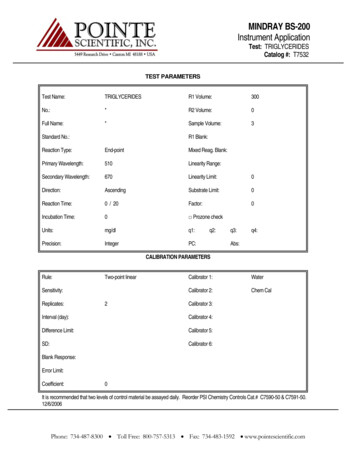
Transcription
Safe Handling and Use ofLiquid Nitrogen1
Characteristics of Nitrogen 78% of AtmosphereColorless, Odorless, Tasteless and NontoxicBoils at -320 degrees Fahrenheit (-196 C)Non-FlammableWILL NOT SUPPORT LIFEGas is slightly lighter than air2
Liquid Nitrogen Facts 1 cubic foot of liquid nitrogen will expand to696 cubic feet of 100% gaseous nitrogen at70 FThe nitrogen gas can displace the oxygen inthe area, leading to asphyxiationCryogenic liquids should always be stored inwell-ventilated spaces3
Oxygen Deficiency Liquid nitrogen, whenreturned to the gaseous state,can displace oxygen from theair under the right conditions.It may be prudent to installoxygen monitors in areaswhere liquid nitrogen isstored and ventilation isminimal.4
Characteristics of Oxygen Normal Concentrations: The normal oxygen concentration in air isabout 21% by volume. This provides for asafe working environment with respect tothe oxygen required to support life. Oxygen concentration below 19.5% isconsidered an oxygen deficientenvironment5
Characteristics of Oxygen Deficiency Physiological Effects: Asphyxia develops slowly as theoxygen content of air is graduallyreduced from 21%.The victim will not be aware of aproblem and generally will notrecognize the symptoms ofgradual asphyxia from decreasingoxygen levels.6
Characteristics of Oxygen Deficiency Oxygen Deficiency Precautions: All cryogenic liquids should be used andstored in well-ventilated areas.Filling between containers, leaking valves,and liquid tank venting are some examplesthat could lead to an oxygen deficientatmosphere.7
Handling Liquid Nitrogen Always read the container label prior to useCryogenic liquid containers must always bestored in the upright positionCryogenic liquids should not be handled inopen pail-type containers or in unapproveddewars.Transfer of liquid into warm lines orcontainers must be done slowly to preventthermal shock and possible buildup ofpressure.8
Handling Liquid Nitrogen Precautions: Always wear safety equipment,including heavy loose fittingleather or cryogenic gloves, andeye and face protection.High concentrations of escapinggas should not be allowed tocollect in an enclosed area.Avoid prolonged breathing ofcryogenic liquid vapors .9
Handling Liquid Nitrogen Avoid rough handling of liquid containersLiquid cylinders should only be movedwith proper handling equipment.Prior to use, ensure the fittings on theregulator match the fittings on the liquidcontainerNever use adaptorsNever attempt to change or remove anyfittings10
Containers for Holding Liquid NitrogenAfter Dispensing Thermos bottles are approvedcontainersUse only containers specially designedto hold liquid nitrogen-Check with themanufacturer of the container to ensureit is approved for holding liquid nitrogen11
Different Types of LiquidCylinders12
Cryogenic Liquid Containers(aka Liquid Cylinders) Advantages:Contain large volumes of gasProvides a source of Cryogenic Liquids whichcan be easily handled Two general types:Low Pressure-For dispensing of liquid only.High Pressure-For dispensing of liquid andgas13
Construction of Liquid Containers Liquid containers aremade somewhat likeThermos bottleswith a vacuumspace and specialinsulation, but theyare not Thermosbottles Annular Space14
Construction of Liquid Container Even with the vacuum and insulation,heat leaks in to the cylinder causing thecryogenic liquid to vaporize and buildpressure.The vaporization rate will depend onseveral factors including the productitself, ambient temperature, conditionof the cylinder’s vacuum, etc.15
Cryogenic Liquid Containers(Liquid Cylinders) Dewars are open, nonpressurized andmanufacturer approved vessels forholding cryogenic liquidsA regular Thermos bottle is not anapproved cryogenic container!!16
Pressure Relief Devices The liquid-to-gas conversionrate is about 2.3% per dayunder perfect conditions, sothe actual vaporization rateexperienced can vary.If gas product is not used,pressure will build until it isreleased by a control valve.Note that this is a highpressure container, with thegauge marked for 350 psig.17
Pressure Relief Devices Hearing a slight hiss from a liquid cylinder isusually the normal operation of its pressurerelief device.Liquid cylinders should always be stored andused in areas with appropriate natural ormechanical ventilation.Never adjust, block, plug or attempt to repairanything on a liquid cylinder.18
Pressure Relief DeviceFormula 4L 292 350 safety4L 200 235 safetyPressure relief devices are prescribedbased on the following formula forvacuum-insulated cylinders. (Cylinder service pressure X 1.25) – 15psi Maximum Pressure Relief Device Rating. Example (200x1.25) – 15psi 235psi19
