Transcription
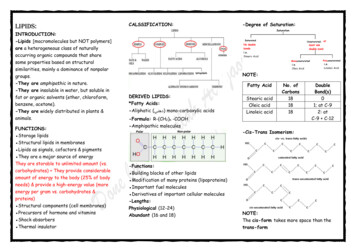
Lipids:CALSSIFICATION:INTRODUCTION:-Lipids [macromolecules but NOT polymers]are a heterogeneous class of naturallyoccurring organic compounds that sharesome properties based on structuralsimilarities, mainly a dominance of nonpolargroups.-They are amphipathic in nature.-They are insoluble in water, but soluble infat or organic solvents (ether, chloroform,benzene, acetone).-They are widely distributed in plants &animals.FUNCTIONS: Storage lipids Structural lipids in membranes Lipids as signals, cofactors & pigments They are a major source of energyThey are storable to unlimited amount (vs.carbohydrates) They provide considerableamount of energy to the body (25% of bodyneeds) & provide a high-energy value (moreenergy per gram vs. carbohydrates &proteins) Structural components (cell membranes) Precursors of hormone and vitamins Shock absorbers Thermal insulator-Degree of Saturation:NOTE:Fatty AcidDERIVED LIPIDS:*Fatty Acids:-Aliphatic ( )دهني mono-carboxylic acids-Formula: R-(CH2)n -COOH-Amphipathic moleculesStearic acidOleic acidLinoleic acidNo. ofCarbons181818DoubleBond(s)01; at C-92: atC-9 C-12-Cis-Trans Isomerism:-Functions: Building blocks of other lipids Modification of many proteins (lipoproteins) Important fuel molecules Derivatives of important cellular molecules-Lengths:Physiological (12-24)Abundant (16 and 18)NOTE:The cis-form takes more space than thetrans-form
-Properties of Fatty Acids:Description of a Fatty Acid:#, #, #, Examples are melting point and solubility,(ω#, #: #, ), where;which are dependent on:-Degree of Saturation [more significant]-Chain Lengthω# رقم أول كربونة عليها رابطة ثنائية بعد بدء التعداد من الكربونة األبعد عن المجموعة الوظيفية باعتبار تلك 1 الكربونة هي الرقم # عدد الكربونات في الجزيء # عدد الروابط الثنائية في الجزيء # رقم الكربونة التي تحمل الرابطة الثنائية Naming Fatty Acids:Exercises:Name Each Molecule and Describe it too:RECALL:1NOTE: 11 – 19; they have compound2names, i.e.:14 4 10 Tetradeca18 8 10 Octadeca3Formula: No. of C -a of deca(Dependingon no. ofdoublebonds)0 a1 e2 die3 trie- noic ionCommon Names:1Palmitoleic Acid2Oleic Acid3Linoleic Acid4Linolenic Acid5Arachidonic Acid6Eicosapentaenoic AcidNOTE:Linoleic acid: precursor of arachidonatesLinolenic acid: precursor of EPA and DHA
-Some Common Fatty Acids: Eicosanoids:-Aspirin:-Derived from Arachidonic AcidA medication that targets both COX 1 andCOX 2. RECALL:-Some Common Fatty Acids (In theOmega- Naming):-Eicosanoids and their mboxaneLeukotrienesFunction(s) Induction ofinflammation Inhibition ofplateletaggregation, thus;inhibition of bloodclotting An inhibitor ofplatelet aggregation A vasodilator Induction ofplatelet aggregation Constriction ofsmooth muscles Constriction ofsmooth muscles,thus; induction ofasthmaThus, no inflammation but with side effects.The Aim is to target COX 2 only, HOW?By using Celebrex [Celecoxib capsules](With a strong warning of side effects onthe label)-Omega Fatty Acids:MoleculeOmega-3 fattyacids;α-linolenic Acid EicosapentaenoicAcid (EPA) DocosahexaenoicAcid (DHA)Function(s) They reduceinflammatoryreactions by:-Reducingconversion ofarachidonic acidinto eicosanoids-Promotingsynthesis of antiinflammatorymolecules
