Transcription
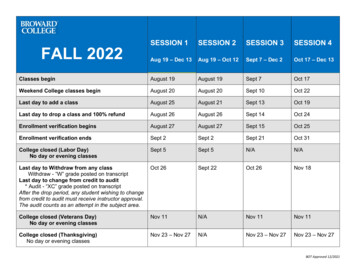
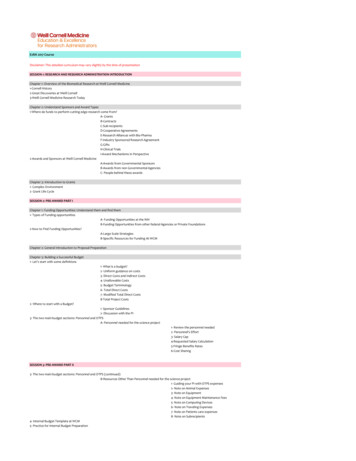
E2RA 2017 CourseDisclaimer: This detailed curriculum may vary slightly by the time of presentationSESSION 1: RESEARCH AND RESEARCH ADMINISTRATION INTRODUCTIONChapter 1: Overview of the Biomedical Research at Weill Cornell Medicine1-Cornell History2-Great Discoveries at Weill Cornell3-Weill Cornell Medicine Research TodayChapter 2: Understand Sponsors and Award Types1-Where do funds to perform cutting edge research come from?A- GrantsB-ContractsC-Sub-recipientsD-Cooperative AgreementsE-Research Alliances with Bio-PharmaF-Industry Sponsored Research AgreementG-GiftsH-Clinical TrialsI-Award Mechanisms in Perspective2-Awards and Sponsors at Weill Cornell MedicineA-Awards from Governmental SponsorsB-Awards from non Governmental AgenciesC- People behind these awardsChapter 3: Introduction to Grants1- Complex Environment2- Grant Life CycleSESSION 2: PRE-AWARD PART IChapter 1: Funding Opportunities: Understand them and find them1- Types of Funding opportunitiesA- Funding Opportunities at the NIHB-Funding Opportunities from other federal Agencies or Private Foundations2-How to Find Funding Opportunities?A-Large Scale StrategiesB-Specific Resources for Funding At WCMChapter 2: General Introduction to Proposal PreparationChapter 3: Building a Successful Budget1- Let's start with some definitions1- What is a budget?2- Uniform guidance on costs3- Direct Costs and Indirect Costs4- Unallowable Costs5- Budget Terminology6- Total Direct Costs7- Modified Total Direct Costs8-Total Project Costs2- Where to start with a Budget?1- Sponsor Guidelines2- Discussion with the PI3- The two main budget sections: Personnel and OTPSA- Personnel needed for the science project1- Review the personnel needed2- Personnel's Effort3- Salary Cap4-Requested Salary Calculation5-Fringe Benefits Rates6-Cost SharingSESSION 3: PRE-AWARD PART II3- The two main budget sections: Personnel and OTPS (continued)B-Resources Other Than Personnel needed for the science project1- Guiding your PI with OTPS expenses2- Note on Animal Expenses3- Note on Equipment4- Note on Equipment Maintenance Fees5- Note on Computing Devices6- Note on Traveling Expenses7- Note on Patients care expenses8- Note on Subrecipients4- Internal Budget Template at WCM5- Practice for Internal Budget Preparation
6- Budget Justification7- NIH budgets classification8- What is a healthy budget?9- Common errors in a budget10- Budget bottom lineChapter 4: Other Important Considerations for proposal preparation1-Other Important information and documents in the proposal1- Standard Intitutional Information2- Frequent other administrative documents3- When Multiple PD/PI on the application4- When there is a sub-recipient5- When there is a consultant2- Compliance Approvals1- When the research involves vertebrate animals2-When the research involves human research3- Special proposal considerations4- More tips on application submissions3- How about eRA commons for NIH applications?SESSION 4: PRE-AWARD PART IIIChapter 5: Proposal Preparation, Submission and Review1- Proposal Preparation in WRG2- OSRA Review and Submission2- Sponsor Review1- Review Process at the NIHChapter 6: Just -in-Time ProcessA- Just in -Time at the NIH1- Current Other Support2- Revised Budget3- IACUC approval4- IRB approval5- CITI certificates6- Genomic Data Sharing Plan7- Other Considerations8- Requests similar to NIH Just-in-TimeChapter 7: Notice of Award and Award AcceptanceSESSION 5: HUMAN SUBJECTS RESEARCHChapter 1: Introduction to translational research and clinical trials1- What is biomedical reseearch?2- What is translational research?3- Translational research aims to accelerate Discoveries4- What are clinical trials?Chapter 2: IRB and Human Subjects Research1- History of the ethical regulations of research on human subjects2- IRB and human subjects protectionA- What is the IRB?B- How the IRB protects Human Subjects1- Criteria for IRB approval2- How the IRB protects human subjects3- Three types if IRB reviews at WCMa- IRB Exempt categoryb- IRB expedited categoryc- Full Board4- How to get a human protocol IRB approved?5- IRB boards and members6- Informed Consent7- IRB info and contacts at WCMChapter 3: Introduction to the CTSC1- The CTSC missions2- How does the CTSC support investigators?A- CTSC Services and ResourcesB- Clinical and Translational Education Programs at the CTSCC- Seed Funding Mechanisms at the CTSCChapter 4: Introduction to the JCTO1- The JCTO missions2- How does the JCTO support investigators?A- ContractsB- Finance1- Basics on Clinical Trials BudgetingC- Study Activation
SESSION 6: RESEARCH COMPLIANCE & INTEGRITYChapter 1: Compliance for Research on AnimalsChapter 2: Compliance for Research on Human Embryonic Stem CellsChapter 3: Compliance for Environmental Health Safety, Biosafety and Radiation SafetyChapter 4: Conflicts for Financial Interests and Commitments, Study Specific Report and Travel DisclosureChapter 5: Research Compliance & Integrity: Responsible Conduct of Research Course (RCR)Chapter 7: Internal Compliance: Research Compliance Training (RCT)SESSION 7 : CASE STUDIES AND EVALUATION ON PRE-AWARD & COMPLIANCeSESSION 8: Correction of Evaluation and New Case studiesSESSION 9: POST-AWARD PART IChapter 1: Introduction to Post Award1- Teams in Post-Award2- Online Systems in Post Award3- Prinicipal Activities in Post AwardChapter 2: Budget Set Up for WBS accounts1- Detailed Budget Set Up2- Advance Account CreationChapter 3: Basics on FundsChapter 4: Change of Funding1- The Basics of COF1- COF definition2- COF example3- When a COF is necessary4- Important Notes about COF5- When COF cannot be used6- Who performs COF?7- How to get access to do COF?8- Training for COF9- Approval of COF10- Late COF11- Understand the pay periods12- Funded amount vs Cash value2- Special Considerations with COFA- Cap at 98% effort on Grants ( in general)B- NIH Salary CapC- Important Considerations between COF and SAPD- Note on Stipends for FellowshipsSESSION 10: POST-AWARD PART IIChapter 1: Effort & ETS1- Introduction to effort1-Total Effort2- Effort in a Life's Grant3- Violation of Federal Regulations4- and Reputation5- Effort Compliance Policy at WCM2- Effort Tracking System ETS1- ETS overview2- Who needs to be ETS tracked?3- ETS at WCM4-Effort Cap at WCM5-ETS important Characteristcis6-When to complete ETS?7- How does an ETS worksheet look like?8-What does contribute to a PI's effort in ETS?9- ETS monitoring and Audits10- 2% effort compliance and Budget subsidy3- Change in EffortA- Change in Effort at the NIHB- Effort Reduction Letter4- Case Study on Effort & multiple Awards1- Effort Over Commitment2- How to reallocate effort % committed to grants?
