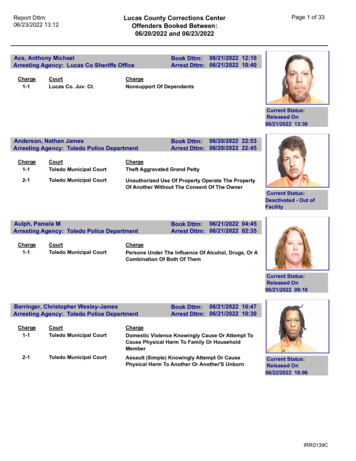
Transcription
Orientation Guidewww.lucas-cpr.com a product by JOLIFE 900080-00 RevB JOLIFE 2012
Refer to the Instructions for Use for completedirections for use, indications, contraindications,warnings, precautions and potential adverseevents.This presentation should be viewed in itsentirety by rescuers being trained for the firsttime on LUCASTM2.LUCAS 2, also referred to as LUCAS, is anelectrically driven chest compression system.Orientation Guide 900080-00 RevB2
LUCAS 2 should only be used by personswith basic medical skills, such as: first responders, ambulance personnel, nurses, physicians,or medical staff who have undertaken a CPR* course according to the resuscitationGuidelines, e.g. American Heart Association or equivalent AND received training in how to use LUCAS*CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitationOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB3
Objectives Explain the emphasis on effective CPR Understand the importance of Coronary PerfusionPressure (CPP) Define the characteristics of effective CPR according toGuidelines Describe the effects of rescuer fatigue on chest compressionsOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB4
ObjectivesReview the use of LUCAS including: Unpacking Ventilation Assembly Transporting the patient Adjustment Changing the Battery Operation Removing from patient Stabilization Strap Cleaning Defibrillation Removing and installing theSuction CupOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB5
Sudden Cardiac Arrest(SCA)Treatment Options CPR Defibrillation Oxygenation with ventilationOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB6
CPR Guidelines have been changed tomake CPR more effectiveWhy is CPR so important?Orientation Guide 900080-00 RevB7
Coronary Perfusion Pressure(CPP) Measure of pressure driving blood flow to theheart muscle Typically 60 mmHg CPP drops dramatically in cardiac arrestOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB8
CPR Provides blood and oxygen tothe brain and heart Generates CPP CPP 15 mmHg associatedwith return of spontaneouscirculation (ROSC)Paradis NA, Gerard B, Rivers EP. et al. Coronary perfusion pressure and the return of spontaneous circulation in humancardiopulmonary resuscitation. JAMA. 1990;263:1106-1113.Orientation Guide 900080-00 RevB9
Three Phases of CardiacArrest1. Electrical:3. Metabolic: 0-3 minutes 10 minutes Immediate defibrillation ROSC highly unlikely2. Circulatory: 4-10 minutes CPR: Ability to generateadequate CPP linked to ROSCWeisfeldt ML, Becker LB. Resuscitation After Cardiac Arrest. A 3-phase time-sensitive model. JAMA. 2002;288(23):3035-3038.Orientation Guide 900080-00 RevB10
Rescuer Fatigue Significant fatigue and shallowcompressions are seen after 1minute of CPR1 Rescuers may deny that fatigueis present for 5 minutes2Quality of CPROchoa et al12010080Incorrectcompressions% May lead to inadequatecompression rates and depths60Correctcompressions4020012345Minutes1Ochoa FJ, Ramalle-Gómara E, Lisa V, Saralegui I. The effect of rescuer fatigue on the quality of chest compressions. Resuscitation. 1998;37:149-52.Hightower D, Thomas S, Stone C, Dunn K, March J. Decay in quality of closed-chest compressions over time. Annals of Emergency Medicine.1995;26:300-303.2Orientation Guide 900080-00 RevB11
CPR Recommendations Ratio: 30 compressions to 2 ventilations Rate: at least 100 compression/minute Depth: at least 2 inches / 5 cm Duty cycle: 50% Allow chest wall to recoil completely Minimize interruptions Change rescuer who provides compressions every second minute2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardio-vascular Care, Circulation2010; 122: S639-946Orientation Guide 900080-00 RevB12
Quality of CPR matters The guidelines are based on a large number of studies of whatCPR technique is optimal to achieve a high coronary perfusionpressure and a successful defibrillation result One study demonstrated it took about 90 seconds after a pauseof compressions to re-establish the previous CPP levels Mechanical chest compressions may eliminate unnecessaryinterruptions to compressionsSteen S, Liao Q, Pierre L, Paskevicius A, Sjöberg T. The critical importance of minimal delay between chest compressions andsubsequent defibrillation: a haemodynamic explanation. Resuscitation. 2003;58:249-258.Orientation Guide 900080-00 RevB13
Bottom Line Heart and brain perfusion is critical The Guidelines changed to make CPRmore effective Most rescuers have difficulty meetingand maintaining CPR according tothe Guidelines Looking for new solutions to improveCPROrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB14
LUCAS 2 LUCAS is a portable device used toprovide external cardiac compressions LUCAS meets all of the recommendedGuidelines for effective CPR and won’tget tired! LUCAS can be used during transport LUCAS is easy to use and a great assetto the teamOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB15
LUCAS 2 Chest Compression SystemOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB16
Uses Adult patients in acute circulatory arrest loss of consciousness absence of spontaneous breathing and pulse LUCAS must only be used in cases where chestcompressions are likely to help the patientOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB17
Contraindications If it is not possible to position LUCAS safelyor correctly on the patient's chest. Too small adult patient Too large patientAlways follow local and/or international Guidelines for CPRwhen using LUCAS.Orientation Guide 900080-00 RevB18
