Transcription
11Venofer must only be administeredintravenously, either by slow injectionor infusion.Dosing & AdministrationGuide
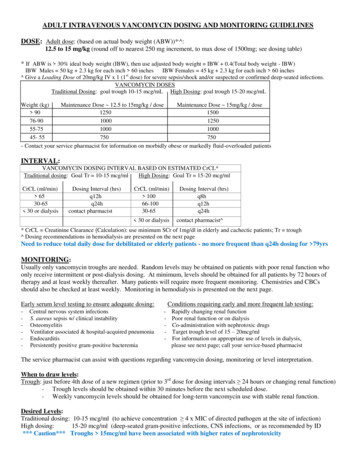
Non-dialysis-dependent CKDadult IV iron dosing algorithm*Evaluate for AnemiaMales with Hb 13 g/dLFemales with Hb 12 g/dLYESCKD andIs Patient Anemic?NOPerform Initial Assessment of Anemia CBC (Hb, RBC indices, WBC withdifferential, platelet count) Absolute reticulocyte count Serum ferritin level – to assess iron stores Serum transferrin saturation (TSAT) – toassess adequacy of iron for erythropoiesis Serum vitamin B12 and folate levelsIron DeficiencyIdentified?NOTSAT 30%Ferritin 500 ng/mLMaintenance MonitoringCheck Hb andiron indicesYESConsider ESA TherapyAdminister Venofer 1†(iron sucrose injection, USP) 200 mg IV push over 2–5 minutesx 5 doses over a 14-day period, or 200 mg in 100 mL NaCI over aperiod of 15 minutes x 5 dosesover a 14-day periodResponseYESIncreases from baselineHb and iron indicesNONo Change Assess for other causes of low Hb Refer to Hematology* Adapted from the KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Anemia in Chronic KidneyDisease. Official Journal of the International Society of Nephrology. Kidney Int.2012;2(4):288-335.† For adult CKD patients on ESA therapy who are not receiving iron supplementation, theguideline suggests a trial of IV iron (or in CKD ND patients alternatively a 1–3 month trialof oral iron therapy) if: An increase in Hb concentration or a decrease in ESA dose is desired, and TSAT is 30% and ferritin is 500 ng/mL ( 500 µg/L )
7-day stability after dilutionVenofer (iron sucrose injection, USP) offers 7-daystability in both plastic syringes and IV admixturesdiluted with 0.9% sodium chloride (NaCl) injection,avoiding potential waste.ConcentrationPlasticSyringeIVAdmixture(PVC andnon-PVC)ControlledRoomTemperature Refrigerated(25 C 2 C) (4 C 2 C) 2 mg–10 mg elementaliron per mL 20 mg of elemental ironper mL (undiluted) 1 mg–2 mg elementaliron per mL Do not dilute in concentrations below 1 mg/mL Do not mix Venofer with other medications Do not add Venofer to parenteral nutrition solutions forintravenous infusionINDICATION AND USAGEVenofer (iron sucrose injection, USP) is indicated for the treatmentof iron deficiency anemia (IDA) in patients with chronic kidneydisease (CKD).IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATIONDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONPediatric Patients (2 Years of Age and Older)The dosing for iron replacement treatment in pediatric patientswith Peritoneal or Hemodialysis-Dependent - CKD or Non-DialysisDependent CKD have not been established.CONTRAINDICATIONSKnown hypersensitivity to Venofer.Please see additional Important Safety Informationthroughout, and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
Dosing and administration for adultCKD patients2The usual adult total treatment course of Venofer (iron sucrose injection,USP) is 1000 mg. Venofer treatment may be repeated if iron deficiencyreoccurs.100 mg over2–5 min H emodialysis-dependentchronic kidney disease(HDD-CKD) C onsecutive dialysis sessions200 mg over2–5 min N on-dialysis-dependentchronic kidney disease(NDD-CKD) F ive occasions over 14 days100 mg/100 mLover 15 min Hemodialysis-dependentchronic kidney disease(HDD-CKD) Consecutive dialysis sessions200 mg/100 mLover 15 min Non-dialysis-dependentchronic kidney disease(NDD-CKD) Five occasions over 14 days2 doses of300 mg/250 mLover 1.5 hrsplus1 dose of400 mg/250 mLover 2.5 hrs Peritoneal-dialysisdependent chronic kidneydisease (PDD-CKD) 14 days apartIV PushInfusion*Diluted with0.9% sodiumchlorideinjection atconcentrationsof 1–2 mg/mL*Administer early during the dialysis session.IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATIONWARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONSSerious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic-typereactions, some of which have been life-threatening and fatal,have been reported in patients receiving Venofer. Patients maypresent with shock, clinically significant hypotension, loss ofconsciousness, and/or collapse. If hypersensitivity reactions orsigns of intolerance occur during administration, stop Venoferimmediately. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms ofhypersensitivity during and after Venofer administration for atleast 30 minutes and until clinically stable following completionof the infusion. Only administer Venofer when personnel andtherapies are immediately available for the treatment of serioushypersensitivity reactions. Most reactions associated withintravenous iron preparations occur within 30 minutes of thecompletion of the infusion.Venofer may cause clinically significant hypotension. Monitorfor signs and symptoms of hypotension following eachadministration of Venofer. Hypotension following administrationof Venofer may be related to rate of administration and/or totaldose delivered.