Omega-6 fattyacids; ArachidonicAcidOmega-9 fattyacids; Oleic Acid Stimulatesplatelet andleukocyte activation Signals pain Inducesbronchoconstriction Regulates gastricsecretion Reducescholesterol in thecirculation-Features of Waxes:*Storage Lipids: Insoluble in water Triglycerides: Are not easily hydrolyzed (fats) & areindigestible by lipases-Classification According to Number ofFatty Acids Attached to the GlycerolBackbone: Are very resistant to rancidity ( )نخر Are of no nutritional value Coatings that prevent loss of water byleaves of plantsCOMPLEX LIPIDS:SIMPLE LIPIDS:*Waxes:A monohydric alcohol (C16 C30 -highermolecular weight than glycerol-) esterifiedto long-chain fatty acids (C14 C36).i.e. Palmitoyl alcohol-Classification According to What FattyAcids are Attached to the GlycerolBackbone:Other Examples:NOTE: In a mixed Triglyceride,differences in fatty acids are: Length Degree of Saturation
-Solid vs. Liquid Fats:-Saponification; A Reaction of-Hydrogenation:Vegetable oils consist almost entirely ofTriglycerides:The process of saturating the unsaturatedunsaturated fatty acids, whereas animalfats contain a much larger percentage ofsaturated fatty acids.This is the primary reason for the differentmelting points of fats and oils.fatty acids. [Alkene Alkane] Partial hydrogenation converts some, butnot all, double bonds into single bondsgenerating (trans fats).-Using a Soap; the Formation of Micelles:The primary health risk identified fortrans-fat consumption is an elevated risk ofCoronary Heart Disease (CHD).Atherosclerosis may also occur.
*Membrane Lipids:-Classification of Glycerophospholipids:Inositides (Phosphatidylinositol);Phosphatidic acids;-Found in brain tissue [Concentrated on the-The simplest (basic) --Phosphatidylcholine (lecithin);-Most abundant membrane lipid-Used in Food Production-Snake venom contain lecithinase, whichcytosolic side of cells]-Structure: Glycerol, saturated FA,unsaturated FA, phosphoric acid, & inositolNitrogenous base: cyclic sugar alcohol(inositol)hydrolyzes polyunsaturated fatty acids and Phospholipids; Glycerophospholipids(Phosphoacylglycerols):[The most prevalent class of membranelipids]converting lecithin into lysolecithin; thus,hemolysis of RBCs-Because of their amphipathic nature, theyact as emulsifying agents, that is substancesthat can surround nonpolar molecules andkeep them in suspension in water.https://www.youtube.com/watch?v ins: Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylserine;-Abundant in brain----------------------------------NOTE: Simplest Phosphoric Acid-Functions: Major component of cell membrane Sends messages across cell membranes Second messenger during signaltransduction [On hydrolysis by phospholipaseC, phosphatidyl-inositol-4,5- diphosphateproduces diacyl-glycerol (DAG) & inositoltriphosphate (IP3); which liberates in;-Di-phosphatidyl-glycerol-Found in the inner membrane ofmitochondria-Initially isolated from heart muscle (cardio)
-Structure: 3 molecules of glycerol, 4 fatty-Major classes of Plasmalogens:acids & 2 phosphate groupsEthanolamine plasmalogen (myelin-nervoustissues)Choline plasmalogen (cardiac tissue); Plateletactivating factorSerine alogens;-They are found in the cell membranephospholipids fraction of brain, muscle, liverand semen.-They have a protective role against reactiveoxygen species (i.e. Oxygen radicals, H2O2)-Structure:Precursor: Dihydroxyacetone phosphate Unsaturated fatty alcohol at C1 connected-The Different Structures ofPhospholipids: Uses of Liposomes: Deliveryby ether bond. In mammals, at C3, phosphate ethanolamine or choline Phospholipids; Sphingomyelin (A Type ofSphingolipids):-A major component of the coating aroundnerve fibers-The group attached to C1 is aphosphocholine.
