inupper abdomen,or sharp pain.2
HerniaTypeTypes of HerniaFemoralHernia Incarcerated Herniahernia that istrapped in theabdominal wall. StrangulatedHernia- Anincarcerated herniathat becomesstrangulated cuttingthe blood flow.Symptoms of thisinclude nausea, highfever, sharp painsand swelling.HiatalHernia Sliding HiatalHernia- Commonhiatal hernia thatoccurs when gastroesophageal junctionand part of thestomach protrudeinto the chest. Para-esophagealHernia- When aportion of thestomach protrudesthrough the holethat the esophaguspasses through tothe diaphragm.DescriptionDiagnosisCause &SymptomsCodesUncommonhernia thatappears as apainful lump inthe inner upperpart of the thighor groin that canoften be pushedback inPhysicalexam,ultrasound.Common causes:fatty tissue orpart of bowelpokes throughinto groin at topof inner thigh;strain onabdomen; weakfemoral canal.49550,49553,49555,49557Protrusion of theupper part of thestomach into thethorax through atear or weaknessin the diaphragm.Upper GIEndoscopy,BariumSwallowStudy, MRI orCT scan.Common cause 2,43333,43334,43335,43336,43337,44239Symptoms caninclude: Acidreflux, chronicheartburn, GERD,difficultyswallowing, orrestricted bloodflow to thestomach.3
HerniaTypeIncisionalHerniaTypes of Hernia Incarcerated Herniahernia that is trappedin the abdominalwall. Strangulated HerniaAn incarceratedhernia that becomesstrangulated cuttingthe blood flow.Symptoms of thisinclude nausea, highfever, sharp pains andswelling.InguinalHernia Incarcerated Herniahernia that is trappedin the abdominalwall. Strangulated HerniaAn incarceratedhernia that becomesstrangulated cuttingthe blood flow.Symptoms of thisinclude nausea, highfever, sharp pains andswelling.DescriptionDiagnosisCause &SymptomsCodesOccurs at thearea of a prioroperation dueto a weakeningof theabdominal wall.Physical exam,blood tests, Xray or CT scan.Common Causes:Obesity,pregnancy,excessivepressure fromcoughing orsneezing, orheavy 49654,49655,49656,49657Symptoms caninclude: Fever,infection, bulging,visual protrusion,pain, ache orswelling.Occurs whentissueprotrudesthrough a weakspot in theabdominalmuscles/groinarea.Physical exam,ultrasound, CTscan or MRI.Common causes:Increasedpressure w/in theabdomen,pregnancy,chronic coughingor sneezing, orstrenuousactivity.Symptoms caninclude: Stomachmuscle weakness,sharp pain,swelling inscrotum or bulgein 507,49520,49521,49525,49650,49651,54640,555404
HerniaTypeSpigelianHerniaTypes of Hernia Incarcerated Herniahernia that is trappedin the abdominalwall. Strangulated HerniaAn incarceratedhernia that becomesstrangulated cuttingthe blood flow.Symptoms of thisinclude nausea, highfever, sharp painsand swelling.UmbilicalHernia Incarcerated Herniahernia that is trappedin the abdominalwall. Strangulated HerniaAn incarceratedhernia that becomesstrangulated cuttingthe blood flow.Symptoms of thisinclude nausea, highfever, sharp painsand swelling.VentralHernia Strangulatedventral hernia- theintestinal tissue isfirmly caught withinthe opening of theabdominal wall andcannot be pushedback. Blood flow iscut off use andSymptomsCodesHernia throughthe Spigelianfascia, defect inthe lateralabdominal wall.This is alsocalled a lateralventral hernia.(At a very highrisk forstrangulation.)Physicalexam,ultrasound,CT scan, X-ray.Common causes:Weaknesses in themuscles of theabdomen, previousinjury, heavy lifting,chronic coughing.49590,49652,49653Occurs whenpart of theintestineprotrudesthrough theumbilicalopening in theabdominalmuscles.Physicalexam; forcomplications,an abdominalultrasound orCT scan.Bulge of tissuesthrough aweakness withinthe abdominalwall muscles.Physicalexam,abdominalultrasound,abdominal CTscan,abdominalMRI Scan.Symptoms mayinclude: Painincreasing withactivities, strainingduring bowelmovements, heavylifting, nausea orvomiting.Common causes ForInfants: Prematurebabies w/low birthweight; For Adultsobesity or 49652,49653,51500Symptoms mayinclude: Swollenbulge near navel.Common causes:pregnancy, obesity,history of previoushernias, previoussurgeries, familyhistory, frequentlifting of heavyobjects, or injuriesto bowel.Symptoms caninclude: Milddiscomfort inabdominal area,pain, bulging of skinor tissues, nauseaor ,49654,49655,49656,496575
Note: Unlisted laparoscopic procedures including, hernioplasty, herniorrhaphy and herniotomy,may be reimbursed when using CPT code 49659, for a laparoscopic repair. Hybrid laparoscopicand open repairs during a hernia repair procedure should include the applicable code for theopen hernia repair.For a complete list of the General Treatment Course see MCG care guidelines and other industrystandard guidelines.Reimbursement Information:Appropriate coding is the key to minimizing delays in claim(s) processing. Please ensure thatrevenue codes and procedure codes reflect the diagnoses and services rendered.Preoperative TestingPreoperative testing before a low risk surgery, for Members needing a hernia repair procedurewithout comorbidities, may not be necessary. The physician is urged to follow the most currentbest practice guidelines for preoperative testing.Preoperative testing that is done in the facility related to hernia repair procedures should beincluded in the same claim submission as the procedure regardless if the testing was done onthe same date. If the testing is done outside of the facility prior to admission, it should be billedseparately. All preoperative testing should be completed within 24 to 72 hours of admissionunless otherwise agreed upon.Member EligibilityThe plan may not reimburse for hernia repairs performed concurrently with procedures that arenot covered by the Members benefit plan, unless deemed medically necessary. For example,Medical Policy SUR716.003 states “Repair of a hiatal hernia at the time of bariatric surgery thatis diagnosed at the time of bariatric surgery or repair of a preoperatively diagnosed hiatal herniain patients who do not have indications for surgical repair, is considered not medicallynecessary.” Claims may be reviewed on a case by case basis. If an eligible or covered procedureis performed concurrently with a hernia repair, providers should submit supportingdocumentation and appropriate code combinations to ensure the claim is paid correctly.Additional Information If the clinical documentation does not support the medical necessity of a hernia repair,hernia repair codes will be denied. All associated services including but not limited to preoperative testing, anesthesiaservices, facility charges, physician fees performed in conjunction with non-coveredprocedures including non-medically necessary hernia repair will be denied. Exclusions can apply under the group or member benefit plan or provider contract. The plan reserves the right to request supporting documentation if claim(s) do notadhere to coding and billing which may result in a denial or reassigned payment rate.6
References:MCG care guidelines 23rd Edition Copyright 2019 MCG Health, LLCMedical Policy: Bariatric Surgery, SUR716.003CPT copyright 2019 American Medical Association (AMA). All rights reserved. CPT is a registeredtrademark of the AMAPolicy Update History:Approval Date02/23/201802/22/201905/29/2020DescriptionNew PolicyAnnual reviewAnnual review, updated disclaimer, references, policy language7
29.05.2020 · not intended to impact care decisions or medical practice. Hernia types listed below is not an all-encompassing coding list and does not guarantee a covered service or reimbursement. A Division of Health Care Service Corporation, a Mutual Legal Reserve Company, an Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association . 2 Hernia Type Types of Hernia Description Diagnosis