Transcription
PRODUCT and PROCESS DESIGNLECTURE 06Equipment Sizing andCapital Cost EstimationWarren D. SeiderUniversity of PennsylvaniaPhiladelphia, PennsylvaniaSelection of Topics - depends on previousexposure to process economicsCan begin with cost accounting – gives a goodview of corporate finances and considerationswhen evaluating a potential design.Given limited time – begin with equipmentsizing and capital cost estimation.Again, coverage depends on previousexposure to sizing of:Pressure vessels, heat exchangers, pumps,compressors, etc.Equipment Sizing and Capital Cost EstimationWarren D. Seider, University of Pennsylvania21
PRODUCT and PROCESS DESIGNLECTURE 06Many sources on selection and sizing of manykinds of equipmentUlrich, G. D., and P. T. Vasudevan, Chemical Engineering ProcessDesign & Economics: A Practical Guide, Second Edition, 2004.Peters, M. S., K. D. Timmerhaus, and R. West, Plant Design andEconomics for Chemical Engineers, Fifth Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2003.Sandler, H. J., and E. T. Luckiewicz, Practical Process Engineering,XIMIX, Philadelphia, PA, 1993.Turton, R., R. C. Bailie, W. B. Whiting, and J. A. Shaeiwitz, Analysis,Synthesis, and Design of Chemical Processes, Second Edition, PrenticeHall, 2003.Seider, W. D., J. D. Seader, and D. R. Lewin, Product and ProcessDesign Principles: Synthesis, Analysis, and Evaluation, SecondEdition, Wiley, 2004.Equipment Sizing and Capital Cost Estimation3One Popular Option – Distillation ComplexCondensercwReflux Accumulator(horiz. process cal processvessel)SteamReboilerCondensateBottoms ProductReboiler PumpEquipment Sizing and Capital Cost EstimationWarren D. Seider, University of Pennsylvania42
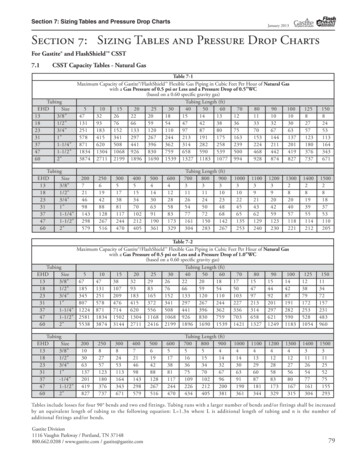
PRODUCT and PROCESS DESIGNLECTURE 06Shell-and-Tube Heat ExchangerTH,outTC,outTH,inTC,inQ UA TLMA QU TLMEquipment Sizing and Capital Cost Estimation5Purchase Costs – Shell-and-tube Heat ExchangersEquipment Sizing and Capital Cost EstimationWarren D. Seider, University of Pennsylvania63
PRODUCT and PROCESS DESIGNLECTURE 06Floating Head{2{2}{2}CB exp 11.667 0.8709 [ ln( A) ] 0.09005 [ ln( A)]}Fixed HeadCB exp 11.0545 0.9228 [ ln( A) ] 0.09861[ ln( A) ]U-tubeCB exp 11.147 0.9186 [ ln( A) ] 0.09790 [ ln( A) ]Kettle Vaporizer{CB exp 11.967 0.8709 [ ln( A) ] 0.09005 [ ln( A) ]2Equipment Sizing and Capital Cost Estimation}7Purchase CostCP FP FM tionEquipment Sizing and Capital Cost EstimationWarren D. Seider, University of Pennsylvania84
PRODUCT and PROCESS DESIGNLECTURE 06Materials of Construction Factors, FM,for Shell-and-Tube Heat Exchangers A FM a 100 Material of constructionShell/TubeCarbon steel/Carbon steelba in Eq. (16.44)b in Eq. (16.44)0.000.00Carbon steel/Brass1.080.05Carbon steel/Stainless steel1.750.13Carbon steel/Monel2.10.13Carbon steel/Titanium5.20.16Carbon steel/Cr-Mo steel1.550.05Cr-Mo steel/Cr-Mo steel1.700.07Stainless steel/Stainless 60.06Equipment Sizing and Capital Cost EstimationPressure Factor9psia P P FP 0.9803 0.018 0.0017 100 100 2Tube-length Correction FactorTube length, ftFL81.25121.12161.05201.00Equipment Sizing and Capital Cost EstimationWarren D. Seider, University of Pennsylvania105
PRODUCT and PROCESS DESIGNLECTURE 06Cost IndexesEquipment Sizing and Capital Cost Estimation11Bare Module Cost – Heat Exchanger –Table 16.10 (SSL, 2004)Equipment Sizing and Capital Cost EstimationWarren D. Seider, University of Pennsylvania126
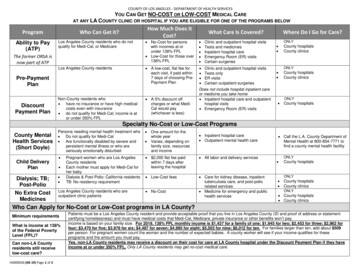
