Transcription
PUBLISHEDSFF-8024 Rev 4.6SFF-8024Specification forSFF Module Management Reference Code TablesRev 4.6February 14, 2019SECRETARIAT: SFF TA TWGThis specification is made available for public review at http://www.snia.org/sff/specifications. Comments may besubmitted at http://www.snia.org/feedback. Comments received will be considered for inclusion in future revisionsof this specification.ABSTRACT:This specification provides codes for module identifiers, encoding values, connector types, extended compliancecodes, host electrical interfaces and module media interfaces.This specification is the reference source for identifiers assigned to interpret the memory maps of self-identifyingmodules.POINTS OF CONTACT:Tom PalkertMolex, LLC.2222 Wellington CourtLisle, IL 60532tom.palkert@molex.comSFF-8024Chairman SFF TA TWGEmail: SFF-Chair@snia.orgPage 1Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
PUBLISHEDSFF-8024 Rev 4.6Intellectual PropertyThe user's attention is called to the possibility that implementation of this specification may require the use of aninvention covered by patent rights. By distribution of this specification, no position is taken with respect to thevalidity of a claim or claims or of any patent rights in connection therewith.This specification is considered SNIA Architecture and is covered by the SNIA IP Policy and as a result goes througha request for disclosure when it is published. Additional information can be found at the following locations: Results of IP Disclosures: http://www.snia.org/sffdisclosuresSNIA IP Policy: http://www.snia.org/ippolicyCopyrightThe SNIA hereby grants permission for individuals to use this document for personal use only, and for corporationsand other business entities to use this document for internal use only (including internal copying, distribution, anddisplay) provided that:1.2.Any text, diagram, chart, table or definition reproduced shall be reproduced in its entirety with noalteration, and,Any document, printed or electronic, in which material from this document (or any portion hereof) isreproduced shall acknowledge the SNIA copyright on that material, and shall credit the SNIA for grantingpermission for its reuse.Other than as explicitly provided above, there may be no commercial use of this document, or sale of any part, orthis entire document, or distribution of this document to third parties. All rights not explicitly granted are expresslyreserved to SNIA.Permission to use this document for purposes other than those enumerated (Exception) above may be requestedby e-mailing copyright request@snia.org. Please include the identity of the requesting individual and/or companyand a brief description of the purpose, nature, and scope of the requested use. Permission for the Exception shallnot be unreasonably withheld. It can be assumed permission is granted if the Exception request is not acknowledgedwithin ten (10) business days of SNIA's receipt. Any denial of permission for the Exception shall include anexplanation of such refusal.DisclaimerThe information contained in this publication is subject to change without notice. The SNIA makes no warranty ofany kind with regard to this specification, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantabilityand fitness for a particular purpose. The SNIA shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental orconsequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this specification.Suggestions for revisions should be directed to http://www.snia.org/feedback/.SFF-8024Page 2Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