Dosing and administrationfor pediatric patients2PediatricPatients(2 years of ageor older) withHDD-CKDPediatricPatients(2 years of ageor older) withNDD-CKD orPDD-CKD who areon erythropoietintherapy for ironmaintenancetreatmentFor iron maintenance treatment,administer Venofer (iron sucroseinjection, USP) At a dose of 0.5 mg/kg, not toexceed 100 mg per dose Every 2 weeks for 12 weeks Given undiluted by slowintravenous injection over5 minutes or diluted in 0.9% NaCl atconcentrations of 1–2 mg/mL andadministered over 5–60 minutesFor iron maintenance treatment,administer Venofer At a dose of 0.5 mg/kg, not toexceed 100 mg per dose Every 4 weeks for 12 weeks Given undiluted by slowintravenous injection over5 minutes or diluted in 0.9% NaCl atconcentrations of 1–2 mg/mL andadministered over 5–60 minutesVenofer treatment may be repeated if necessary. The dosing foriron replacement treatment in pediatric patients with HDD-CKD,NDD-CKD, or PDD-CKD has not been established.Venofer has not been studied in patients younger than 2 years old.IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION (CONTINUED)WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (CONTINUED)Excessive therapy with parenteral iron can lead to excess storageof iron with the possibility of iatrogenic hemosiderosis. Alladult and pediatric patients receiving Venofer require periodicmonitoring of hematologic and iron parameters (hemoglobin,hematocrit, serum ferritin and transferrin saturation). Do notadminister Venofer to patients with evidence of iron overload.Transferrin saturation (TSAT) values increase rapidly afterintravenous administration of iron sucrose; do not performserum iron measurements for at least 48 hours afterintravenous dosing.Please see additional Important Safety Informationthroughout, and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
For Intravenous Use OnlyINDICATION AND USAGEVenofer (iron sucrose injection, USP) is indicated for the treatmentof iron deficiency anemia (IDA) in patients with chronic kidneydisease (CKD).IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATIONDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONPediatric Patients (2 Years of Age and Older)The dosing for iron replacement treatment in pediatric patientswith Peritoneal or Hemodialysis-Dependent - CKD or Non-DialysisDependent CKD have not been established.CONTRAINDICATIONSKnown hypersensitivity to Venofer.WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONSSerious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic-typereactions, some of which have been life-threatening and fatal, havebeen reported in patients receiving Venofer. Patients may presentwith shock, clinically significant hypotension, loss of consciousness,and/or collapse. If hypersensitivity reactions or signs of intoleranceoccur during administration, stop Venofer immediately. Monitorpatients for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity during and afterVenofer administration for at least 30 minutes and until clinicallystable following completion of the infusion. Only administer Venoferwhen personnel and therapies are immediately available for thetreatment of serious hypersensitivity reactions. Most reactionsassociated with intravenous iron preparations occur within 30minutes of the completion of the infusion.Venofer may cause clinically significant hypotension. Monitor forsigns and symptoms of hypotension following each administrationof Venofer. Hypotension following administration of Venofer may berelated to rate of administration and/or total dose delivered.Excessive therapy with parenteral iron can lead to excess storage ofiron with the possibility of iatrogenic hemosiderosis. All adult andpediatric patients receiving Venofer require periodic