Transcription
2015 IBCAccessibilityBased on the 2015 International Building Code and the ICC/ANSI A117.1 - 2009 Accessible andUsable Buildings and Facilities
Disability Definition“A physical or mentalimpairment which substantiallylimits one or more of a person’smajor life activities.”2
Built Environment Physical impairments3
What are we talking about?disabilityability4
ICC Goals Coordinate the building code requirements withthe5
2015 IBC - Philosophy 101Everything must be accessible, andthen allow for a degree ofinaccessibility that is logical andreasonable.6
Requirements ScopingRequirements: “What, Whereand How Many” (2015 IBC ) TechnicalRequirements: “How” (ICC/ANSI A117.12009)7
Mainstreaming8
ADA & ABA StandardsSection 207 Require compliance with the International BuildingCode (IBC) for accessible means of egressORIBC 2003Section 1007IBC 2000 with2001 SupplementSection 1003.2.139
ADA & ABA Standards What about compliancewith later editions? Permitted where equivalentor better (“equivalentfacilitation” in the ADAStandards Section 103)201510
11
“Safe Harbor” means that requirements in the document have beenreviewed by HUD and meet or exceed thebuilding construction requirements in the FHA. 2009, 2012 and 2015 IBC and 2009 ICC A117.1are currently under review by HUD.12
Role of the Code Official13
Enforcement of FederalRequirementsComplaintsInspection andReviewMediationThrough the courts14
Exterior Accessible Route
Public Arrival Points Accessible routesstart at public arrivalpoints such as: Accessible parkingspaces Bus drop offs Public transportationstops Where a buildingsidewalk connects tothe public sidewalk16
Accessible Entrances Accessible routesconnection publicarrival points toaccessible entrances17
SignageWhere not all entrancesare accessible At accessibleentrances Directional signage atnon-accessibleentrances18
Other elements on the site Accessible routes arerequired to all facilitiesoffered on the site. Exception: Where theonly access is by avehicular route, then theaccessible route can alsobe provided by thatvehicular route.19
Hazards Grates Platform edges Raised and markedcrossings20
Protruding Objects21
Protruding Objects22
Cut-in Curb RampsX 36” minimum in new constructionOn existing sites, if landing is 36” then slope of flared sides shall notexceed 1:12.23
Built-Up Curb Ramps36” minimumOn existing sites, if landing is 36” then slope of flared sidesshall not exceed 1:12.24
DetectableWarningsat Curb Ramps Detectable warnings arenot required on curbramps by IBC or A117.1 If a designer chooses toprovide detectablewarnings, then technicalprovisions are providedfor area covered,location, pattern andcontrast.25
Accessible parking andpassenger loading zones
Accessible Parking Spaces Based on number of parking spaces provided. Number of parking spaces required per zoningordinances. Accessible spaces required: Table 1106.1 for general parking.2% for Group R-2 and R-3.10% at hospitals facilities.20% at mobility treatment centers.1 of 6 accessible spaces sized for a van27
Dispersion by Type Parking lotsParking garagesCarportsPrivate garagesPay/freeEmployee/visitoronly28
Parking Locations Locate on the shortestaccessible route to anaccessible entrance. Multi-entrance buildingor multi-building sites –disperse spaces Exception: Van spaces on groundlevel of parking garages(vertical clearance of 98inches) Grouped where betteraccess is provided29
Signage Accessible parking must havea sign Exceptions: Fewer than 4 total parkingspaces In Group I-1, R-2, R-3 and R-4where parking is assigned toresidents Access aisles should bemarked to discourage parkingon them The space is not required to bemarked Accessible passenger loadingzones must have a sign30
Passenger Loading Zones At least one in Group I-1 and I-2 At the entrance where valet parking is provided Where passenger loading zones are provided,they must be accessible31
Allowances Passenger loadingzones do not have tohave a confinedlength. The intent isto allow for a locationwhere people cantransfer in safety. Vertical clearance is114” minimum32
Accessible Entry vs.Accessible Exits