PUBLISHEDSFF-8024 Rev 4.6ForewordThe development work on this specification was done by the SNIA SFF TWG, an industry group. Since its formationas the SFF Committee in August 1990, the membership has included a mix of companies which are leaders acrossthe industry.For those who wish to participate in the activities of the SFF TWG, the signup for membership can be found athttp://www.snia.org/sff/join.Revision HistoryRev 0.7RevRevRevRevRev0.80.91.01.11.2Rev 1.3Rev 1.4RevRevRevRevRevRev1.51.61.71.81.92.0Rev 2.1Rev 2.2Rev 2.3-Rev 2.4Rev 2.5-Rev 2.6-Rev 2.7Rev 2.8SFF-8024Table 3-1 changed per comments received during ballotFigure 3-3 example addedAs requested by Transceiver SSWG, added color to Figure 3-3As requested, filled in more cells for SFP and CXP.Corrected CXP 802.3ba as applicable to SFF-8647Removed logo on connectors in Figure 3-1 and Figure 3-2Changed ‘ ’ to ‘and’ in Table 3-1Added master table for Identifier Values as per Transceiver SSWGAdded master table for Encoding ValuesAdded SFP 4 Gb/s to Table 3-1Expanded the Identifier Values tableAdded master table for Specification Compliance CodesAdded master table for Extended Specification Compliance CodesExpanded single sentence about SFF-8063 to a paragraph with emphasisIdentified superseded specifications in Table 3-1Expanded HD to include unshielded and add 24 Gb/sAligned SFP naming w/QSFP nomenclatureAdded 0Bh to the Extended Specification Compliance CodesChanged SFP Common Management Spec to SFF-8472Deleted 802.3bj from 28 Gb/s CXPAligned CXP and HD naming w/QSFP nomenclatureReplaced duplicated codes 08-0Ah in the Extended Specification Compliance CodesClarified active cable and CWDM4 codesExpanded 0Bh in Identifier Values to include SFP Added 13-16h to the Extended Specification Compliance CodesThe Encoding Values which were thought to be common between SFF-8472 and SFF-8636 are not.The table was deleted and restored to SFF-8636.The Specification Compliance Codes are not subject to change. The table was deleted and restoredto SFF-8636.Added 13h to Identifier ValuesRestored the Encoding Values from SFF-8472 and SFF-8636Added Connector Types from SFF-8472 and SFF-8636Added 07h to Encoding ValuesAdded 0Dh and 24h to Connector TypesSplit Table 3-1 Integrated Pluggable Solution specifications which were referenced by anotherIntegrated Pluggable Solution: o SFF-8084 reference changed to SFF-8071o SFF-8431 reference changed to SFF-8419o SFF-8643 reference changed to SFF-8613o SFF-8644 reference changed to SFF-8614o SFF-8647 reference changed to SFF-8617Added note in 4.1 about overlap with CFP MSA codesRemoved IEEE references from CXP rowsAdded 14-15h Fanouts to Identifier ValuesAdded specification numbers for QSFPx managementPage 3Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
PUBLISHEDRevRevRevRev2.93.03.13.2Rev 3.3Rev 3.4RevRevRevRevRevRev3.53.63.73.83.94.0Rev 4.2Rev 4.3Rev 4.4Rev 4.5Rev 4.6-SFF-8024 Rev 4.6Added SFF-8418 to Table 3-1Added 16h 10GBASE-T with SFI electrical interface to Extended Specification Compliance CodesAdded 17h QSFP28 100G CLR4 to Extended Specification Compliance CodesRenamed Table 3-1 and added Table 3-2 Device ConnectorsRenamed Mini-SAS HD as Mini Multilane HD in Figure 3-2Updated Identifier Values with backward compatible cables and modulesAdded 25G Ethernet and AOC, ACC equivalents to Extended Specification Compliance CodesAdded Extended SCC 17h microQSFPAdded Extended SCC 1Ah 2 lambda DWDM 100GAdded Encoding Value 08h PAM4Replaced Table 3-2Removed reference to SFF-8436 for Extended Compliance Codes in 4Corrected entries for CWDM4Added 25GBASE to 03h and 04h 100GBASEChanged 1Ah acronym to 100GE-DWDM2 and added descriptionAdded new codes 1Bh-20h in Extended compliance codes Table 4-4Added new