LUCAS 2Chest Compression System- ON/OFFUser Control Panel:- ADJUST- PAUSE (locked)- ACTIVE (continuous) – LUCAS performs continuouschest compressions.The green LED signal will blink 8times per minute to alert for ventilation- ACTIVE (30:2) – LUCAS performs 30 chestcompressions and then temporarily stops for 3 seconds.During the stop, the operator can perform 2 ventilations.After the stop the cycle starts again. An intermittent LEDin combination with an alarm signal sequence will alertthe operator before each ventilation pause- MUTE- Battery indicator- Alarm indicatorOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB19
Basic Steps for Use Arrival at the patient Ventilation Unpacking Transporting the patient Assembly Changing the Battery Adjustment Removing from the patient Operation Cleaning Stabilization Strap Removing and installing theSuction Cup DefibrillationOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB20
Arrival at the patient Confirm cardiac arrest Begin manual CPR until LUCASis readyOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB21
Unpacking of LUCAS 2 Position the bag with its top nearestto you Put your left hand on the black strapon the left side and pull the redhandle so that the bag unfoldsOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB22
Activate LUCAS 2 Push ON/OFF on the User ControlPanel for 1 second to power up LUCASin the bag and start the self test. Thegreen LED adjacent to the ADJUST keyilluminates when LUCAS is ready foruseNote: LUCAS powers downautomatically after 5 minutes if you let itstay in the ADJUST mode.Orientation Guide 900080-00 RevB23
Assembly Remove the Back Plate from theCarrying Bag. Stop manual CPR Make sure that you support thepatient's head Carefully put the Back Plate underthe patient, immediately below thearm pits Start manual CPR againNote: An accurate position of theBack Plate makes it easier and fasterto position the Suction Cup correctly.Orientation Guide 900080-00 RevB24
Assembly Hold the handles on the supportlegs to remove the LUCASUpper Part from the bag Pull the release ringsonce to make sure thatthe claw locks are open Let go of the releaseringsOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB25
Assembly Attach the support leg that is nearestto you to the Back Plate Stop manual CPR Attach the other support leg to theBack Plate, so that the two supportlegs lock against the Back Plate.Listen for click Pull up once to make sure that theparts are correctly attachedOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB26
Positioning of theSuction CupFor the compression to be effective and toavoid serious patient injuries, it is veryimportant that the Suction Cup is properlypositioned and centered over the sternum ofthe patient: The compression point should be the at thesame spot as for manual CPR and accordingto guidelines When the pressure pad in the Suction Cup isin the correct positing, the lower edge of theSuction Cup is immediately above the endof the sternumOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB27
Adjustment procedure If necessary, move the device bypulling the support legs to adjustthe position Compress in the right spot to avoidserious patient injury and geteffective compressions Start manual CPR again if it is notpossible to position LUCAS safelyand correctly on the patient's chestOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB28
Adjustment procedure Make sure that LUCAS is in the ADJUSTmodePush the Suction Cup down with twofingers until the pressure pad touches thepatient's chest without compressing thechestPush PAUSE to lock the Start Position then remove your fingers from the SuctionCup*If you cannot enter the PAUSE mode orACTIVE mode when the pressure padtouches the patient's chest and LUCASalarms with 3 fast signals, then thepatient is too small. Start manualcompressions again*for software version 2.1. LUCAS will adjust the pressure pad to the correct Start Position (within a range of 30 mm / 1.2 inches) if thepressure pad is pushed down too hard, or too loose to the chestOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB29
Adjustment procedure Do not use LUCAS if: pressure pad doesn’t touch chest Upper Part won’t fit aroundpatient or claw locks won’t fastento Back Plate Continue with manualcompressionsOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB30
Adjustment procedure Critical to make necessary adjustments rapidly to minimize “noflow” time or time without compressions After the Back Plate is placed under the patient, it should take lessthan 20 seconds to stop manual compressions, connect the UpperPart of LUCAS, and start mechanical compressions “Practice makes perfect”Orientation Guide 900080-00 RevB31
Operation Check for proper position. If not: Push ADJUST, pull up the SuctionCup to readjust the central and/orheight position for a new StartPosition. Push PAUSE Push ACTIVE (continuous) ORACTIVE (30:2) to start thecompressions.Note: LUCAS in PAUSE modestops the compressions butremembers the patient settingsOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB32