monitoring ofhematologic and iron parameters (hemoglobin, hematocrit, serumferritin and transferrin saturation). Do not administer Venofer topatients with evidence of iron overload. Transferrin saturation (TSAT)values increase rapidly after intravenous administration of ironsucrose; do not perform serum iron measurements for at least 48hours after intravenous dosing.ADVERSE REACTIONSAdult Patients: The most common adverse reactions ( 2%) includediarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, hypotension,pruritus, pain in extremity, arthralgia, back pain, muscle cramp,injection site reactions, chest pain and peripheral edema.Pediatric Patients: The most common adverse reactions ( 2%) areheadache, respiratory tract viral infection, peritonitis, vomiting,pyrexia, dizziness, cough, nausea, arteriovenous fistula thrombosis,hypotension and hypertension.Post-Marketing ExperienceBecause these reactions are reported voluntarily from a populationof uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate theirfrequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. In postmarketing safety studies of Venofer in 1,051 patients with HDD-CKD,adverse reactions reported by 1% were cardiac failure congestive,sepsis and dysgeusia.6
Immune system disorders: anaphylactic-type reactions,angioedema Psychiatric disorders: confusion Nervous system disorders: convulsions, collapse,light-headedness, loss-of-consciousness Cardiac disorders: bradycardia Vascular disorders: shock Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders:bronchospasm, dyspnea Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders:back pain, swelling of the joints Renal and urinary disorders: chromaturia General disorders and administration site conditions:hyperhidrosisSymptoms associated with Venofer total dosage or infusing toorapidly included hypotension, dyspnea, headache, vomiting, nausea,dizziness, joint aches, paresthesia, abdominal and muscle pain, edemaand cardiovascular collapse. These adverse reactions have occurred upto 30 minutes after the administration of Venofer injection. Reactionshave occurred following the first dose or subsequent doses of Venofer.Slowing the infusion rate may alleviate symptoms.Injection site discoloration has been reported following extravasation.Assure stable intravenous access to avoid extravasation.DRUG INTERACTIONSVenofer may reduce the absorption of concomitantly administeredoral iron preparations.USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONSPregnancy: Risk Summary-Clinical ConsiderationsUntreated IDA in pregnancy is associated with adverse maternaloutcomes such as post-partum anemia. Adverse pregnancyoutcomes associated with IDA include increased risk for pretermdelivery and low birth weight.Severe adverse reactions including circulatory failure (severehypotension, shock including in the context of anaphylacticreaction) may occur in pregnant women with parenteral ironproducts (such as Venofer) which may cause fetal bradycardia,especially during the second and third trimester.Geriatric UseDose administration to an elderly patient should be cautious,reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiacfunction, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.OVERDOSAGENo data are available regarding overdosage of Venofer in humans.Excessive dosages of Venofer may lead to accumulation of iron instorage sites potentially leading to hemosiderosis. Do not administerVenofer to patients with iron overload.Please see additional Important Safety Informationthroughout, and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.You are encouraged to report Adverse Drug Eventsto American Regent, Inc. at 1-800-734-9236 or to theFDA by visiting www.fda.gov/medwatch or calling1-800-FDA-1088.REF-0262 9/20207