code 21h (100G PAM4 BiDi)in Extended compliance code Table 4-4Added new code 19h for OSFP in Identifier values Table 4-1Added new code 22h for 4WDM-10 MSA in Table 4-4Added new code 23h for 4WDM-20 MSA in Table 4-4Added new code 24h for 4WDM-40 MSA in Table 4-4Incorporated changes from June 7 2017 meeting including:Deleted all references to Seagate FTP siteRestructured Table 3-1Updated Fig 3-3Added multi-lane text to section 4.4Changed ANSI reference to INCITSUpdated Tables 3-1, 3-2Added new code 1Ah for SFP-DD in Table 4-1Added new codes for CS and mini CS connectors to Table 4-3Added new codes for 50G/lane and 100G PMDs in Table 4-4Added new codes for 64GFC and 128GFC in Table 4-4Added Module-Host Electrical Interface Codes as Table 4-5March 8, 2019Changed name from 'SFF Cross Reference to Industry Products' to 'SFF Module ManagementReference Code Tables'Deleted Tables 3-1, 3-2 (See REF-TA-1011)Added new Module Media code Tables 4-6,7,8,9,10Updated Module-Host Electrical Interface Codes Table 4-5Added codes for DSFP, x4 MiniLink/OCuLink, x8 MiniLink, QSFP with CMIS (Table 4-1)Reworded description of 0Dh code in Table 4-1Added text to note 2 in Table 4-1Added note 1 in Table 4-5Corrected BER from 2.4x10-6 to 2.6x10-6 in Table 4-9Added code for active cable with BER 10-6 in Table 4-9SFF-8024Page 4Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
PUBLISHEDSFF-8024 Rev 4.6Contents1.Scope72.References, Conventions, Keywords, Definitions2.1Industry Documents2.2Sources2.3Conventions2.4Keywords, Acronyms, and Definitions2.4.1 Keywords2.4.2 Acronyms and Abbreviations2.4.3 Definitions7789101010113.General Description3.1Configuration Overview/Descriptions12124.Transceiver or Cable Management4.1Overview4.2Transceiver References4.3Encoding References4.4Connector References4.5Extended Specification Compliance References4.6Host Electrical and Media Interface Codes13131415161619SFF-8024Page 5Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
PUBLISHEDSFF-8024 Rev 4.6FiguresFigure 2-1 Plug and Receptacle Definition11TablesTable 3-1 Module form factors and management interface specificationsTable 4-1 Identifier ValuesTable 4-2 Encoding ValuesTable 4-3 Connector TypesTable 4-4 Extended Specification Compliance CodesTable 4-5 Host Electrical Interface CodesTable 4-6 850 nm MM media interface codesTable 4-7 SM media interface codesTable 4-8 Passive Copper Cable interface codesTable 4-9 Active Cable assembly media interface codesTable 4-10 BASE-T media interface advertising codes1214151617202324252626SFF-8024Page 6Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
PUBLISHEDSFF-8024 Rev 4.61. ScopeThis specification defines the SFF Module Management Reference Codes. This specification provides codes formodule identifiers, encoding values, connector types, extended compliance codes, host electrical interface andmodule media interface. These codes are used to advertise module capabilities in a module memory map.2. References, Conventions, Keywords, Definitions2.1Industry Documents- InfiniBand Architecture Specification Volume 2-CPRI V7.0ITU-T G.709/Y.1331IEEE Std 802.3ITU-T ,5,6,6p,7417 SAS-1.1 (Serial Attached SCSI - 1.1)457 SAS-2 (Serial Attached SCSI - 2)478 SAS-2.1 (Serial Attached SCSI - 2.1)519 SAS-3 (Serial Attached SCSI - 3)534 SAS-4 (Serial Attached SCSI - 4)SFF-8024SFP 1X 0.8mm Card Edge ConnectorXFP 1X 10 Gb/s Pluggable ModuleSFP 1X 16 Gb/s Pluggable Transceiver Solution (SFP16)SFP 1X 10 Gb/s Pluggable Transceiver Solution (SFP10)SFP 1X 4 Gb/s Pluggable Transceiver SolutionSFP 1X 28 Gb/s Pluggable Transceiver Solution (SFP28)SFP 10 Gb/s Electrical InterfaceSFP Power and Low Speed InterfaceSFP Module and CageSFP Ganged