PRODUCT and PROCESS DESIGNLECTURE 06Bare Module Factors - Table 16.11 (SSL, 2004)Equipment Sizing and Capital Cost Estimation13Total Capital Investment – Table 16.9 (SSL, 2004)Equipment Sizing and Capital Cost EstimationWarren D. Seider, University of Pennsylvania147
PRODUCT and PROCESS DESIGNLECTURE 06Cost EquationsSSL (2004) – Purchase Cost Equations for numerousprocess units – see Table 16.32 for “other” equipmentitems. Available literature sources back to 1960 consulted. After determining a suitable equipment size factor,all of the cost data were plotted. When a wide spread in the data was evident, whichwas not uncommon, an attempt was made to assessthe validity of the data by comparison with costs ofsimilar equipment. When the validity could not be determined, the datawere averaged. In some cases, cost data were obtained from vendors.Equipment Sizing and Capital Cost Estimation15Table 16.32 contains cost equations for:Agitators, autoclaves, crystallizers, dryers, dust collectors,evaporators, fired heaters, heat exchangers, liquid-liquidextractors, membrane separations, mixers, turbines, screens,size enlargers, size reducers, solid-liquid separators, solidshandling systems, storage tanks, vacuum systems, wastewater treaters.Equipment Sizing and Capital Cost EstimationWarren D. Seider, University of Pennsylvania168
PRODUCT and PROCESS DESIGNLECTURE 06Aspen Icarus Process Evaluator (IPE)Extends results of process simulationsGenerates rigorous size estimates for processingequipment and estimates costs based upon extensivedataPerforms preliminary mechanical designsEstimates purchase and installation costs, indirect costs,the total capital investment, the engineeringprocurement-construction schedule, and profitabilityanalysisEquipment Sizing and Capital Cost Estimation17Aspen IPE uses five key steps1. Simulation results are loaded into Aspen IPE.2. Process simulation units are mapped into more descriptivemodels of process units and associated plant bulks – includinginstallation items, such as piping, instrumentation, paint, etc.3. Equipment items are sized and re-sized when modified.4. Capital costs, operating costs, and the total investment areevaluated for a project.5. Results are presented to be reviewed, with modificationsas necessary.Equipment Sizing and Capital Cost EstimationWarren D. Seider, University of Pennsylvania189
PRODUCT and PROCESS DESIGNLECTURE 06Aspen IPE FeaturesNumerous default design basis parameters are built in foruse in rigorous equipment-sizing routines – for manyequipment types.Bare module factors are not used. Extensive data are usedto estimate the costs of materials, labor, and constructionequipment –based upon detailed design calculations for foundations,platforms, piping, instrumentation, electrical connections,insulation, painting, Equipment Sizing and Capital Cost Estimation19SeeSection 16.7 (SSL, 2004) – Equipment Sizing andCapital Cost Estimation Using The Aspen IcarusProcess Evaluator (IPE)Course Notes (SSL, 2004) – Aspen Icarus ProcessEvaluator (IPE) – Equipment Sizing and Costing UsingASPEN PLUS to Initiate Evaluation.Equipment Sizing and Capital Cost EstimationWarren D. Seider, University of Pennsylvania2010
Aspen Icarus Process Evaluator (IPE) Extends results of process simulations Generates rigorous size estimates for processing equipment and estimates costs based upon extensive data Performs preliminary mechanical designs Estimates purchase and installation costs, indirect costs, the