Transcription
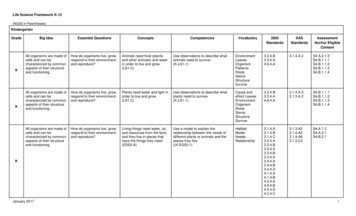
Life Science Framework K-12(NGSS in Parentheses)KindergartenGradeKKBig IdeaEssential QuestionsConceptsAll organisms are made ofcells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand functioning.How do organisms live, grow,respond to their environment,and reproduce?Animals need food (plantsand other animals) and waterin order to live and grow.(LS1.C)Use observations to describe whatanimals need to .4.A.2S4 A.2.1.3S4.B.1.1.1S4.B.1.1.2S4.B.1.1.3S4.B.1.1.4All organisms are made ofcells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand functioning.How do organisms live, grow,respond to their environment,and reproduce?Plants need water and light inorder to live and grow.(LS1.C)Use observations to describe whatplants need to survive.(K-LS1-1)Cause andeffect S4.B.1.1.2S4.B.1.1.3S4.B.1.1.4All organisms are made ofcells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand functioning.How do organisms live, grow,respond to their environment,and reproduce?Living things need water, air,and resources from the land,and they live in places thathave the things they need.(ESS3.A)Use a model to explain therelationship between the needs ofdifferent plants or animals and theplaces they .1.3S4.A.2.1S4.B.2.1KJanuary sAssessmentAnchor EligibleContent1
Life Science Framework K-124.5.3.A4.5.4.DHow do organisms live, grow,respond to their environment,and reproduce?Animals have identifiablestructures and behaviors.Observe and describe structures oforganisms and functions of 3.A.53.1.k.A.53.1.1.A.5S4.B.1.1.2KAll organisms are made ofcells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand functioning.How are the characteristics ofone generation passed to thenext? How can individuals ofthe same species and evensiblings have ty refers to specificmechanisms by whichcharacteristics or traitsare passed from onegeneration to the next viagenes, and explains whyoffspring resemble, butare not identical to, theirparents.How can there be so manysimilarities among organismsyet so many different kinds ofplants, animals, andmicroorganisms?N/AN/AN/AN/AN/AN/AKBiological evolutionexplains both the unityand diversity of speciesand provides a unifyingprinciple for the historyand diversity of life onEarth.First GradeGrade11Big IdeaEssential QuestionsAll organisms are made ofcells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand functioning.How do organisms live, grow,respond to their environment,and reproduce?Organisms have externalstructures that serve variousfunctions in growth, survival,behavior, and reproduction.(LS1.A)Observe and categorize living andnonliving things by 4S4.B.1. 1.1S4.B.1.1.2All organisms are made ofHow do organisms live, grow,Organisms have externalMake observations and describe theGrow3.3.4.A3.1.2.CS4.A.3.1.1January StandardsAssessmentAnchor EligibleContent2
Life Science Framework K-1211111cells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand functioning.respond to their environment,and reproduce?structures that help themsurvive, grow and meet theirneeds.(LS1.A)different parts of organisms that helpthem survive, grow, and meet theirneeds.(1-LS1-2)MovementObservationsParts (roots,leaves, flowers,stems, A3.2.4.B3.2.4.C4.7.4.A4.7.4.BAll organisms are made ofcells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand functioning.How do organisms live, grow,respond to their environment,and reproduce?Organisms have externalstructures that help themsurvive, grow and meet theirneeds.(LS1.A)Design a model that replicates thefunction of an organism’s .B.1.1.3S4.B.1.1.4S4.A.2.1.1All organisms are made ofcells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand functioning.How do organisms live, grow,respond to their environment,and reproduce?Parents and offspring engagein behaviors that help theoffspring to survive.(LS1.B)Observe and determine patterns inbehavior of parents and offspringthat help offspring s have externalstructures that help themsurvive, grow and meettheir needs.Organisms have externalstructures that help themsurvive, grow and meet theirneeds.Organisms have externalstructures that help themsurvive, grow and meet theirneeds.(LS1.A)Classify plants and animalsaccording to physical characteristicsthey AS4.B.1.1S4.B.1.1.1S4.B.1.1.3Organisms have externalstructures that help themsurvive, grow and meettheir needs.Organisms have externalstructures that help themsurvive, grow and meet theirneeds.Every human made product isdesigned by applyingknowledge of the naturalworld and is built usingmaterials from nature.(LS1.A)Use materials to design a solution toa human problem by mimicking howplant or animals use their externalparts to help them survive, grow andmeet their 6.4.AS.4.A.1.1.2S4.B.1.1.3Organisms grow,How and why do organismsN/AN/AN/AN/AN/AN/AJanuary 2017S4.B.1.1.1S4.B.1.1.33