CageQSFP 4X 10 Gb/s Pluggable TransceiverQSFP 4X 4 Gb/s Transceiver (Quad SFP)Management Interface for SAS Shielded CablesManagement Interface for SFP Serial Attachment 2X Unshielded ConnectorMini Multilane 4/8X Unshielded Connector (HDun)Mini Multilane 4/8X Shielded Cage/Connector (HDsh)Mini Multilane 12X Shielded Cage/Connector (CXP)Serial Attachment 4X 12 Gb/s Unshielded ConnectorQSFP 4X 10 Gb/s Pluggable Transceiver Solution (QSFP10)Management Interface for Cabled EnvironmentsMultifunction 6X Unshielded ConnectorSerial Attachment 4X 24 Gb/s Unshielded ConnectorMini Multilane 12X 10 Gb/s Shielded Connector (CXP10)Mini Multilane 4/8X 12 Gb/s Unshielded Connector (HD12un)Mini Multilane 4/8X 12 Gb/s Shielded Cage/Connector (HD12sh)Mini Multilane 12X 14 Gb/s Shielded Cage/Connector (CXP14)Mini Multilane 12X 28 Gb/s Shielded Cage/Connector (CXP28)QSFP 4X Pluggable ModuleQSFP 4X Connector (Style A)QSFP Cage (Style A)Page 7Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
PUBLISHEDSFF-8024 Rev 4.6-SFF-8665 QSFP 4X 28 Gb/s Pluggable Transceiver Solution (QSFP28)SFF-8672 QSFP 4X Connector (Style B)SFF-8678 Serial Attachment 2X 6 Gb/s Unshielded ConnectorSFF-8679 QSFP 4X Base Electrical SpecificationSFF-8680 Serial Attachment 2X 12 Gb/s Unshielded ConnectorSFF-8681 Serial Attachment 2X 24 Gb/s Unshielded ConnectorSFF-8682 QSFP 4X ConnectorSFF-8683 QSFP CageSFF-8685 QSFP 4X 14 Gb/s Pluggable Transceiver Solution (QSFP14)REF-TA-1011 Cross Reference to Select SFF Connectors and ww.dsfpmsa.orgCommon Management Interface Specification (CMIS)Management Interface Specification ww.4wdm-msa.orgSourcesThe complete list of SFF documents which have been completed, are currently being worked on, or that have beenexpired by the SFF Committee can be found at http://www.snia.org/sff/specifications. Suggestions for improvementof this specification will be welcome, they should be submitted to http://www.snia.org/feedback.Copies of INCITS standards may be obtained from the InterNational Committee for Information TechnologyStandards (http://www.techstreet.com/incitsgate.tmpl).Copies of PCIe standards may be obtained from the PCI-SIG (http://pcisig.com).Copies of InfiniBand standards may be obtained from the InfiniBand Trade Association (IBTA)(http://www.infinibandta.org).Copies of IEEE standards may be obtained from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)(https://www.ieee.org).Copies of SAS standards may be obtained from the International Committee for Information Technology Standards(INCITS) (http://www.incits.org).Copies of OIF Implementation Agreements may be obtained from the Optical Internetworking Forum(http://www.oiforum.com).Copies of Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) standards may be obtained from the Electronic Components IndustryAssociation (ECIA) (https://www.ecianow.org).Copies of SFP-DD specifications may be obtained from the SFP-DD MSA group (https://www.sfp-dd-msa.org).Copies of QSFP-DD specifications may be obtained from the QSFP-DD MSA group (https://www.qsfp-dd.com)Copies of CMIS (Common Management Interface Specification) may be obtained from the QSFP-DD MSA group(https://www.qsfp-dd.com)SFF-8024Page 8Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
PUBLISHEDSFF-8024 Rev 4.6Copies of DSFP specification may be obtained from the DSFP MSA group (https://www.dsfpmsa.org).Copies of the microQSFP beobtainedfromthemicroQSFPMSAgroupConventionsThe following conventions are used throughout this document:DEFINITIONSFanout Cable: A single connector cable assembly which splits into a number of connectors at the other end.NUMBERING CONVENTIONSThe ISO convention of numbering is used i.e., the thousands and higher multiples are separated by a space and aperiod is used as the decimal point. This is equivalent to the English/American convention of a comma and a 61 0001 323 462,9ISO0.61 0001 323 462.9Page 9Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