1Available in the Following SizesStrengthPack NDC#(Each mLcontains 20 mg ofElemental Iron)0517-2310-05200 mg0517-2325-1050 mg0517-2340-10100 mg0517-2340-25100 mgSupplied As10 mLSingle-Dose Vial2.5 mLSingle-Dose Vial5 mLSingle-Dose Vial5 mLSingle-Dose Vial1You are encouraged to report Adverse Drug Eventsto American Regent, Inc:Email: pv@americanregent.com; Fax: 1-610-650-0170Phone: 1-800-734-9236ADEs may also be reported to the FDAat 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatchDrug Information:1-888-354-4855 (9:00 am–5:00 pm Eastern Time, Monday–Friday)For urgent drug information outside of normal business hours,assistance is available at 1-877-845-63711-800-645-1706AMERICAN REGENT.COMREFERENCES1. IQVIA [NSP Audit from MAT November 2013 to November 2018].2. Venofer [package insert]. Shirley, NY: American Regent, Inc.; 9/2020.Millions prescribed. Millions treated.TMVenofer and the Venofer logo are registered trademarks of Vifor (International), Inc.,Switzerland. Venofer is manufactured under license from Vifor (International) Inc., Switzerland. 2020 American Regent, Inc. PP-VE-US-0092 10/2020
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to useVENOFER safely and effectively. See full prescribing information forVENOFER.Venofer (iron sucrose) injection, for intravenous useInitial U.S. Approval: 2000-----------------------------INDICATIONS AND USAGE---------------------------Venofer is an iron replacement product indicated for the treatment of irondeficiency anemia (IDA) in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). (1)-------------------------DOSAGE AND dult patientsPediatric patientsHemodialysis DependentChronic Kidney Disease(HDD-CKD) (2.2)Non-Dialysis DependentChronic Kidney Disease(NDD-CKD) (2.3)Peritoneal DialysisDependent-ChronicKidney Disease (PDDCKD) (2.4)HDD-CKD (2.5), PDDCKD or NDD-CKD TIONS---------------------------- Known hypersensitivity to Venofer. (4)----------------------------WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS-------------------- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Observe for signs and symptoms ofhypersensitivity during and after Venofer administration for at least 30minutes and until clinically stable following completion of eachadministration. Only administer Venofer when personnel and therapies areimmediately available for the treatment of serious hypersensitivityreactions. (5.1) Hypotension: May cause hypotension. Monitor for signs and symptoms ofhypotension during and following each administration. (5.2) Iron Overload: Regularly monitor hematologic responses during therapy.Do not administer to patients with iron overload. (5.3)100 mg slowintravenous injection orinfusion200 mg slowintravenous injection orinfusion300 mg or 400 mgintravenous infusion-----------------------------------ADVERSE REACTIONS-------------------------- Adult patients: The most common adverse reactions ( 2%) are diarrhea,nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, hypotension, pruritus, pain inextremity, arthralgia, back pain, muscle cramp, injection site reactions,chest pain, and peripheral edema. (6.1) Pediatric patients: The most common adverse reactions ( 2%) areheadache, respiratory tract viral infection, peritonitis, vomiting, pyrexia,dizziness, cough, nausea, arteriovenous fistula thrombosis, hypotension,and hypertension. (6.1)0.5 mg/kg slowintravenous injection orinfusionTo report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AmericanRegent, Inc. at 1-800-734-9236 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 AGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS---------------------See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATIONInjection: 50 mg/2.5 mL, 100 mg/5 mL, or 200 mg/10 mL (20 mg/mL) in singledose vials. (3)FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*1INDICATIONS AND USAGE2DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION2.1Mode of Administration2.2Adult Patients with Hemodialysis Dependent-ChronicKidney Disease (HDD-CKD)2.3Adult Patients with Non-Dialysis Dependent-ChronicKidney Disease (NDD-CKD)2.4Adult Patients with Peritoneal Dialysis DependentChronic Kidney Disease (PDD-CKD)2.5Pediatric Patients (2 Years of Age and Older) withHDD-CKD for Iron Maintenance Treatment2.6Pediatric Patients (2 Years of Age and Older) withNDD-CKD or PDD-CKD who are on ErythropoietinTherapy for Iron Maintenance Treatment3DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS4CONTRAINDICATIONS5WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS5.1Hypersensitivity Reactions5.2Hypotension5.3Iron Overload6ADVERSE REACTIONS6.1Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials6.2Adverse Reactions from Post-Marketing Experience7DRUG INTERACTIONS8USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS8.1Pregnancy8.2Lactation8.4Pediatric Use8.5Geriatric UseRevised: 