Life Science Framework K-12reproduce, andperpetuate their speciesby obtaining necessaryresources throughinterdependentrelationships with otherorganisms and thephysical environment.interact with their environmentand what are the effects ofthese interactions?How are the characteristics ofone generation passed to thenext? How can individuals ofthe same species and evensiblings have differentcharacteristics?Young animals are very muchbut not exactly like theirparents. Plants also are verymuch, but not exactly, liketheir parents.(LS3.A)Make observations and to constructan evidence-based account thatyoung plants and animals are alikebut not exactly like their .B.2.2.11Heredity refers to specificmechanisms by whichcharacteristics or traitsare passed from onegeneration to the next viagenes, and explains whyoffspring resemble, butare not identical to, theirparents.How are the characteristics ofone generation passed to thenext? How can individuals ofthe same species and evensiblings have differentcharacteristics?Adult plants and animals haveyoung. In many kinds ofanimals, parents and theoffspring engage in behaviorsthat help the offspring tosurvive.(LS1.B)Note patterns in characteristics orbehaviors that appear in adult andoffspring (e.g. hair color, eye y refers to specificmechanisms by whichcharacteristics or traitsare passed from onegeneration to the next viagenes, and explains whyoffspring resemble, butare not identical to, theirparents.How are the characteristics ofone generation passed to thenext? How can individuals ofthe same species and evensiblings have differentcharacteristics?Offspring resemble theirparents, but can also vary inmany ways.(LS3.A)Conduct an investigation (e.g. plantseeds, eggs) and cite evidence ofchange from young to Heredity refers to specificmechanisms by whichcharacteristics or traitsare passed from onegeneration to the next viagenes, and explains whyoffspring resemble, butare not identical to, theirparents.Heredity refers to specificmechanisms by whichcharacteristics or traitsHow are the characteristics ofone generation passed to thenext? How can individuals ofPlants and animals have a lifecycle.Observe and compare the stages oflife cycles of organisms (plants &animals).PlantsAnimalsLife B.1.1.5January 20174
Life Science Framework K-121are passed from onegeneration to the next viagenes, and explains whyoffspring resemble, butare not identical to, theirparents.the same species and evensiblings have differentcharacteristics?Biological evolutionexplains both the unityand diversity of speciesand provides a unifyingprinciple for the historyand diversity of life onEarth.How can there be so manysimilarities among organismsyet so many different kinds ofplants, animals, andmicroorganisms?N/AN/AN/AN/AN/AN/ASecond GradeGradeBig IdeaEssential QuestionsHow do organisms live, grow,respond to their environment,and reproduce?N/AN/AN/AN/AN/AN/A2All organisms are made ofcells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand functioning.How and why do organismsinteract with their environmentand what are the effects ofthese interactions?Animals can move around,but plants cannot, and theyoften depend on animals forpollination or seed dispersal.(LS2.A)Develop a model to demonstratedifferent modes of seed dispersal.Plan and investigate effectiveness ofdifferent types of seed dispersal.(2-LS2-2)PollinationSeed 4.2.4.CS4.B.1.1.1S4.B.1.1.5S4.B.2.1.12Organisms grow,reproduce, andperpetuate their speciesby obtaining necessaryresources throughinterdependentrelationships with otherorganisms and thephysical environment.How and why do organismsinteract with their environmentand what are the effects ofthese interactions?Different plants survive betterin different settings becausethey have varied needs forwater, minerals, and sunlight.(LS2.A)Plan and carry out investigations totest whether plants from differentsettings have different needs forwater, sunlight, and type of 1.1S4.B.2.1.22Organisms grow,reproduce, andperpetuate their speciesby obtaining necessaryresources throughinterdependentJanuary StandardsAssessmentAnchor EligibleContent5