PUBLISHED2.4SFF-8024 Rev 4.6Keywords, Acronyms, and DefinitionsFor the purposes of this document, the following keywords, acronyms, and definitions apply.2.4.1 KeywordsMay/may not: A keyword that indicates flexibility of choice with no implied preference.Obsolete: A keyword indicating that an item was defined in prior specifications but has been removed from thisspecification.Optional: A keyword that describes features which are not required by the SFF specification. However, if anyfeature defined by the SFF specification is implemented, it shall be done in the same way as defined by thespecification. Describing a feature as optional in the text is done to assist the reader.Reserved: A keyword used for defining the signal on a connector contact [when] its actual function is set asidefor future standardization. It is not available for vendor specific use. Where this term is used for bits, bytes, fields,and code values; the bits, bytes, fields, and code values are set aside for future standardization. The default valueshall be zero. The originator is required to define a Reserved field or bit as zero, but the receiver should not checkReserved fields or bits for zero.Shall: A keyword indicating a mandatory requirement. Designers are required to implement all such mandatoryrequirements to ensure interoperability with other products that conform to this specification.Should: A keyword indicating flexibility of choice with a strongly preferred alternative.Vendor specific: A keyword indicating something (e.g., a bit, field, code value) that is not defined by thisspecification. Specification of the referenced item is determined by the manufacturer and may be used differentlyin various implementations.2.4.2 Acronyms and Abbreviations4WDMAOC: Active Optical CableBNC: Bayonet Neill-ConcelmanCAUI: 100G Attachment Unit InterfaceCDFP: 16 Lane Form factor Pluggable ModuleCLR4CMIS: Common Management Interface SpecificationCS: Corning/SenkoCXP: 100G 12 lane Pluggable ModuleDAC: Direct Attach Copper (passive)ACC: Active Copper CableDSFP: Dual Small Form Factor PluggableDWDM: Dense Wavelength Division MultiplexingGBIC: Giga Bit Interface ConverterHSSDC: High Speed Serial Data ConnectorLC: Lucent ConnectorMPO: Multi-fiber Push-On connectorMT-RJMUMXC: Multi-media eXtension ConnectorOSFP: Octal Small Form Factor PluggablePAM4: Pulse Amplitude Modulation 4 levelsPSM4: Parallel Single Mode 4 laneSFF-8024Page 10Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
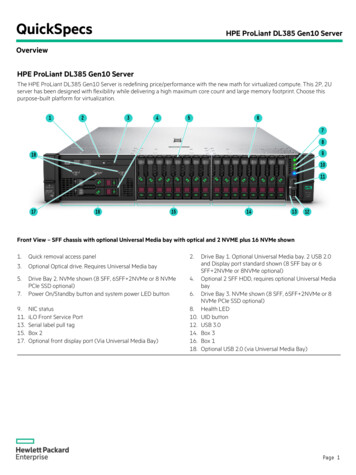
PUBLISHEDSFF-8024 Rev 4.6QSFP: Quad Small Form Factor PluggableQSFP-DD: Quad Small Form Factor Pluggable Double DensityRJ45SCSFI: SFP high speed electrical interfaceSFP: Small Form Factor PluggableSFP-DD: Small Form Factor Pluggable Double DensitySGSWDMTNC: Threaded Neill-ConcelmanX2: 10G form factor pluggableXAUI: 10 lane Attachment Unit InterfaceXENPAK: 10Gbit Ethernet transceiver PackageXFFXFF-EXFI: XFP high speed electrical InterfaceXFP: 10G Form factor PluggableXPAK: 10G form factor pluggable2.4.3 DefinitionsConnector: Each half of an interface that, when joined together, establish electrical contact and mechanicalretention between two components. In this specification, the term connector does not apply to any specific gender;it is used to describe the receptacle, the plug or the card edge, or the union of receptacle to plug or card edge.Other common terms include: connector