-Zooming into the Myelin:(Sulfides: Galactocerebroside Derivative)WRAP UP [Sphingolipids]:CYCLIC LIPIDS: STEROIDS*Structure: Globosides & Gangliosides are more Glycolipids; Sphingolipids:Sphingolipids containing carbohydratesattached at C-1.-Found on cell membranes and act as cellsurface receptors that can function in cellrecognition (i.e. Pathogens) and chemicalmessengers-Types of Glycolipids: Cerebrosides: the simplest glycolipids,contain a single hexose (galactose orglucose).complex glycolipids.Both contain glucose, galactose, and N-acetylgalactosamine, but gangliosides must alsocontain sialic acid.NOTE: The steroid nucleus is composed ofNOTE:17 carbons within 4 rings.Gangliosides are targeted by cholera toxinin the human intestine.*The Common Steroid: Cholesterol-Composed of 27 carbons.-As proteins do, sphingolipids affect bloodgroups.[Amphipathic]
-Products of Cholesterol:Exercise:-Function: HormonesName Each of the Following Molecules.Transport of different types of lipidsi.e. Sex hormones (Androgens, Estrogens,Progestins) Some vitamins such as vitamin DVitamins A, D, E, and K are made fromisoprenoidsVitamin D -in specific- is made from[Strategy:Cholesterol (Acid Name -ic)-ate](cholesterol, cholesterol esters [CE],phospholipids & triacylglycerols [TG]) inblood plasma.-Different Types of Lipoproteins:cholesterol Bile acids (for intestinal absorption of fat)HOW?Answer: Cholesterol StearateAnswer: Cholesterol Palmitate-Cholesterol Esters:A cholesterol with a fatty acid attached at(-OH) of C3*Lipids Transporting:-By a lipoprotein (micelle structuredmolecule)NOTE:As lipid content increases, the densitydecreasesAs protein content increases, the densityincreases The Dark Side of LDL:LDL can accumulate in blood vessels causingatherosclerosis, thus, heart attacks.
CELL MEMBRANE: Cholesterol Peripheral Membrane Proteins:*Introduction:[In animal cells only. Plant cells have anotherThey are associated with membranes but do-The hypothesized model is the fluidmosaic model-Components: 45% lipid, 45% protein and10% carbohydrate[They exist side by side without formingsome other substance of intermediatesteroid. Prokaryotic cells have non]-It stabilizes the extended straight-chainarrangement of saturated fatty acids by Vander Waals interactions.-Cholesterol makes a membrane less solid atlow temperatures (It interferes with closenot penetrate the hydrophobic core of themembrane.Often associated with integral membraneproteins.They are not strongly bound to themembrane and can be removed withoutnature]packing of fatty acid tails in the crystaldisrupting the membrane structurestate)and(treatment with mild detergent)*Composition:-The two leaflets of the membrane differfrom each other in the composition.The outer leaflet: phosphatidylcholine,sphingomyelin and glycolipids (cellrecognition)The inner e and phosphatidylinositol(signaling)*Fluidity: Degree of SaturationMore saturated phospholipids, less fluidityand vice versa. TemperatureHigher temperature, more fluidity and viceversa.more solid at high temperatures (Itdecreases the mobility of hydrocarbon tailsof phospholipids) Integral Membrane Proteins:Can be associated with the lipid bilayer inseveral ways;*Membrane Proteins:The membrane integral domains are:1. Single or multiple2. -helix or -sheetPeripheral proteins:They are associated with the exterior ofmembranes (or loosely with the phosphateSome can form channels.-Functions:Transport:head of a phospholipid) via noncovalentinteractionsIntegral membrane proteins:They are anchored into membrane viahydrophobic regionsLipid-anchored:Membranes are impermeable barrier.Proteins can be carriers or channelsSignaling:Protein receptors and small molecules (somecan be lipids themselves)Catalysis:They are associated via a lipid groupEnzyme-linked receptors