Life Science Framework K-12relationships with otherorganisms and thephysical environment.3.1.5.C.1How and why do organismsinteract with their environmentand what are the effects ofthese interactions?Organisms obtain thematerials they need to growand survive from theirenvironment.(LS2.A)Obtain, evaluate, and communicateinformation that in any particularenvironment, some kinds oforganisms survive well and some 22Organisms grow,reproduce, andperpetuate their speciesby obtaining necessaryresources throughinterdependentrelationships with otherorganisms and thephysical environment.How and why do organismsinteract with their environmentand what are the effects ofthese interactions?Plants depend on water andlight to grow.LS2.A)Plan and conduct an investigation todetermine if plants need sunlight andwater to .1S4.B.2.1.1S4.B.2.1.22Organisms grow,reproduce, andperpetuate their speciesby obtaining necessaryresources throughinterdependentrelationships with otherorganisms and thephysical environment.How are the characteristics ofone generation passed to thenext? How can individuals ofthe same species and evensiblings have ty refers to specificmechanisms by whichcharacteristics or traitsare passed from onegeneration to the next viagenes, and explains whyoffspring resemble, butare not identical to, theirparents.How can there be so manysimilarities among organismsyet so many different kinds ofplants, animals, andmicroorganisms?Living things can survive onlywhere their needs are met.(LS4.D)Construct an explanation about whyliving things can only survive wheretheir needs are 4.B.2.1.22Biological evolutionexplains both the unityand diversity of speciesand provides a unifyingprinciple for the historyand diversity of life onEarth.January 20176
Life Science Framework K-122Biological evolutionexplains both the unityand diversity of speciesand provides a unifyingprinciple for the historyand diversity of life onEarth.How can there be so manysimilarities among organismsyet so many different kinds ofplants, animals, andmicroorganisms?There are many differentkinds of living things in anyarea, and they exist indifferent places on land and inwater.(LS4.D)Observe and compare the differentkinds of living things that are found indifferent ing CS4.B.2.1.1S4.B.2.1.2Big IdeaEssential QuestionsConceptsCompetenciesAll organisms are made ofcells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand functioning.How do organisms live, grow,respond to their environment,and reproduce?Reproduction is essential tothe continued existence ofevery kind of organisms.(LS1.B)Use models to explain howreproduction is essential for everykind of organism.(3-LS1-1)Life .2S4.B.1.1.5All organisms are made ofcells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand functioning.How do organisms live, grow,respond to their environment,and reproduce?Plants and animals haveunique and diverse life cyclesthat include birth, growth,reproduction, and death.(LS1.B)Develop a model to describe thecommonalities of life cycles ofdifferent organisms.(3-LS2-1)Life .2.S4.B.1.1.5Organisms grow,reproduce, andperpetuate their speciesby obtaining necessaryresources throughinterdependentrelationships with otherorganisms and thephysical environment.How and why do organismsinteract with their environmentand what are the effects ofthese interactions?Animals depend on eachother and their surroundingsto get what they need,including food, water, shelter,and a stable temperature.Groups serve differentfunctions and vary in size.(LS2.D)Based on observations, construct anargument that some animals formgroups that help members survive.(3-LS2-1)Basic S4.B.3.1.1Third GradeGrade333January nchor EligibleContent7
Life Science Framework K-124.5.4.DOrganisms grow,reproduce, andperpetuate their speciesby obtaining necessaryresources throughinterdependentrelationships with otherorganisms and thephysical environment.How and why do organismsinteract with their environmentand what are the effects ofthese interactions?When the environmentchanges in physicalcharacteristics, temperature,availability of resources, someorganisms survive, othersmove, yet others may die.(LS4.C)Construct an argument with evidencethat within a specific habitat, someorganisms survive well, some not sowell, and others cannot survive at all.(3-LS4-3)3Heredity refers to specificmechanisms by whichcharacteristics or traitsare passed from onegeneration to the next viagenes, and explains whyoffspring resemble, butare not identical to, theirparents.How are the characteristics ofone generation passed to thenext? How can individuals ofthe same species and evensiblings have differentcharacteristics?Different organisms vary inhow they look and functionbecause they have differentinherited information.(LS3.B)Analyze and interpret data to provideevidence that plants and animalshave traits inherited from parentsand that variation of these traitsexists in a group of similarorganisms.(3-LS3-1; 3-LS3-2)How are the characteristics ofone generation passed to thenext? How can individuals ofthe same species and evensiblings have differentcharacteristics?The environment also affectsthe traits that an organismdevelops.(LS3.B)3Heredity refers to specificmechanisms by whichcharacteristics or traitsare passed from onegeneration to the next viagenes, and explains whyoffspring resemble, butare not identical to, theirparents.3Heredity refers to specificmechanisms by whichHow are the characteristics ofone generation passed to theMany characteristics involveboth inherited traits and3January 1.3S4.B.2.2.Use evidence to support anexplanation that the environment caninfluence C3.1.3.B1S4.A.2.1.3S4.B.2.2.Use evidence to comparecharacteristics inherited 4.BS4.B.2.1.1S4.B.2.2.18
Life Science Framework K-12characteristics or traitsare passed from onegeneration to the next viagenes, and explains whyoffspring resemble, butare not identical to, theirparents.next? How can individuals ofthe same species and evensiblings have differentcharacteristics?environmental factors.(LS3.B)parents, characteristics caused bythe environment, and those resultingfrom both.(3-LS3-1; riationHow can there be so manysimilarities among organismsyet so many different kinds ofplants, animals, andmicroorganisms?Some plants and animals thatonce lived on earth are nolonger found anywhere.(LS4.A)Analyze and interpret data fromfossils to provide evidence of theorganisms and environments inwhich they lived long ago.(3-LS4-1)ExtinctFossils4.7.4.C3Biological evolutionexplains both the unityand diversity of speciesand provides a unifyingprinciple for the historyand diversity of life onEarth.How can there be so manysimilarities among organismsyet so many different kinds ofplants, animals, andmicroorganisms?Fossils provide evidenceabout types of organisms thatlived long ago as well asabout the nature of theenvironment.(LS4.A)Analyze and interpret data fromfossils to provide evidence of theorganisms and environments inwhich they lived long S.4.A.2.1.43Biological evolutionexplains both the unityand diversity of speciesand provides a unifyingprinciple for the historyand diversity of life onEarth.Biological evolutionexplains both the unityand diversity of speciesand provides a unifyingprinciple for the historyand diversity of life onEarth.How can there be so manysimilarities among organismsyet so many different kinds ofplants, animals, andmicroorganisms?Changes in an organism'shabitat can be beneficial orharmful to the organism.(LS4.D)Use evidence to argue that when theenvironment changes in ways thataffect a place’s physicalcharacteristics, organisms maysurvive, move to new locations, .A.3.3.23January 20173.1.4.C4.5.4.D4.2.4.CS.4.A.2.1.49
Life Science Framework K-12Biological evolutionexplains both the unityand diversity of speciesand provides a unifyingprinciple for the historyand diversity of life onEarth.How can there be so manysimilarities among organismsyet so many different kinds ofplants, animals, andmicroorganisms?Populations live in a variety ofhabitats and changes in thosehabitats impacts theorganisms living there.(LS4.D)Using evidence, make a claim aboutmerits of solutions to problemscaused when the environmentchanges and types of animals andplants that live there may .3.4.D4.7.4.A4.7.4.BBiological evolutionexplains both the unityand diversity of speciesand provides a unifyingprinciple for the historyand diversity of life onEarth.How can there be so manysimilarities among organismsyet so many different kinds ofplants, animals, andmicroorganisms?Sometimes differences incharacteristics betweenindividuals of the samespecies provide advantagesin surviving, finding mates,and reproducing.(LS4.B)Use evidence to construct anexplanation for how the variations incharacteristics among individuals ofthe same species may provideadvantages in surviving, findingmates, and reproducing.(3-LS4-S)Biological evolutionexplains both the unityand diversity of speciesand provides a unifyingprinciple for the historyand diversity of life onEarth.How can there be so manysimilarities among organismsyet so many different kinds ofplants, animals, andmicroorganisms?Fossils provide evidenceabout the types of organisms(both visible and microscopic)that lived long ago and alsoabout the nature of theirenvironments.(LS4.A)Use evidence to construct anexplanation that some rocks andminerals record the remains l evolutionexplains both the unityand diversity of speciesand provides a unifyingprinciple for the historyand diversity of life onEarth.How can there be so manysimilarities among organismsyet so many different kinds ofplants, animals, andmicroorganisms?Fossils provide evidenceabout the types of organisms(both visible and microscopic)that lived long ago and alsoabout the nature of theirenvironments.(LS4.A)Obtain and communicate informationthat some organisms that once livedon earth are no longer foundanywhere, although other organismsnow may resemble .B.2.1.23333January .A.3.2.1S4.A.3.3.2S4.A.1.3.410
Life Science Framework K-12How can there be so manysimilarities among organismsyet so many different kinds ofplants, animals, andmicroorganisms?Fossils can be compared withone another and to livingorganisms according to theirsimilarities and differences.(LS4.A)Use evidence from fossil records toconstruct an explanation of therelationship between types oforganisms living today and types oforganisms that lived in the past.(3-LS4-4)ExplanationFossil .B.2.1.23Biological evolutionexplains both the unityand diversity of speciesand provides a unifyingprinciple for the historyand diversity of life onEarth.How can there be so manysimilarities among organismsyet so many different kinds ofplants, animals, andmicroorganisms?Fossils can be compared withone another and to livingorganisms according to theirsimilarities and differences.(LS4.B)Use evidence to constructexplanations for how environmentstoday may be different from pastenvironments in which fossilizedorganisms once .2.4.CS4.B.2.1.23Biological evolutionexplains both the unityand diversity of speciesand provides a unifyingprinciple for the historyand diversity of life onEarth.How can there be so manysimilarities among organismsyet so many different kinds ofplants, animals, andmicroorganisms?Sometimes the differences incharacteristics betweenindividuals of the samespecies provide advantagesin surviving, finding mates,and reproducing.(LS4.B)Use evidence to explain how somecharacteristics that vary amongindividuals of the same kind oforganism can provide advantages tosurvive, find mates, and 3.1.4.A3.1.4.C4.5.4.D4.2.4.CS4.B.2.1.23Biological evolutionexplains both the unityand diversity of speciesand provides a unifyingprinciple for the historyand diversity of life onEarth.Biological evolutionexplains both the unityand diversity of speciesand provides a unifyingprinciple for the historyand diversity of life onEarth.How can there be so manysimilarities among organismsyet so many different kinds ofplants, animals, andmicroorganisms?Humans, like all otherorganisms, obtain living andnonliving resources from theirenvironments.Use evidence to demonstrate howhumans, like all other organisms,obtain living and non-living resourcesfrom their 4S4.B.3.3.5S4.A.1.1.2S4.A.1.3.5S4.A.3.1.43January 201711