interface, mating interface, and separable interface.Module: In this specification, module refers to:1) an assembly that is terminated with a plug (See Figure 2-1) at the end of a direct attach copper (DAC), an activecopper cable (ACC) or an active optical cable(AOC) intended to mate to a receptacle .or2) an optical transceiver typically inserted into a front panel socket that connects to the electrical interface of thesystem with a plug (See Figure 2-1) and the optical interface of the outside worldPlug: A term used to describe the connector that contains the penetrating contacts of the connector interface asshown in Figure 2-1. Plugs typically contain stationary contacts. Other common terms include male, pin connector,and card edge.Figure 2-1 Plug and Receptacle DefinitionReceptacle: A term used to describe the connector that contains the contacts that accept the plug contacts asshown in Figure 2-1. Receptacles typically contain spring contacts. Other common terms include female and socketconnector.SFF-8024Page 11Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
PUBLISHEDSFF-8024 Rev 4.63. General Description3.1Configuration Overview/DescriptionsThis specification provides reference tables for pluggable modules. These tables are updated with additional codesreflecting industry developments.Revisions 4.5 and earlier of this specification provided a tabular representation of pluggable I/O configurationsalong with the naming conventions that were used. This content is now provided in REF-TA-1011 “Cross Referenceto Select SFF Connectors and Modules”.To request the addition of a code send the following information to the contacts on page 1 of this document. Therequest should include the following:1) Relevant table2) Recommended information (Form factor name, Management interface name) to include in table3) Publically available reference specification e.g. data sheet or MSA specificationThe relation between module form factors and management interface specifications is shown in Table 3-1.Table 3-1 Module form factors and management interface specificationsForm factorSFP /SFP28QSFP QSFP QSFP28QSFP-DDOSFPSFF-8024Management interface MISPage 12Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
PUBLISHEDSFF-8024 Rev 4.64. Transceiver or Cable Management4.1OverviewSelf-identifying information is provided by modules or cables that use the 2-wire interface based managementinterfaces listed in Table 3-1.The information will only be current if the developers of new modules and the standards incorporating new speedsand technologies request updates to the tables.The tables below are not static. They have been removed from the subject specifications (listedbelow) to prevent multi-revisions with no new technical content.To request a new identifier (Table 4-1), connector type (Table 4-3), compliance code (Table 4-4)or compliance code (Tables 4-5 to 4-10) please send an email request to points of contact listedon title page.The tables below are referenced by the using specifications because either the content is common, or the contentsare regularly updated. Maintaining the tables in SFF-8024 avoids having to revise specifications for non-technicalchanges. The registers for each table are:Table 4-1 Identifier ValuesSFF-8472 A0h, Byte 0SFF-8636 and CMIS Page 00h Byte 0 and Page 00h Byte 128Table 4-2 Encoding ValuesSFF-8436, SFF-8636 and CMIS Page 00h Byte 139SFF-8472 A0h Byte 11Table 4-3 Connector TypesSFF-8436, SFF-8636 and CMIS Page 00h Byte 130SFF-8472 A0h Byte 2Table 4-4 Extended Specification Compliance CodesSFF-8636 and CMIS Page 00h Byte 192SFF-8472 A0h Byte 364.2Host Electrical and Media Interface CodesThe following tables provide codes for the various electrical interface and optical or media interfacespecifications that may apply to pluggable modules. Separate codes for the electrical and media interfacesenable modules to identify the specific combination of electrical and media specifications that the modulesupports. Codes for all publically available networking industry specifications should be included.Table 4-5 Host Electrical Interface CodesCMIS lower page, bytes 86, 90, 94, 98, 102, 106, 110, and 114Table 4-6 to Table 4-10 Module-Media Interface CodesCMIS lower page, bytes 87, 91, 95, 99, 103, 107, 111, and 115SFF-8024Page 13Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
PUBLISHED4.3SFF-8024 Rev 4.6Transceiver ReferencesThe Identifier Value assigned to the module is essential to interpreting the contents of the memory map.Table 4-1 Identifier 0DhDescription of ModuleUnknown or unspecifiedGBICModule/connector soldered to motherboard (using SFF-8472)SFP/SFP /SFP28300 pin XBIXENPAKXFPXFFXFP-EXPAKX2DWDM-SFP/SFP (not using SFF-8472)QSFP (INF-8438)QSFP or later with SFF-8636 or SFF-8436 management interface (SFF-8436, SFF-8635, SFF-8665,SFF-8685 et al.) *1CXP or laterShielded Mini Multilane HD 4XShielded Mini Multilane HD 8XQSFP28 or later with SFF-8636 management interface (SFF-8665 et al.) *2CXP2 (aka CXP28) or laterCDFP (Style 1/Style2)Shielded Mini Multilane HD 4X Fanout CableShielded Mini Multilane HD 8X Fanout CableCDFP (Style 3)microQSFPQSFP-DD Double Density 8X Pluggable Transceiver (INF-8628)OSFP 8X Pluggable TransceiverSFP-DD Double Density 2X Pluggable TransceiverDSFP Dual Small Form Factor Pluggable Transceiverx4 MiniLink/OcuLinkx8 MiniLinkQSFP or later with Common Management Interface Specification h1Dh1Eh1FH20h21h-7FhReserved80-FFhVendor Specific*1 0Dh is the preferred coding, it supports multi-speed implementations and provides backward compatibility*2 11h may prevent the use of new 25G-class modules on old hosts. Not recommended for new designsNOTE: The Identifier Values assigned by the CFP MSA overlap with the above, and this should not be an issuebecause CFP does not use I2C for the management protocol, it uses MDIO. Software which bases actions onIdentifier Values needs to recognize that synonyms exist and qualify the values by the management protocol.SFF-8024Page 14Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
PUBLISHED4.4SFF-8024 Rev 4.6Encoding ReferencesThe values established by SFF-8436 and SFF-8636 are similar but not identical to those assigned by SFF-8472.Maintaining a single reference will prevent further divergence.Table 4-2 Encoding ValuesDescription of Encoding pecified8B/10B4B/5BNRZManchester04h06hSONET Scrambled05h04h64B/66B06h05h256B/257B (transcoded FEC-enabled data)07hPAM408hReserved09h-FFhNote: For modules supporting multiple encoding types, the primary product application dictates the valuechosen e.g. for Fibre Channel 16G/8G/4G or Ethernet 10G/1G, the value of 64B/66B should be chosen. Incase of a conflict between modulation and coding, use the code for modulation. I.e. for 200GAUI-4 use codefor PAM4.SFF-8024Page 15Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
PUBLISHED4.5SFF-8024 Rev 4.6Connector ReferencesThe Connector Types are common between SFF-8436, SFF-8472 and SFF-8636. Maintaining a single reference willprevent divergence.Table 4-3 Connector 4.6Description of Media ConnectorUnknown or unspecifiedSC (Subscriber Connector)Fibre Channel Style 1 copper connectorFibre Channel Style 2 copper connectorBNC/TNC (Bayonet/Threaded Neill-Concelman)Fibre Channel coax headersFiber JackLC (Lucent Connector)MT-RJ (Mechanical Transfer - Registered Jack)MU (Multiple Optical)SGOptical PigtailMPO 1x12 (Multifiber Parallel Optic)MPO 2x16ReservedHSSDC II (High Speed Serial Data Connector)Copper pigtailRJ45 (Registered Jack)No separable connectorMXC 2x16CS optical connectorMini CS optical connectorMPO 2x12MPO 1x16ReservedVendor specificExtended Specification Compliance ReferencesThe Extended Specification Compliance Codes identify the electronic or optical interfaces which are not included inSFF-8472 Optical and Cable Variants Specification Compliance or SFF-8636 Specification Compliance Codes. A multi-SFF-8024Page 16Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
PUBLISHEDSFF-8024 Rev 4.6lane pluggable module may support more than a single instantiation of the specified compliance code.Table 4-4 Extended Specification Compliance CodesSFF-8024Page 17Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
h1Dh1Eh1Fh20h21h22h23h24h25h26h27h28h – 2Fh30h31h32h33h34h – 3FhSFF-8024SFF-8024 Rev 4.6Description of Module CapabilityUnspecified100G AOC (Active Optical Cable) or 25GAUI C2M AOC. Providing a worst BER of 5 10-5100GBASE-SR4 or 25GBASE-SR100GBASE-LR4 or 25GBASE-LR100GBASE-ER4 or 25GBASE-ER100GBASE-SR10100G CWDM4100G PSM4 Parallel SMF100G ACC (Active Copper Cable) or 25GAUI C2M ACC. Providing a worst BER of 5 10-5Obsolete (assigned before 100G CWDM4 MSA required FEC)Reserved100GBASE-CR4 or 25GBASE-CR CA-25G-L25GBASE-CR CA-25G-S25GBASE-CR CA-25G-NReserved40GBASE-ER44 x 10GBASE-SR40G PSM4 Parallel SMFG959.1 profile P1I1-2D1 (10709 MBd, 2km, 1310 nm SM)G959.1 profile P1S1-2D2 (10709 MBd, 40km, 1550 nm SM)G959.1 profile P1L1-2D2 (10709 MBd, 80km, 1550 nm SM)10GBASE-T with SFI electrical interface100G CLR4100G AOC or 25GAUI C2M AOC. Providing a worst BER of 10-12 or below100G ACC or 25GAUI C2M ACC. Providing a worst BER of 10-12 or below100GE-DWDM2 (DWDM transceiver using 2 wavelengths on a 1550 nm DWDM grid with a reachup to 80 km)100G 1550nm WDM (4 wavelengths)10GBASE-T Short Reach (30 meters)5GBASE-T2.5GBASE-T40G SWDM4100G SWDM4100G PAM4 BiDi4WDM-10 MSA (10km version of 100G CWDM4 with same RS(528,514) FEC in host system)4WDM-20 MSA (20km version of 100GBASE-LR4 with RS(528,514) FEC in host system)4WDM-40 MSA (40km reach with APD receiver and RS(528,514) FEC in host system)100GBASE-DR, with CAUI-4 without FEC100G-FR, with CAUI-4 without FEC100G-LR, with CAUI-4 without FECReservedActive Copper Cable with 50GAUI, 100GAUI-2 or 200GAUI-4 C2M. Providing a worst BER of 10-6or belowActive Optical Cable with 50GAUI, 100GAUI-2 or 200GAUI-4 C2M. Providing a worst BER of 10-6or belowActive Copper Cable with 50GAUI, 100GAUI-2 or 200GAUI-4 C2M. Providing a worst BER of 2.6x104 for ACC, 10-5 for AUI, or belowActive Optical Cable with 50GAUI, 100GAUI-2 or 200GAUI-4 C2M. Providing a worst BER of 2.6x104 for AOC, 10-5 for AUI, or belowReservedPage 18Copyright 2018 SNIA. All rights reserved.
PUBLISHEDCode40h41h42h43h44h45h46h47h – 4Fh50h51h52h53h54h55h56h - FFh4.7SFF-8024 Rev 4.6Description of Module Capability50GBASE-CR, 100GBASE-CR2, or 200GBASE-CR450GBASE-SR, 100GBASE-SR2, or 200GBASE-SR450GBASE-FR or 200GBASE-DR4200GBASE-FR4200G 1550 nm PSM450GBASE-LR200GBASE-LR4Reserved64GFC EA64GFC SW64GFC LW128GFC EA128GFC SW128GFC LWReservedHost Electrical and Media Interface CodesThe following tables provide codes for the various electrical interface and optical or media interface specif
of this specification. ABSTRACT: This specification provides codes for module identifiers, encoding values, connector types, extended compliance codes, host electrical interfaces and module media interfaces. This specification is the reference source for identifiers assigned to interpret the memory maps of self-identifying modules.