Entrance/ExitRequirements—Introduction Requirements for both entry and egress must beaddressed and the most restrictive applied.34
Accessible Entrance Special entrances – atleast one: Parking garagesTunnelsElevated walkwaysRestrictedInmates or detainees Public entrances – 60%. Individual entrance Tenants Accessible Group I and Rdwelling and sleeping units35
Exceptions Areas not required to be accessible. Doors that serve as means of egress only. Service entrances that are not the only entranceto a tenant.36
Doors SizeSwingVestibulesHardwareOpening forceManeuvering clearanceSurfaceVision panelsAutomatic doors37
Vestibules Where doors at avestibule are not in astraight line of travel, theystill have to meet thevestibule requirements. A wheelchair spaceshould be provided pastthe swing of the first door. A turning space must beavailable in the vestibulein case the 2nd door islocked or too difficult toopen.38
Accessible Means of Egress(MOE)
Means of Egress (MOE) A means of egress is an unobstructed path to leave buildings,structures, and spaces Comprised of: Exit Access Exits Exit Discharge 40
MOE: Exit Access The path fromany location ina building toan exit Drawing courtesy of Access Board41
Accessible Exit AccessRampsHorizontal surfacesPlatform lifts withstandby power42
MOE: Exits Exits includedoors to theoutside,enclosed exitstairways, orhorizontalexitsDrawing courtesy of Access Board43
Exit StairsAccessible ExitExit DoorHorizontal ExitElevator with standby power44
MOE: Exit Discharge The path froman exit to apublic way (i.e.,street or alley)Drawing courtesy of Access Board45
Accessible Exit Discharge
Accessible MOE Assisted rescuewhen necessary Defend in place (i.e.,hospitals, jails) Assisted evacuationat stairways Assisted evacuationat elevators withstandby power47
Accessible MOE An accessible means of egress is: A continuous and unobstructedaccessible route of egress travel fromany accessible point in a building orfacility to a public way.48
MOE: Minimum NumberMOE required from each space and roomDrawing courtesy of Access Board49
Accessible Exit Discharge If exit discharge is not accessible: Steps Steep site Snow Interior area of refuge, or Exterior area of rescue assistance. No exceptions for sprinklered buildings.50
Accessible Exit DischargeAllow for self evacuation when possibleDrawing courtesy of Access Board51
Exit DischargeInterior Area of RefugeDrawing courtesy of Access Board52
Exit DischargeExterior Area for Assisted RescueDrawing courtesy of Access Board53
Exterior Area for Assisted RescueDrawing courtesy of Access Board54
Exterior Area for Assisted Rescue2012 IBC: New provision for alternative protectionfrom opening on one sideDrawing courtesy of Access Board55
Stairways and Ramps
Stairways Not part of the accessible route into building. Part of an accessible means of egress out ofbuilding with assistance. Mainstreamed requirements with no reference toICC A117.1. Safety provisions for persons with mobility andvisually impairments addressed in IBC.57
11 inches min. tread depthRiser height 4” to 7”1-1/4” max projection ofnosingsHandrails and GuardsHandrailExtensionsStairway width58
Handrail Extension The handrail extension athe bottom is 1 tread depthminimum and sloped. The 2010 ADA has removedthe requirement for theadditional 12” horizontalextension at the bottom. The handrail extension atthe top is 12” minimumhorizontal. The extension must be inthe direction of the stairwayrun59
Solid tread and risers? Treads allow foropening ½” or smaller Risers should notallow for someone toget their foot caughtunder the tread.60
Ramp Technical Criteria 1:20 slope.1:12 slope maximum on accessible routes.Change in level at start of rampSurfaces – slip resistantCross slope - 1:48Minimum width – 36” between handrailsMaximum rise – 30” between landingsAdequate landings61
Edge Protection, Handrails & GuardsGuards 30” drop offNo drop offCurb or rail edge protection with 30” drop off62
Ramp Allowances Ramps can havegrilled surfaces incold or wet areas. Where the rampmoves up with thegrade, edgeprotection may beprovided by a widersurface63
Existing buildings
Which book to use? Chapter 34 was deletedfrom the 2015 IBC The 2015 IEBC hasthree options – Prescriptive ComplianceMethod – Chapter 4 Work Area Method –Chapters 5 through 13 Performance compliancemethod – Chapter 1465
Where are the accessibilityprovisions? There are accessibility requirements in the prescriptive andwork area method. These provisions are intended to beconsistent. There are some variations due to the chaptersbeing heard by different code development committees. The performance method references the other two methodsfor accessibility. In the prescriptive method, the accessibility provisions are inSection 410. In the work area method, most of the provisions are inSection 705, however, they are split up somewhat into thedifferent chapters.66
MaintenanceA facility that isconstructed accessiblemust be maintainedaccessible.67
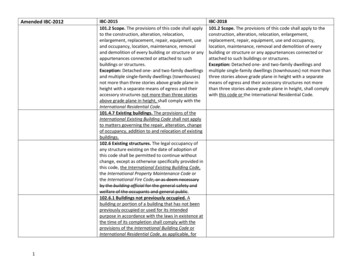
Existing Buildings Maintenance.Alteration.Change of occupancy.Addition.Historic buildings.68
Extent of ApplicationWhen an existing facility is being altered, it is notrequired to provide a higher level of accessibilitythan that which would be required for a newbuilding.69
Alterations to Existing Buildings– Part 1When altering an existing building, everything thatis altered must meet new constructionrequirements for accessibility.70
General Exceptions Accessible means of egress. Technically infeasible. When historical significance is adverselyaffected. Type B units when the alteration is to less than50% of the area of the building (Level 1 or 2)71
Technically Infeasible Removal or alteration of a load-bearing memberthat is an essential part of the structural frame Existing physical or site constraints72
Alterations to Existing Buildings– Part 2 If the area being altered contains a primaryfunction area, the route to that area and anytoilet rooms or drinking fountains that serve thatarea must be evaluated for accessibility. If they are not accessible, additionalimprovements are required.73
Primary Function Area A major activity for which the facility is intended. Excluding areas such as: Mechanical room or boiler roomSupply storageEmployee lounge or locker roomJanitors closetEntrancesCorridorsRestrooms74
Extent of application for additionalaccessible route criteria The route improvements (including improvingthe bathrooms and drinking fountains) arelimited to those that serve the area beingaltered. For example, if an alteration is only to the firstfloor, and the route is compliant, a designer isnot required to fix non-compliant items on theupper floors.75
HISTORIC BUILDING.Any building or structure that is one or more of thefollowing:1. Listed, or certified as eligible for listing, by theState Historic Preservation Officer or the Keeper ofthe National Register of Historic Places, in theNational Register of Historic Places.2. Designated as historic under an applicable state orlocal law.3. Certified as a contributing resource within aNational Register, state designated or locallydesignated historic district.76
IEBC Appendix BSection B101: Qualified historical buildings andfacilities. Explains what a qualified historic building is Requires consultations with interested persons Where compliance with accessibility wouldthreaten the historical significance, alternativesare available.77
Historic Building When compliance would be detrimental to thehistorical significance of a registered building. Minimum requirements Site arrival points.Access to main level.Alternative entrance.Unisex toilet room.78
Special Scoping Entrances.Elevators.Platform lifts.Stair and Escalators.Ramps.Dwelling and sleeping units – Accessible, Type Aand Type B.79
Special Scoping Jury boxes and witness stands.Toilet rooms.Dressing, fitting and locker rooms.Fuel dispensers.Thresholds.Amusement rides.80
Thank you for attending.Questions?
Based on the 2015 International Building Code . Require compliance with the International Building Code (IBC) for accessible means of egress OR IBC 2003 Section 1007 IBC 2000 with 2001 Supplement Section 1003.2.13 . ADA & ABA Standards What about compliance