Q-BANK FROM PAST PAPERS:4) Which of the following is correct7) What's true about the structure of the1) Lecithin is a designation of:regarding integral proteins?following fatty acid?A) PhosphatidylinositolB) PhosphatidylserineC) CardiolipinD) PhosphatidylcholineE) PlasmalogenA) They can be affected by mild detergentsB) They contain a hydrophobic regionembedded in the membraneC) They are exposed from the extracellularside onlyD) All of the above are correctA) PalmitateB) Precursor for eicosanoidsC) Trans fatty acidD) Cis-delta 9 hexadecenoic acidE) More than one of the above2) Which of the following is falseregarding vLDL?A) It transports dietary TG to the liverB) Its diameter is larger than HDLC) It contains cholesterolD) All of the above are falseE) None of the above is false3) What is the following molecule?E) None of the above is correct5) Which of the following is falseregarding this molecule?A) Humans are unable to digest it and it is9) Fatty acid 16:1, 9 is the structureuselessB) Insoluble in waterC) Made of two fatty acidsD) Has no nutritional valueE) The ester group is the only hydrophilicpart of itof:A) Stearic acidB) Oleic acid6) Aspirin works through inhibition of theA) GlucocerebrosideB) CeramideC) GalactocerebrosideD) SphingomyelinE) Globoside8) Which one of the following common inall sphingolipid?A) GlycerolB) PhosphateC) N-acetylgalactoamineD) CeramideE) More than one of the aboveproduction of:A) ProstaglandinsB) ProstacyclinC) ThromboxaneD) LeukotrienesE) All EicosanoidsC) Oleinoic acidD) Mystiric acidE) Palmitoleic acid
10) After you test a patient, it turns out13) Gangliosides contain all the following16) All of the following are fromthat the material surrounding her nervesEXCEPT:cholesterol except:is destroyed. This material is:A) PhosphatidylinositolB) CerebrosidesC) SphingomyelinsD) GlycoproteinsE) CephalinA) Fatty acidB) PhosphateC) CeramideD) HexoseE) N-acetyl neuraminic acid (Sialic acid)A) TestosteroneB) Vitamin DC) ThromboxaneD) EstradiolE) None of the above14) All sphingolipids have in common:A) CeramideB) PhosphorylcholineC) N-acetylneuraminic acidD) GlycerolE) Phosphate17) Regarding the COX isoenzymes. Allare true except:A) COX-1 is present in all tissuesB) COX-2 is inducible by inflammatorystimuliC) Aspirin inhibits COX-1 and COX-2D) All of the aboveE) None of the above11) The name of the following structureis:15) Arrange the following fatty acidsaccording to their melting point startingA) Cholesteryl oleateB) Cholesteryl palmitateC) Cholesteryl stearateD) Cholesteryl laurateE) None of the above12) The following membrane lipid is amajor component of the innermitochondrial membrane:A) LecithinB) CephalinC) CardiolipinD) GlycolipidsE) Phosphatidylinositolfrom the largest to the smallest (oleicacid, linoleic acid, palmitic acid andpalmitoleic acid):A) palmitic acid, oleic acid, palmitoleic acidand linoleic acidB) palmitic acid, palmitoleic acid, oleic acidand linoleic acidC) linoleic acid, palmitoleic acid, palmitic acidand oleic acidD) linoleic acid, palmitoleic acid, oleic acidand palmitic acidE) oleic acid, linoleic acid, palmitoleic acid,and palmitic acid Answers:Q. No.123456789Ans.DAABCADDEQ. No.1011121314151617Ans.CACBAACEDone by: Abdullah Al-Jaouni
-Properties of Fatty Acids: Examples are melting point and solubility, which are dependent on: -Degree of Saturation [more significant] -Chain Length Naming Fatty Acids: RECALL: NOTE: 11 - 19; they have compound names, i.e.: 14 4 10 Tetradeca 18 8 10 Octadeca Formula: No. of C - - noic acid Description of a Fatty Acid: