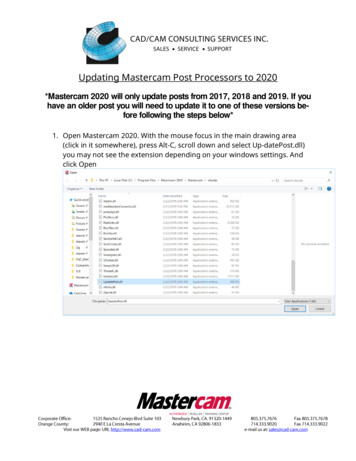
Transcription
Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM)INTRODUCTION TOCOMPUTERNUMERICALCONTROL (CNC)Assoc. Prof. Dr. Tamer S. Mahmoud
1. What is NC? Numerical control (NC) refer to control of amachine or a process using symbolic codesconsisting of characters and numerals. The word CNC came into existence in 7thwhen microprocessors and microcomputersreplaced integrated circuit IC based controlsused for NC machines. The concept of NC was proposed in the late1940s by John Parsons who recommended amethod of automatic machine control thatwould guide a milling cutter to produce acurvilinear motion in order to generatesmooth profiles on the work-pieces.2
2. Components of traditional NC systems3
3. Advantages of NC systems over manualmethods of production Better control of the tool motion underoptimum cutting conditions. Improved part quality and repeatability. Reduced tooling costs, tool wear, and jobsetup time. Reduced time to manufacture parts. Reduced scrap. Better production planning andplacement of machining operations inthe hand of engineering.4
4. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Computer numerical control (CNC) is thenumerical control system in which adedicated computer is built into thecontrol to perform basic and advancedNC functions. CNC controls are also referred to as softwired NC systems because most of theircontrol functions are implemented by thecontrol software programs. CNC is a computer assisted process tocontrol general purpose machines frominstructions generated by a processorand stored in a memory system.5
5. Components of modern CNC systems6
6. Advantages of CNC systems CNC machines can be used continuouslyand only need to be switched off foroccasional maintenance. These machines require less skilled peopleto operate unlike manual lathes/millingmachines etc. CNC machines can be updated by improvingthe software used to drive the machines. Training for the use of CNC machines can bedone through the use of “virtual software”.7
6. Advantages of CNC systems The manufacturing process can be simulatedvirtually and no need to make a prototype or amodel. This saves time and money. Once programmed, these machines can be leftand do not require any human intervention,except for work loading and unloading. These machines can manufacture severalcomponents to the required accuracy withoutany fatigue as in the case of manuallyoperated machines. Savings in time that could be achieved withthe CNC machines are quite significant.8
8. Disadvantages of CNC systems CNC machines are generally more expensivethan manually operated machines. The CNC machine operator only needs basictraining and skills, enough to supervise severalmachines. Increase in electrical maintenance, high initialinvestment and high per hour operating coststhan the traditional systems. Fewer workers are required to operate CNCmachines compared to manually operatedmachines. Investment in CNC machines canlead to unemployment.9
9. Direct Numerical Control (DNC) In a Direct Numerical Control system (DNC),a mainframe computer is used to coordinatethe simultaneous operations of a number NCmachines. The main tasks performed by the computerare to program and edit part programs aswell as download part programs to NCmachines. Machine tool controllers have limitedmemory and a part program may containfew thousands of blocks. So the program isstored in a separate computer and sentdirectly to the machine, one block at a time.DNC systems10
10. Distributed Numerical Control (DNC) Distributed NC is known by the same acronym asDirect Numerical Control (DNC). After the introduction of CNC, the machine tools havehad the capability of storing large amount ofinformation. Therefore, there have been no need tohave drip feed information system, like, DirectNumerical Control. Instead, Distributed NumericalControl is introduced. In such a system, a hostcomputer communicate with many CNC machinetools via networks and download or upload programs. With Distributed Numerical Control systems, it ispossible to monitor the activities in individual CNCmachine tools on host computer. Therefore, bettershop floor control can be achieved.DNC systems11
11. Application of CNC Machine Tools CNC was initially applied to metalworking machinery: Mills, Drills,boring machines, punch pressesetc and now expanded to robotics,grinders, welding machinery,EDM's, flame cutters and also forinspection equipment etc.12
11. Application of CNC Machine Tools The machines controlled by CNC can be classified into the followingcategories: CNC mills and machining centers, CNC lathes and turning centers CNC electrical discharge machining (EDM) CNC grinding machines CNC cutting machines (laser, plasma, electron, or flame) CNC fabrication machines (sheet metal punch press,bending machine, or press brake) CNC welding machines13
11. Application of CNC Machine ToolsCNC Vertical Machining Center14
11. Application of CNC Machine ToolsCNC Turning Machining Center15
11. Application of CNC Machine ToolsCNC Laser Cutting Machine16
11. Application of CNC Machine ToolsCNC EDM Machine17
11. Application of CNC Machine ToolsCNC Hydraulic Plate Punching And Marking Machine18
11. Application of CNC Machine ToolsCNC Four-point Welding Machine19
12. Classification of CNC Machines1. Classification based on themotion type.2. Classification based on thecontrol loops.3. Classification based on thenumber of axes.4. Classification based on thepower supply.20
12. Classification based on the motion type.Point-to-Point Systems.1. It is used in some CNC machines such asdrilling, boring and tappingmachines etc.2. The control equipment for use withthem are known as point-to-pointcontrol equipment.3. Feed rates need not to be programmed.4. In theses machine tools, each axis isdriven separately.21
12. Classification based on the motion type.Contouring Systems (Continuous Path Systems) It is used in CNC machine tools such as millingmachines. These machines require simultaneous controlof axes. Contouring machines can also be used aspoint-to-point machines, but it will beuneconomical to use them unless the workpiece also requires having a contouringoperation to be performed on it.22
12. Classification based on the motion type.23
13. Classification based on the control loopsOpen Loop Systems Programmed instructions are fed into thecontroller through an input device. These instructions are then converted toelectrical pulses (signals) by the controllerand sent to the servo amplifier to energizethe servo motors. The primary drawback of the open-loopsystem is that there is no feedback system tocheck whether the program position andvelocity has been achieved.24
13. Classification based on the control loopsOpen Loop Systems the open -loop system isgenerally used in point-topoint systems where theaccuracy requirements arenot critical. Very few continuous-pathsystems utilize open-loopcontrol.25
13. Classification based on the control loopsClosed Loop Systems The closed-loop system has afeedback subsystem to monitor theactual output and correct anydiscrepancy from the programmedinput. These systems use position andvelocity feed back. The feedback system could beeither analog or digital.26
13. Classification based on the control loopsClosed Loop Systems The analog systems measure the variation ofphysical variables such as position andvelocity in terms of voltage levels.Digital systems monitor output variations bymeans of electrical pulses.Closed-loop systems are very powerful andaccurate because they are capable ofmonitoring operating conditions throughfeedback subsystems and automaticallycompensating for any variations in real-time.27
14. Classification based on the number of axes2&3 axes CNC Machines CNC lathes will be coming under 2 axesmachines. There will be two axes along whichmotion takes place. The saddle will be moving longitudinally onthe bed (Z-axis) and the cross slide movestransversely on the saddle (along X-axis). In 3-axes machines, there will be one moreaxis, perpendicular to the above two axes. By the simultaneous control of all the 3 axes,complex surfaces can be machined.28
14. Classification based on the number of axes29
14. Classification based on the number of axes30
14. Classification based on the number of axes31
14. Classification based on the number of axesImportance of higher axes machining: Reduced cycle time by machining complexcomponents using a single setup. In addition to time savings, improvedaccuracy can also be achieved aspositioning errors between setups areeliminated. Improved surface finish and tool life bytilting the tool to maintain optimum toolto part contact all the times.32
14. Classification based on the number of axesImportance of higher axes machining: Improved access to under cuts and deeppockets. By tilting the tool, the tool canbe made normal to the work surface andthe errors may be reduced as the majorcomponent of cutting force will be alongthe tool axis. Higher axes machining has been widelyused for machining sculptures surfaces inaerospace and automobile industry.33
14. Classification based on the power supply Mechanical power unit refers to adevice which transforms some formof energy to mechanical power whichmay be used for driving slides,saddles or gantries forming a part ofmachine tool. The input power may be of electrical,hydraulic or pneumatic.AC Servo Motor for CNC Machine Tool34
Thank You35
the servo motors. The primary drawback of the open-loop system is that there is no feedback system to check whether the program position and velocity has been achieved. 24. 13. Classification based on the control loops Open Loop Systems the open -loop system is generally used in point-to- point systems where the accuracy requirements are not critical. Very few continuous-path systems utilize .