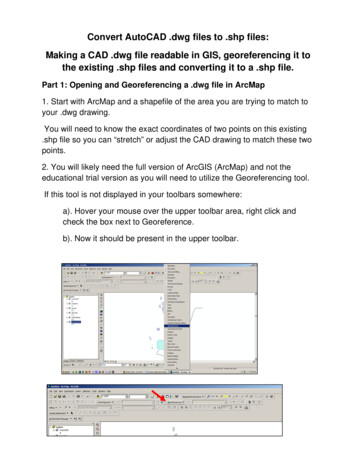
Transcription
Geocoding andGeoreferencingScott BellGIS Institute
Learning Outcomes Define coordinate system and mapprojection Relate coordinate systems and mapprojectionsDistinguish between defining andchanging coordinate systems Create new GIS data from addressesand paper maps Explain how to integrate GPS pointdata 2
Processing Geographic Information Georeferencing and Geocoding Linking data we have to geographic frames ofreference Supporting the display of our data in a GIS and itsintegration with other geographic data 3Geocoding: matching addresses to geographiccoordinates (latitude and longitude)Georeferencing: matching geographic imagesto coordinates
Frames of Reference Global: systems that providediscrete coordinates for locationsanywhere on the Earth’s surfaceThe geodetic latitude of a pointis the angle between theequatorial plane and a line normalto the reference ellipsoid.The geodetic longitude of apoint is the angle between areference plane and a planepassing through the point, bothplanes being perpendicular to theequatorial plane.The geodetic height at a point isthe distance from the referenceellipsoid to the point in a directionnormal to the ellipsoid.4
Frames of Reference Global Frames of reference are appliedto a model of the Earth (size and shape)Earth’s actual shape is too complicated Spheroidal and Ellipsoidal models areused Any single model of the Earth’s size andshape is called a geodetic datum 5
Geographic and ProjectedCoordinates(φ, λ)6Map Projection(x, y)
Coordinate Systems in ArcGIS Latitude and Longitude (3-D object surface,locations indicated in degrees)Projected (2 D and Planar, X, Y in distances)All GIS data is stored according to a coordinatesystem Sometimes the information about the coordinate systemDOESN’T come with the data (but the underlyinginformation is still stored with respect to one) In these situations we need to define or specify the coordinatesystem (“define” command) Sometimes we want to change the data from onecoordinate system to another In these situations need to transform or project the data from onecoordinate system to another (“project” command)7
Address Matching and Geocoding Frames of Reference ContinuousDiscrete, Objects, and Areas Street Address:Palmetto Seafood Co.2200 Gervais St.Columbia, SC 29204-1808 USA Section, ¼ section, township Larger? City, province, etc 8Uh-oh, problemsFor the most part databases produce successfulgeocoding results
9
10
11S4, Brown University
Georeferencing a Paper Map Sometimes the data we want is onlyavailable in a hard copy 12Or is an imageIf we know some important things about thecontents of the image or map we cancoordinate it with global reference systemsEstablish links between the image and ageographically known database
13S4, Brown University
Control PointsLink points are called “control points” Control points should be: Easy to confirm (same location in the world) Be spread across the space beinggeoreferenced Have good overlap between the two datasets Established by clicking as close as possible toyour intended target is important (zooming inhelps) 14
Frames of Reference Global Frames of reference areapplied to a model of the Earth (sizeand shape)Earth’s actual shape is toocomplicated Spheroidal and Ellipsoidal models areused Any single model of the Earth’s sizeand shape is called a geodetic datum 15
Universal Transverse Mercator Locations indicated in meters (from apair of origins)Lat/Long locations in degrees make itdifficult to derive distances betweenplaces or make measurements in nonspherical coordinates Most of us intuitively understandmeters, kilometers, etc. for distanceand area better than degrees,minutes, and seconds 16
UTMHowever This apparent simplicity comes at thecost of a complex frame of referenceand multiple origins 17S4, Brown University
18S4, Brown University
19
Geodetic Datums20
Georeferencing and Geocoding Linking data we have to geographic frames of reference Supporting the display of our data in a GIS and its integration with other geographic data Geocoding: matching addresses to geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) Georeferencing: matching geographic images to coordinates