9/202010OVERDOSAGE11DESCRIPTION12CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY12.1Mechanism of NCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY13.1Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility14CLINICAL STUDIES14.1Clinical Studies Overview14.2Study A: Hemodialysis Dependent-Chronic KidneyDisease (HDD-CKD)14.3Study B: Hemodialysis Dependent-Chronic KidneyDisease (HDD-CKD)14.4Study C: Hemodialysis Dependent-Chronic KidneyDisease (HDD-CKD)14.5Study D: Non-Dialysis Dependent-Chronic KidneyDisease (NDD-CKD)14.6Study E: Peritoneal Dialysis Dependent-Chronic KidneyDisease (PDD-CKD)14.7Study F: Iron Maintenance Treatment Dosing inPediatric Patients Ages 2 Years and Older with ChronicKidney Disease16HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING16.1How Supplied16.2Stability and Storage17PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION* Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing informationare not listed.1
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION1INDICATIONS AND USAGEVenofer is indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia (IDA) in patients with chronic kidneydisease (CKD).2DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION2.1 Mode of AdministrationAdminister Venofer only intravenously by slow injection or by infusion. The dosage of Venofer isexpressed in mg of elemental iron. Each mL contains 20 mg of elemental iron.2.2 Adult Patients with Hemodialysis Dependent-Chronic Kidney Disease (HDD-CKD)Administer Venofer 100 mg undiluted as a slow intravenous injection over 2 to 5 minutes, or as aninfusion of 100 mg diluted in a maximum of 100 mL of 0.9% NaCl over a period of at least 15 minutes,per consecutive hemodialysis session [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.2)]. AdministerVenofer early during the dialysis session (generally within the first hour). The usual total treatment courseof Venofer is 1000 mg. Venofer treatment may be repeated if iron deficiency reoccurs.2.3 Adult Patients with Non-Dialysis Dependent-Chronic Kidney Disease (NDD-CKD)Administer Venofer 200 mg undiluted as a slow intravenous injection over 2 to 5 minutes or as aninfusion of 200 mg in a maximum of 100 mL of 0.9% NaCl over a period of 15 minutes. Administer on5 different occasions over a 14 day period. There is limited experience with administration of an infusionof 500 mg of Venofer, diluted in a maximum of 250 mL of 0.9% NaCl, over a period of 3.5 to 4 hourson Day 1 and Day 14 [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.2)]. Venofer treatment may berepeated if iron deficiency reoccurs.2.4 Adult Patients with Peritoneal Dialysis Dependent-Chronic Kidney Disease (PDD-CKD)Administer Venofer in 3 divided doses, given by slow intravenous infusion, within a 28 day period: 2infusions each of 300 mg over 1.5 hours 14 days apart followed by one 400 mg infusion over 2.5 hours14 days later. Dilute Venofer in a maximum of 250 mL of 0.9% NaCl [see How Supplied/Storage andHandling (16.2)]. Venofer treatment may be repeated if iron deficiency reoccurs.2.5 Pediatric Patients (2 Years of Age and Older) with HDD-CKD for Iron MaintenanceTreatmentFor iron maintenance treatment: Administer Venofer at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg, not to exceed 100 mg perdose, every two weeks for 12 weeks given undiluted by slow intravenous injection over 5 minutes ordiluted in 0.9% NaCl at a concentration of 1 to 2 mg/mL and administered over 5 to 60 minutes. Do notdilute to concentrations below 1 mg/mL [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.2)]. Venofertreatment may be repeated if necessary.The dosing for iron replacement treatment in pediatric patients with HDD-CKD has not been established.2
2.6 Pediatric Patients (2 Years of Age and Older) with NDD-CKD or PDD-CKD who are onErythropoietin Therapy for Iron Maintenance TreatmentFor iron maintenance treatment: Administer Venofer at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg, not to exceed 100 mg perdose, every four weeks for 12 weeks given undiluted by slow intravenous injection over 5 minutes ordiluted in 0.9% NaCl at a concentration of 1 to 2 mg/mL and administered over 5 to 60 minutes. Do notdilute to concentrations below 1 mg/mL [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.2)]. Venofertreatment may be repeated if necessary.The dosing for iron replacement treatment in pediatric patients with NDD-CKD or PDD-CKD has notbeen established.3DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSInjection: 50 mg/2.5 mL, 100 mg/5 mL, or 200 mg/10 mL (20 mg/mL) in single-dose vials.4CONTRAINDICATIONS Known hypersensitivity to Venofer.5WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS5.1 Hypersensitivity ReactionsSerious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic-type reactions, some of which have been lifethreatening and fatal, have been reported in patients receiving Venofer. Patients may present with shock,clinically significant hypotension, loss of consciousness, and/or collapse. If hypersensitivity reactions orsigns of intolerance occur during administration, stop Venofer immediately. Monitor patients for signsand symptoms of hypersensitivity during and after Venofer administration for at least 30 minutes anduntil clinically stable following completion of the infusion. Only administer Venofer when personnel andtherapies are immediately available for the treatment of serious hypersensitivity reactions. Mostreactions associated with intravenous iron preparations occur within 30 minutes of the completion of theinfusion [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 and 6.2)].5.2 HypotensionVenofer may cause clinically significant hypotension. Monitor for signs and symptoms of hypotensionfollowing each administration of Venofer. Hypotension following administration of Venofer may berelated to the rate of administration and/or total dose administered [see Dosage and Administration (2),Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Adverse Reactions (6.2)].5.3 Iron OverloadExcessive therapy with parenteral iron can lead to excess storage of iron with the possibility of iatrogenichemosiderosis. All adult and pediatric patients receiving Venofer require periodic monitoring ofhematologic and iron parameters (hemoglobin, hematocrit, serum ferritin and transferrin saturation). Donot administer Venofer to patients with evidence of iron overload. Transferrin saturation (TSAT) valuesincrease rapidly after intravenous administration of iron sucrose; do not perform serum ironmeasurements for at least 48 hours after intravenous dosing [see Dosage and Administration (2) andOverdosage (10)].3
6ADVERSE REACTIONSThe following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling: Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] Iron Overload [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]6.1 Adverse Reactions in Clinical TrialsBecause clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observedin the clinical trials of a drug may not reflect the rates observed in practice.Adverse Reactions in Adult Patients with CKDThe frequency of adverse reactions associated with the use of Venofer has been documented in six clinicaltrials involving 231 patients with HDD-CKD, 139 patients with NDD-CKD and 75 patients with PDDCKD. Adverse reactions reported by 2% of treated patients in the six clinical trials for which the ratefor Venofer exceeds the rate for comparator are listed by indication in Table 1. Patients with HDD-CKDreceived 100 mg doses at 10 consecutive dialysis sessions until a cumulative dose of 1000 mg wasadministered. Patients with NDD-CKD received either 5 doses of 200 mg over 2 weeks or 2 doses of500 mg separated by fourteen days, and patients with PDD-CKD received 2 doses of 300 mg followedby a dose of 400 mg over a period of 4 weeks.Table 1. Adverse Reactions Reported in 2% of Study Populations and for which the Rate for VenoferExceeds the Rate for ComparatorBody System/Adverse ReactionsSubjects with any adverse reactionEar and Labyrinth DisordersEar PainEye DisordersConjunctivitisGastrointestinal DisordersAbdominal painDiarrheaDysgeusiaNauseaVomitingGeneral Disorders andAdministration Site ConditionsAstheniaChest painFeeling abnormalInfusion site pain or burningInjectionsiteextravasationPeripheral edemaPyrexiaHDD-CKDVenofer(N 231)%78.8NDD-CKDVenoferOral Iron(N 139)(N 139)%%76.373.4PDD-CKDVenofer EPO* Only(N 46)(N .72.72.70005.31.30000010.904
