Transcription
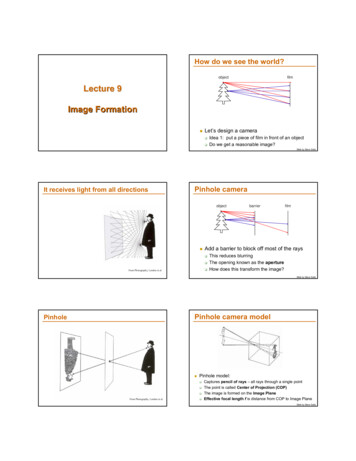
How do we see the world?objectfilmLecture 9Image Formation Let’s design a camera Idea 1: put a piece of film in front of an objectDo we get a reasonable image?Slide by Steve SeitzIt receives light from all directionsPinhole cameraobject filmAdd a barrier to block off most of the rays From Photography, London et al.barrierThis reduces blurringThe opening known as the apertureHow does this transform the image?Slide by Steve SeitzPinhole camera modelPinhole Pinhole model: From Photography, London et al. Captures pencil of rays – all rays through a single pointThe point is called Center of Projection (COP)The image is formed on the Image PlaneEffective focal length f is distance from COP to Image PlaneSlide by Steve Seitz1
Pinhole size?Lenses gather morelight!But need to befocusedFrom Photography, London et al.From Photography, London et al.Dimensionality Reduction Machine(3D to 2D)3D worldFunny things happen 2D imagePoint of observation What have we lost? AnglesDistances (lengths)Figures Stephen E. Palmer, 2002Distant objects are smallerParallel lines aren’t but humans adopt!length of B 2*length of Clength of B’ length of C’Müller-Lyer IllusionWe don’t make measurements in the image planeForsyth&Poncehttp://www.michaelbach.de/ot/sze muelue/index.html2
Perspective projection The equation of projectionAbstract camera model - box with a small hole in itIn an ideal pinhole camera everything is in focus2D image3D worldForsyth&PonceThe equation of projection Cartesian coordinates: We have, by similar triangles, that( x, y , z ) ( f The camera matrixTurn previous expression into HC’s x y, f , f )zzHC’s for 3D point are (x,y,z,1)HC’s for point in image are (u,v,w) u 1 0 v 0 1 w 0 0 Ignore the third coordinate, and getx y( x, y , z ) ( f , f )zz Issues: perspective effects, but not over the scale of individual objectscollect points into a group at about the same depth, then divideeach point by the depth of its groupAdv: easyDisadv: wrong01f x 0 y0 z0 1 Position of the point in the image from HC u x v y w z f Weak perspective0 normalize by w u x1 f v yw z w z f fx z fy z 1 Orthographic projectionTelescope projection can be modeled by orthographic projection3
Orthographic Projection Building a real cameraSpecial case of perspective projection Distance from the COP to the PP is infiniteImage WorldAlso called “parallel projection”What’s the projection matrix?Slide by Steve SeitzCamera ObscuraHome-made pinhole cameraCamera Obscura, Gemma Frisius, 1558Why soblurry? The first camera Known to AristotleDepth of the room is the effective focal lengthhttp://www.debevec.org/Pinhole/Shrinking the aperture Shrinking the apertureWhy not make the aperture as small as possible? Less light gets throughDiffraction effects Slide by Steve Seitz4
The reason for lensesFocusSlide by Steve SeitzFocus and DefocusobjectlensThin lensesfilm“circle ofconfusion” A lens focuses light onto the film There is a specific distance at which objects are “in focus” Changing the shape of the lens changes this distance Thin lens equation: other points project to a “circle of confusion” in the image Any object point satisfying this equation is in focusWhat is the shape of the focus region?How can we change the focus region?Thin lens applet: http://www.phy.ntnu.edu.tw/java/Lens/lens e.html(by Fu-Kwun HwangSlide by Steve Seitz)Slide by Steve SeitzVarying FocusDepth Of FieldRen Ng5
Depth of FieldAperture controls Depth of Field Changing the aperture size affects depth of field A smaller aperture increases the range in which the object isapproximately in focusBut small aperture reduces amount of light – need to utorials/depth-of-field.htmVarying the apertureLarge apeture small DOFNice Depth of Field effectSmall apeture large DOFField of View (Zoom)Field of View (Zoom)6
Field of View (Zoom)FOV depends of Focal LengthfSmaller FOV larger Focal LengthField of View / Focal LengthLarge FOV, small fCamera close to carSmall FOV, large fCamera far from the carFrom Zisserman & HartleyLens Flaws: Chromatic Aberration Dispersion: wavelength-dependent refractive index Lens Flaws(enables prism to spread white light beam into rainbow) Modifies ray-bending and lens focal length: f(λ) color fringes near edges of imageCorrections: add ‘doublet’ lens of flint glass, etc. 7
Chromatic AberrationRadial Distortion (e.g. ‘Barrel’ and‘pin-cushion’)straight lines curve around the image centerNear Lens CenterNear Lens Outer EdgeRadial DistortionNo distortion Pin cushionRadial DistortionBarrelRadial distortion of the image Caused by imperfect lensesDeviations are most noticeable for rays that passthrough the edge of the lens8
3 Perspective projection Abstract camera model - box with a small hole in it In an ideal pinhole camera everything is in focus Forsyth&Ponce The equation of projection 2D image 3D world The equation of projection Cartesian coordinates: We have, by similar triangles, that Ignore the third coordinate, and get z y f z x x y z f .