Liquid-to-Gas Conversion Liquid is converted to gas atabout 2.3% per day evenunder ideal containerconditions.If the liquid is not usedregularly, the vessel will beempty in a certain amount oftime.20
Storage in Cold Rooms Contrary to popular belief,storage of liquid containers incold rooms will not slow downthe liquid to gas conversion.Storage in cold rooms cancreate an oxygen deficientatmosphere if the room doesnot have adequate ventilationto remove the nitrogen gasgenerated.21
Cryogenic Liquid Containers(Liquid Cylinders) Always check the type of container that is beingdelivered or before use.One lab had ordered low pressure and received highpressure by mistake. The lab personnel assumed itwas low pressure and began to use it. This couldhave resulted in an unsafe condition. Low pressurehas an operating pressure of 22 psig!!!High pressure operates at 230 psig or above. Alwayscheck the pressure gauge to determine the type ofcontainer.22
Content Gauge on Liquid CylindersThe container contents gauge is a floattype liquid level sensor that indicates thelevel of the liquid.The gauge is an indication of approximatecontainer content, and should not be usedfor judging the weight of the container.Containers are always filled by Weight!23
Cryogenic Liquid Containers(Liquid Cylinders) Make sure you know the type ofcontainer that is used by your lab!!Low pressure is used only for thedelivery of LIQUID, not gasIt’s operating pressure is 22 psigCaution Signs should be posted in thearea warning that liquid nitrogen isbeing stored and used.24
Cryogenic Liquid Containers(Liquid Cylinders)Head pressure Results when heat leaks into the containerThe safety valve will periodically release this pressureIf the safety valve malfunctions, a backup disk willrupture and relieve the pressureThe rupture of the backup disk will produce a loudsound and may release a large quantity of liquid andgas. Evacuation of the area is required to preventasphyxiation25
26
Low Pressure Liquid ContainerComponents Liquid Withdrawal ValveLiquid is withdrawn through this valve Pressure GaugeDisplays internal pressure of the container Contents GaugeA float-type liquid level gauge-indicates approximatelevel of liquid27
Low Pressure Liquid ContainerComponents Vent ValvePrimarily used in the fill process to vent the vaporspace while filling. Can be used to vent unwantedpressure during storage and use Pressure Relief Devices (2)Protect vessel from over-pressurization-Re-seating spring-loaded relief valve releases at22 psig-Burst disk rated to protect the inner vessel28
Low Pressure Liquid ContainerComponents Outlet RestraintsThese are to prevent the dangerous practice ofchanging outlet connections at user sites. Theserestraints may be twist ties, wire, or other.Removal of these restraints will void all productwarranties!!Changing outlet connections is an extremelydangerous practice and can result in serious injury ordeath if an incompatible product is introduced into auser’s system29
Warning!!!! Never plug, restrict, or remove any reliefdevice.Never attempt to cap or seal a venting reliefdevice in any way.Ice or frost buildup on a pressure relief valvecan be removed with a damp cloth. (Wearproper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)when removing the frost.)30
Moving Liquid Cylinders Liquid cylinders range in differentweights and sizes. They are heavy andcumbersome, especially when filledwith liquid nitrogen.They may require for two people tohandle in order to do so safely.Containers can cause crushing injuryto the feet. Wear proper shoes.Tennis shoes and open toed shoes arenot proper foot protection!!31
Moving Liquid Cylinders Never try to rollliquid cylinders byusing the LiquidLevel Gauge tube.Note the properstance and use ofthe cylinder’s haloring for moving.32
Emergencies If there is a large spill or rupture of acontainer, call 911, warn others in buildingEvacuate!! There may be oxygendeficiency in the area of the spill!!If there is injury to the body from liquidnitrogen, seek immediate medical assistance33
Emergencies If liquid is splashed in the eyes, flush with water forat least 15 minutes. Seek immediate medicalattention. Call 911Skin contact may cause frostbite and burns. Soakaffected part in tepid water and seek immediatemedical attention. Call 911Skin contact is a medical emergency. Lack of promptmedical attention may result in amputation!!!CALL 91134