Stabilization Strap The LUCAS Stabilization Strap helps secure thecorrect position during operation Apply it while LUCAS is active to keep interruptions toa minimum Carefully lift the patient's head and put the cushionbehind the patient's neck Connect the buckles on the support leg straps with thebuckles on the cushion strap Hold the LUCAS support legs stable and tighten thecushion strap tightlyNote: Delay the application of the LUCAS StabilizationStrap if this prevents or delays any medical treatmentof the patientOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB33
Defibrillation Defibrillation can be performed whileLUCAS operates You can apply the defibrillationelectrodes before or after LUCAShas been put in positionNote: Make sure pads or wires arenot under the Suction CupOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB34
Defibrillation Perform the defibrillation accordingto the instructions from themanufacturer of the defibrillator After defibrillation, make sure thatthe position of the Suction Cup iscorrect. If necessary, adjust theposition LUCAS needs only to be stoppedfor ECG analysis – chestcompressions interfere with ECGanalysisOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB35
Ventilation Unprotected airway Protected airway Operate LUCAS in ACTIVE (30:2)modeDeliver breaths during pause accordingto the GuidelinesOperate LUCAS in ACTIVE(continuous) modeDeliver breaths independently ofLUCAS operation according to theGuidelinesAlways follow local and/or internationalguidelines for ventilationOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB36
Transporting the patient Secure the patient’s arms Apply Patient Straps on LUCAS topatient arms Make sure that IV access is notobstructed when using PatientStraps Do not lift LUCAS by the PatientStrapsOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB37
Lifting the patient One person on each side and oneperson supporting the patient’s head,even with Stabilization Strap in place Those at patient’s side lift with onehand beneath claw locks of backplate keeping fingers clear of clawlocks Other hand lifts patient’s legOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB38
Lifting the patient Push PAUSE to temporarily stop thecompressions during the lift Make sure that the Suction Cup is inthe correct position on the patient'schest Push ACTIVE (continuous) orACTIVE (30:2) to start thecompressions againOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevBor39
Transporting the patientLUCAS can be active while youmove the patient if: LUCAS and the patient are safelypositioned on the transportationdevice LUCAS stays in the correctposition and angle on the patient'schestOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB40
Changing Battery duringoperation Have a spare, fully charged Battery ready Push PAUSE to temporarily stop the compressions Pull the empty Battery out and then upwards to removeit. Install the fully-charged LUCAS Battery. Wait until the green PAUSE mode LED illuminates Push ACTIVE to start the chest compressions againKeep interruptions to a minimum while changing the Battery.To minimize interruptions, werecommend to always have a charged spare LUCAS Battery in the Carrying Bag.The LUCAS Smart Restart feature remembers the settings and Start Position for 60seconds.Orientation Guide 900080-00 RevB41
Removing from the patient Push ON/OFF for 1 second to power off the device If a LUCAS Stabilization Strap is attached to LUCAS, remove thecushion strap, which is part of the Stabilization Strap, from thesupport leg straps Pull the release rings to remove the Upper Part from the Back Plate If the patient's condition allows it, remove the Back PlateOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB42
Cleaning LUCAS 2 Remove the used and contaminated Suction Cup Clean all surfaces and straps with a soft cloth and warm water witha mild cleaning agent or disinfectant agent, e.g. 70% isopropyl alcohol solutionquaternary ammonium compound45% isopropyl alcohol with added detergent10% bleach Do not immerse LUCAS in liquid. The device can be damaged ifliquid enters the hoodOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB43
Changing the Suction Cup Remove the used andcontaminated Suction Cup Mount a new Suction Cupaccording to the picture to therightOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB44
Side Effects Bruising and soreness of the chest is common during useof LUCAS The International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation(ILCOR) states the following side effects of CPR: Rib fractures and other injuries are common but acceptableconsequences of CPR given the alternative of death from cardiac arrest After the resuscitation, all patients should be reassessed andreevaluated for resuscitation-related injuries2005 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Emergency Cardiovascular Care (ECC) Science withTreatment Recommendations. Circulation. 2005;112(suppl III):III-11.Orientation Guide 900080-00 RevB45
Summary CPR is receiving renewed attention More emphasis on meeting Guideline recommendations for CPR LUCAS achieves effective and consistent compressions easily LUCAS helps minimize unnecessary interruptions to compressions LUCAS benefits both rescuer and patientOrientation Guide 900080-00 RevB46
Orientation Guide 900080-00 RevB47
LUCAS is easy to use and a great asset to the team . Orientation Guide 900080-00 RevB 16 . *for software version 2.1. LUCAS will adjust the pressure pad to the correct Start Position (within a range of 30 mm / 1.2 inches) if the . for ECG analysis - chest compressions interfere with ECG analysis. Orientation Guide 900080-00 RevB 36 .