Body System/Adverse ReactionsInfections and tory tract infections, PharyngitisInjury, Poisoning and ProceduralComplicationsGraft complicationMetabolism and Nutrition DisordersFluid al and ConnectiveTissue DisordersArthralgiaBack painMuscle crampMyalgiaPain in extremityNervous System DisordersDizzinessHeadacheRespiratory, Thoracic andMediastinal DisordersCoughDyspneaNasal congestionSkin and SubcutaneousTissue DisordersPruritusVascular DisordersHypertensionHypotension* EPO ErythropoietinHDD-CKDVenofer(N 231)%NDD-CKDVenoferOral Iron(N 139)(N 139)%%PDD-CKDVenofer EPO* Only(N 46)(N .2One hundred thirty (11%) of the 1,151 patients evaluated in the 4 U.S. trials in HDD-CKD patients(studies A, B and the two post marketing studies) had prior other intravenous iron therapy and werereported to be intolerant (defined as precluding further use of that iron product). When these patientswere treated with Venofer there were no occurrences of adverse reactions that precluded further use ofVenofer [see Warning and Precautions (5)].5
Adverse Reactions in Pediatric Patients with CKD (ages 2 years and older)In a randomized, open-label, dose-ranging trial for iron maintenance treatment with Venofer in pediatricpatients with CKD on stable erythropoietin therapy [see Clinical Studies (14.7)], at least one adversereaction was experienced by 57% (27/47) of the patients receiving Venofer 0.5 mg/kg, 53% (25/47) ofthe patients receiving Venofer 1 mg/kg, and 55% (26/47) of the patients receiving Venofer 2 mg/kg.A total of 5 (11%) subjects in the Venofer 0.5 mg/kg group, 10 (21%) patients in the Venofer 1 mg/kggroup, and 10 (21%) patients in the Venofer 2 mg/kg group experienced at least 1 serious adverse reactionduring the study. The most common adverse reactions ( 2% of patients) in all patients were headache(6%), respiratory tract viral infection (4%), peritonitis (4%), vomiting (4%), pyrexia (4%), dizziness(4%), cough (4%), nausea (3%), arteriovenous fistula thrombosis (2%), hypotension (2%), andhypertension (2.1%).6.2 Adverse Reactions from Post-Marketing ExperienceThe following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of Venofer. Becausethese reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible toreliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.In the post-marketing safety studies in 1,051 treated patients with HDD-CKD, the adverse reactionsreported by 1% were cardiac failure congestive, sepsis and dysgeusia. Immune system disorders: anaphylactic-type reactions, angioedemaPsychiatric disorders: confusionNervous system disorders: convulsions, collapse, light-headedness, loss-of-consciousnessCardiac disorders: bradycardiaVascular disorders: shockRespiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: bronchospasm, dyspneaMusculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: back pain, swelling of the jointsRenal and urinary disorders: chromaturiaGeneral disorders and administration site conditions: hyperhidrosisSymptoms associated with Venofer total dosage or infusing too rapidly included hypotension, dyspnea,headache, vomiting, nausea, dizziness, joint aches, paresthesia, abdominal and muscle pain, edema, andcardiovascular collapse. These adverse reactions have occurred up to 30 minutes after the administrationof Venofer injection. Reactions have occurred following the first dose or subsequent doses of Venofer.Symptoms may respond to intravenous fluids, hydrocortisone, and/or antihistamines. Slowing theinfusion rate may alleviate symptoms.Injection site discoloration has been reported following extravasation. Assure stable intravenous accessto avoid extravasation.7DRUG INTERACTIONSVenofer may reduce the absorption of concomitantly administered oral iron preparations.6
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS8.1 PregnancyRisk SummaryPublished studies on intravenous iron sucrose treatment after the first trimester of pregnancy have notshown adverse maternal or fetal outcomes (see Data). Available reports of intravenous iron sucrose usein pregnant women during the first trimester are insufficient to assess the risk of major birth defects andmiscarriage. There are risks to the mother and fetus associated with untreated IDA in pregnancy as wellas risks to the fetus associated with maternal severe hypersensitivity
adult IV iron dosing algorithm* *Adapted from the KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease. Official Journal of the International Society of Nephrology. Kidney Int. 2012;2(4):288-335. † For adult CKD patients on ESA therapy who are not receiving iron supplementation, the