Life Science Framework K-124.5.4.A4.5.4.CFourth GradeGrade4444Big IdeaEssential QuestionsAll organisms are made ofcells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand functioning.How do organisms live, grow,respond to their environment,and reproduce?Plants and animals haveinternal and externalstructures that serve variousfunctions to survive.(LS1.A)Construct an argument that plantsand animals have internal andexternal structures that function tosupport survival, growth, behavior,and reproduction.(4-LS1-1)BehaviorsCause alSystemSystem Models3.3.4 .1S4.B.1.1.5All organisms are made ofcells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand functioning.How do organisms live, grow,respond to their environment,and reproduce?N/AN/AN/AN/AN/AN/AOrganisms grow,reproduce, andperpetuate their speciesby obtaining necessaryresources throughinterdependentrelationships with otherorganisms and thephysical environment.How and why do organismsinteract with their environmentand what are the effects ofthese interactions?N/AN/AN/AN/AN/AN/ABiological evolutionexplains both the unityand diversity of speciesand provides a unifyingprinciple for the historyand diversity of life onHow can there be so manysimilarities among organismsyet so many different kinds ofplants, animals, andmicroorganisms?N/AN/AN/AN/AN/AN/AJanuary StandardsAssessmentAnchor EligibleContent12
Life Science Framework K-12Earth.Fifth GradeGradeBig IdeaEssential QuestionsHow do organisms live, grow,respond to their environment,and reproduce?Food provides animals withmaterials needed for bodyrepair and growth.(PS3.D)Use a model to describe that energyin animal’s food was once energyfrom the sun.(5-PS3-1)Food chainFood web3.3.7.A3.2.7.B3.1.7.A3.1.7.C3.1.7.A85All organisms are made ofcells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand .3How do organisms live, grow,respond to their environment,and reproduce?Food provides animals withmaterials needed for energyand to maintain body warmthand for motion.(LS1.C)Use a model to describe that energyin animal’s food was once energyfrom the sun.(5-PS3-1)Food chainFood web3.3.7.A3.2.7.B3.1.7.A3.1.7.C3.1.7.A85All organisms are made ofcells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand .3How do organisms live, grow,respond to their environment,and reproduce?Plants acquire their materialfor growth primarily from airand water.(LS1.C)Using evidence, present anargument that plants get thematerials they need for growthprimarily from air and 7.B3.1.7.A3.1.7.C3.1.7.A85All organisms are made ofcells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand .3All organisms are made ofcells and can becharacterized by commonaspects of their structureand functioning.How do organisms live, grow,respond to their environment,and reproduce?Animals and plants alike takein gases and water andrelease waste matter into theenvironment; animals musttake in food, and plants needlight and minerals.(LS2.B)Construct and communicate modelsof food webs that demonstrate thetransfer of matter and energy amongorganisms within an ecosystem.(5-LS2-1)EcosystemFood S8.B.3.1.3S8.A.3.2.1S8.A.3.2.3Organisms grow,reproduce, andperpetuate their speciesby obtaining necessaryresources throughinterdependentrelationships with otherorganisms and theHow and why do organismsinteract with their environmentand what are the effects ofthese interactions?Organisms can survive only inenvironments in which theirparticular needs are met.(LS2.A)Ask researchable questions aboutthe ways organisms obtain matterand energy across multiple andvaried ecosystems.(5-LS2-1)ResearchableSpeciesWeb of life3.3.7.A3.2.7.B3.1.6.A2S8.B.3.1.155January StandardsAssessmentAnchor EligibleContent13
Life Science Framework K-12physical environment.How and why do organismsinteract with their environmentand what are the effects ofthese interactions?A healthy ecosystem is one inwhich multiple species ofdifferent types are each ableto meet their needs in arelatively stable web of life.(LS2.A)Con
Life Science Framework K-12 January 2017 2 4.5.3.A 4.5.4.D K All organisms are made of cells and can be characterized by common aspects of their structure and functioning. How do organisms live, grow, respond to their environment, and reproduce? Animals have identifiable str