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) forCryogenics If you fill cryogenic liquids the possibility of cryogenicliquid coming in contact with the skin is reduced withthe use of proper Personal Protective Equipment(PPE). Full Face Shield with safety glasses Heavy, Loose Fitting leather or Cryogenic Gloves Long Sleeve Shirt, or Arm Protection Pants should be cuff-less Do not tuck pants into shoes, boots.35
Liquid Nitrogen Burn36
Liquid Withdrawal Caution!!Always wear a full face shield, goggles, leather orcryogenic gloves, safety shoes, and aprons whentransferring liquid.Ensure that the liquid cannot collect in pants cuffs ortravel down into shoes. Do not tuck cuffs into pants!Cuff gloves over sleeves.Transfer of liquids at pressures higher than 22 psiginto open vessels such as small dewars can lead toexcessive splashing. This could result in injury fromfreezing of the body part37
Liquid Withdrawal Ensure that withdrawal hose isequipped with a phase separator toprevent splashing. Check withsupervisor or supplier.Never dispense liquid into anunapproved container, such as aThermos bottle. It will shatter!38
Trouble Shooting39
Trouble Shooting Issue: Gas vents intermittently through safety relief valvePossible cause: Probably normal operation. Gasgenerated due to heat leak into cylinder causes head pressureto build Recommended Activity:Ensure inactivecontainers are stored in well ventilated area. Rotate inventory40
Trouble Shooting Issue: Gas vents continuously through safety valvePossible Cause: Possible relief valve failure orexcessive heat leak Recommended Activity:Remove container orvent the exhaust to a well ventilated area. Relieve productthrough vent valve. Check to see if safety relief valve is frozenopen. Contact supervisor or supplier for assistance41
Trouble Shooting Issue: Gas vents during use through safety relief valvePossible Cause: Set point on regulators exceeds safetyrelief valve setting Recommended Activity:Reduce set point onpressure building regulator-Contact supervisor or supplier forassistance42
Trouble Shooting Issue: Pressure in the container is lowPossible Cause: Leak from containerRecommended Activity: Use appropriate leakdetection fluid to check for leaks in connections. Examinecontainer for signs of frost. If leaks are on container itself,contact supervisor or supplier43
Trouble Shooting Issue: Pressure in the container is lowPossible Cause: Pressure building valve is not fullyopened Recommended Activity:Open valve fully44
Trouble Shooting Issue: Pressure in the container is lowPossible Cause: Pressure building regulator not sethigh enough Recommended Activity:Adjust to increasepressure-contact supervisor or supplier45
Trouble Shooting Issue: Pressure in the container is lowPossible Cause: Pressure building valve is openRecommended Activity: Close the valve if frost isvisible on the pressure building vaporizer near the bottom of thetank-contact supervisor or supplier46
Trouble Shooting Issue: Pressure in the container is too highPossible Cause: Leaking or improper setting ofpressure building regulator Recommended Activity:Reduce regulator settingto achieve desired pressure level-contact supervisor or supplier47
Trouble Shooting Issue: Pressure in the container is too highPossible Cause: Vacuum integrity failingRecommended Activity: If container walls arecovered with frost, contact supervisor or supplier48
Trouble Shooting Issue: Container top covered with frostPossible Cause: High product useRecommended Activity: Normal operation49
Trouble Shooting Issue: Container has isolated spots of frostPossible Cause: Container may have been damaged,compromising integrity of insulation Recommended Activity:Contact supervisor or callsupplier for replacement50
Trouble Shooting Issue: Container surface is uniformly covered with frostPossible Cause: Vacuum integrity compromisedRecommended Activity: If accompanied by a highrate of product venting through the safety relief valve, or highrate of pressure increase, call supplier51
References and Assistance Airgas East (800-524-7427)Airgas (Formerly AirProducts) Safetygram-27,Cryogenic Liquid ContainersCompressed Gas Association (703-412-0900)MSDS on Liquid Nitrogen- DES Web sitewww.inform.umd.edu/desDES at 301-405-396152
Questions?Contact the Department of EnvironmentalSafety (315)787-2350 or E-mail atssk19@cornell.edu53
Please be SAFETHE END54
25 Cryogenic Liquid Containers (Liquid Cylinders) Head pressure Results when heat leaks into the container The safety valve will periodically release this pressure If the safety valve malfunctions, a backup disk will rupture and relieve the pressure The rupture of the backup disk will produce a loud sound and may release a large quantity of liquid and