3- Effort Reduction and Budget Reallocation4- How to follow up with effort % reallocation ?5- Unfunded Research Fund for SalaryChapter 2: Activity Distribution Report1-ADR2- Who must complete an Activity Distribution Report3- How does an ADR look like?4- Tips to complete an ADR5- ADR signature6- ETS vs ADRSESSION 11: POST-AWARD Part IIIChapter 1: Sub-Recipients and Consultants1- Sub-Recipients1- Sub-recipient Agreement2- MOU with Ithaca3- Focus on Sub-Award4- About outgoing subawards5- Sub-awards SOP from OSRA2- Consultants1- Consultants Agreements2- Contractor Questionnaire and Checklist3- W-9 Form for new consultants4- How to pay your consultants?Chapter 2 : Purchasing1- Purchasing with vendors1- Purchasing Introduction2- SciQuest3- Methods of procurement4- Purchasing in Sci Quest5- Line of Credit (LOC)6- When PO placed for non-SciQuest vendors7- New Vendor Request2- Corporate Cards1- Coroporate Cards2- Policies on Corporate Cards3- Corporate Cards Holders4-Commonly Allowable Purchases5- Commonly Prohibited Purchases6- How to obtain a corporate card?7- How to access the corporate card training course?8- Support on Corporate cards3- Competitive Bids and Single Source1- Bids and Single source2- Single /Sole source3- Single /Sole source justification form4- Fund Reservation5- Animal Expenses1- Animal Expenses2- Animal Protocol and Accounts3- Animal Billing4- Surcharge when paying for animal bills5- Updates/ Modifications for animal charges6- Sub-recipients & Finance1- How to set up a financial collaboration with your subs?2- Sub-awards invoicing WCMChapter 3: Accounts Payable1- Vendor Invoices on PO2- Payment Requisitions3- Travel & Business Expenses Reimbursement4- Petty CashSESSION 12: POST-AWARD Part IVChapter 1: Financial Modifications to an Award1- Cost Transfers1- Definition of Cost transfer2- Let's talk about Cost Transfers (video)3- Cost transfer process at WCM4- Appropriate circumstances for Cost transfers5- Inappropriate Justifications for Costs transfers6- Insufficient Justifications for Cost Transfers7- Cost Transfers Justifications Quiz
8- Federal Expectations for cost transfers9- Late Cost transfers 90 days of a grant2- Rebudgeting1- Rebudgeting at the NIH2- Rebudgeting activity3- Carry-Over1- Carry over definition2- Automatic CO3- Non automatic COA- Carry over request LetterB- Unobligated balance justificationsC- Carry over Approval4- CO consequences4- No Cost Extension1- NCE introduction2- NCE timing considerations3- NCE Process at the NIH with new online pre-approvalChapter 2: If something changes in the project1- Expanded Authorities at the NIH1- Prior Approval at the NIH2- Grantees Authorities at the NIH3- Prior Written ApprovalA-Change in key personnelB- Effort Reduction on GrantsC- Change in ScopeD- Additional FundsChapter 3: Monitoring your PI's account1- Grant Statement Overview (BI Report in SAP)2- Research Finance DashboardChapter 4: Annual and Final Post-Award Responsibilities1- Progress Reports1- Progress Reports2- Private Foundations3- Annual RPPR at the NIHA- Who does the RPPR?B- NIH SNAP and NIH non -SNAP4- Final RPPR5- PHS-2590 at the NIH6- Issues with the RPPR7- And what if there is no formal Progress report due?2- Responsibilities with your sub-awards1- Sub-Awards PO at the end of a budget period2- How to liquidate a PO with your sub?3- Subrecipients Monitoring3- Federal Financial Report (FFR)1- Federal Financial Reporting2- FFR based on SAP3- When is the FFR due?4- Note to understand cash collection5- Importance of Federal Financial Reporting4- Closeout of an account1- Definition of a closeout2- Closeout Process big picture3- What finance looks at, at closeout?4- Closeout and Final reports5- Closeout and Final reports discrepancies6- Be Proactive to prepare your closeout!7- To remember for Closeout with the NIHSESSION 13: CASE STUDIES AND EVALUATION ON POST-AWARDSESSION 14: Correction of the Post Award EvaluationLast Updated 04/06/17For any questions, email Helene Brazier-Mitouart, Education Manager at ETRA, heb2020@med.cornell.edu
3- Federal Financial Report (FFR) 1- Federal Financial Reporting 2- FFR based on SAP 3- When is the FFR due? 4- Note to understand cash collection 5- Importance of Federal Financial Reporting 4- Closeout of an account 1- Definition of a closeout 2- Closeout Process big picture 3- What finance looks at, at closeout? 4- Closeout and Final reports