Transcription
Oral Structures and Types ofteethBy:Ms. Zain Malkawi, MSDH
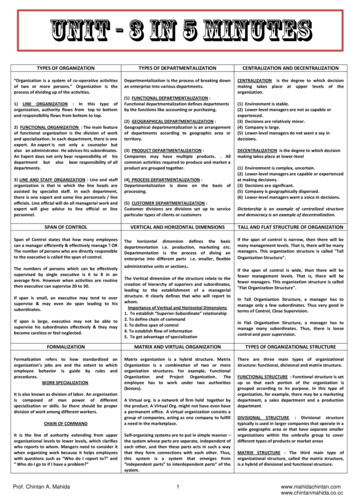
Introduction Oral structures areessential in reflecting localand systemic health Oral anatomy: afundamental of dentalsciences on which the oralhealth care provider isbased. Oral anatomy used toassess the relationship ofteeth, both within andbetween the arches
The color and morphology of the structures mayvary with genetic patterns and age.
One Quadrant at the Dental Arches
Parts of a Tooth Crown Root
Parts of a Tooth Crown: part of the toothcovered by enamel,portion of the tooth visiblein the oral cavity. Root: part of the toothwhich covered bycementum.
Posterior teeth Anterior teeth
Root Apex: rounded end of theroot Periapex (periapical): areaaround the apex of a tooth Foramen: opening at theapex through which bloodvessels and nerves enters Furcation: area of a two orthree rooted tooth wherethe root divides
Tooth Layers Enamel: the hardest calcifiedtissue covering the dentine inthe crown of the tooth (96%)mineralized. Dentine: hard calcified tissuesurrounding the pulp andunderlying the enamel andcementum. Makes up thebulk of the tooth, (70%)mineralized.
Tooth Layers Pulp: the innermostnoncalsified tissuescontaining bloodvessels, lymphaticsand nerves Cementum: bone likecalcified tissuecovering the dentin inthe root of the tooth,50% mineralized.
Tooth Layers
Tooth Surfaces Facial: Labial , Buccal Lingual: called palatalfor upper arch. Proximal: mesial , distal Contact area: areawhere that touches theadjacent tooth in thesame arch.
Tooth Surfaces Incisal: surface of an incisor which toward theopposite arch, the biting surface, the newlyerupted “permanent incisors have mamelons”:projections of enamel on this surface. Occlusal: surface of posterior teeth that istoward the opposite arch, the chewing surface.
Tooth Sides
One Quadrant at the Dental Arches
Types of Teeth Primary Teeth (Deciduous Teeth) Permanent Teeth (Adult Teeth)
The Primary Dentition Primary dentition (decidous) consists of 20teeth, 8 incisors, 4 canines, and 8 molars.
Primary Teeth (Dental arch)
The Primary Dentition The anatomy of the primary teeth is similar tothat of permanent teeth except : primary teeth are smaller in sizeThey are whiterThe crowns are shorterThe occlusal table is narrower faciolinguallyPulp chambers are largerRoots are longer and slenderRoot Trunk: area from the cementoenamel junction tothe furcation are shorter Have fewer anomalies and variations in tooth form
Permanent Dentition Consists of 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars and12 molars Teeth have one, two, or three roots
Oral anatomy: a fundamental of dental sciences on which the oral health care provider is based. Oral anatomy used to assess the relationship of teeth, both within and between the arches. The color and morphology of the structures may vary with genetic patterns and age. One Quadrant at the Dental Arches. Parts of a Tooth Crown Root. Parts of a Tooth Crown: part of the tooth .