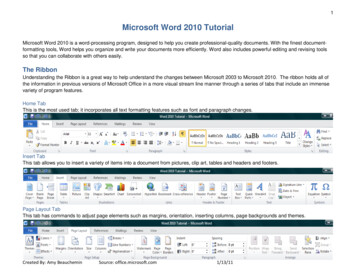
Transcription
CSUDH, Division of Information TechnologyCreating AccessibleDocuments usingMicrosoft OfficeCreating Accessible Documents With Office 2013 – Updated 10-2016
CONTENTSSteps To Make Files Accessible . 11. Use Styles to Add Appropriate Font Style, Size and Color . 1Style Elements . 2Heading Styles In The Correct Order . 22. Add Alternative Texts and captions . 3Adding Alt Text To Images And Objects (Word 2013). 3Long Description For Charts And Graphs . 43. Specify Column Header Rows in Tables . 5Set A Table Header . 5Simple Table Structure . 5Reading Order For Easy Table Navigation . 6Avoid Blank Cells In Formatting . 64. Use Meaningful Hyperlinks In Documents . 7To Add A Hyperlink To Your Document: . 75. Set Document Pproperties . 8Setting Document Properties: Title, Subject, Keywords, Author, Company & Language . 8Avoid Image Watermarks . 96. Check Accessibility In Office 2013 . 97. Save Office 2013 Files as a Tagged PDF . 11Save A Word Document as a Tagged PDF . 11Save An Excel Workbook as a Tagged PDF . 11Save A Powerpoint Presentation as a Tagged PDF. 11Save A Publisher Publication as a Tagged PDF . 12
DIVISION OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYCalifornia State University, Dominguez HillsCREATING ACCESSIBLE DOCUMENTSIt is estimated that up to 4% of the population relies on some sort of Assistive Technology to access electronicdocuments and Web pages. Assistive Technology includes; Screen Reading software, Refreshable Braille displays,and Screen Magnifiers.Because many files are often viewed electronically, governments and industries around the world areimplementing policies that require electronic and information technology to be accessible to people withdisabilities. For example, the amended Section 508 of the United States Rehabilitation Act of 1973 requires Federalagencies to make all of their electronic and information technology accessible. – CA Department of RehabilitationTIPIT IS HIGHLY RECOMMENDED TO MAKE DOCUMENTS ACCESSIBLE AS THEY ARE CREATED; IT IS EASIER THANMAKING ADJUSTMENTS LATER ON.STEPS TO MAKE FILES ACCESSIBLE1.2.3.4.5.6.7.Use Styles to Add Appropriate Font Style, Size and ColorAdd Alternative Texts and CaptionsSpecify Column Header Rows in TablesUse Meaningful Hyperlink TextSet Document PropertiesCheck Accessibility (Word, Excel, and PowerPoint)Save Office 2013 Files as a Tagged PDF1. USE STYLES TO ADD APPROPRIATE FONT STYLE, SIZEAND COLORHeading and paragraph styles, as well as tables of contents when necessary, make it easier for all readers of yourdocument to follow it more easily. In longer documents, these elements can add structure for users who are usinga screen reader, or who rely on the visual cue of section headings to navigate as they read.NOTEUSING THE NAVIGATION PANE IN WORD LETS YOU BROWSE THE DOCUMENT BY HEADINGS.To apply heading styles to your document:1.2.Select the text you want to make into a heading.On the Home tab, in the Styles group, select the appropriate level heading style from the Stylesgallery.p. 1Creating Accessible Documents using Microsoft OfficePublished: 11/14/2016
DIVISION OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYCalifornia State University, Dominguez HillsSTYLE ELEMENTS1.2.3.Use Word's Styles to format page titles and section headings; don't just use bigger, bolder text toindicate the hierarchical level of a title or heading.a.Use Heading 1 for the document's title.b.Use Heading 2 for the document's main section headings.c.Use Heading 3 for subsection headings.d.Use Normal for regular paragraph text.Lists: Use Word’s Bullet and Numbering preformatted lists as a tool to make your lists accessible.Colors: Some people have color vision problems which prevents them from distinguishing betweencertain colors. When developing documents using color to distinguish between more than one option,always provide a redundant element to allow for understanding. See the example below for using colorand text to convey a message:HEADING STYLES IN THE CORRECT ORDERBy using heading levels in a logical order, for example Heading 4 is a child of Heading 3, not Heading 2, assists usersin navigating the document and finding information.You can view and update your document’s organization by clicking on the View tab and, in the Show group, selectthe Navigation Pane check box.To help longer documents maintain clear navigation, make sure you have at least one heading about every twopages, and that your headings are in the correct order (Heading 2 under Heading 1, etc.).p. 2Creating Accessible Documents using Microsoft OfficePublished: 11/14/2016
DIVISION OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYCalifornia State University, Dominguez Hills2. ADD ALTERNATIVE TEXTS AND CAPTIONSA screen reader will not be able to interpret graphic elements placed on the page. When descriptive or alternatetext is added, it will be read aloud by a screen reader.Alternate text does not change the visual appearance of the document. As a general rule, adding alternate text tothe original document in its native format (for example: Word, WordPerfect) is considered best practice.Alternate text should provide meaningful, detailed description of the graphic element.For many readers, this is the only information they have about the images and objects in your document. Alt textshould be included for any of the following objects in your document: Pictures/Clip ArtChartsTablesShapes (that don’t contain text and are not in groups)/ SmartArt graphicsGroups (all objects in this list, with the exception of shapes, should also have alt text when in groups)Embedded objectsVideo and audio filesNOTE IF THE IMAGE DOES NOT ADD MEANING TO THE DOCUMENT (LOGO, BANNER, BORDER, ETC.), IT SHOULD BEMARKED AS BACKGROUND USING THE TOUCH UP READING ORDER TOOL. BACKGROUND IMAGES OR WATERMARKS DONOT HAVE TO BE TAGGED. WHEN THE DOCUMENT IS CONVERTED TO PDF THESE IMAGES WILL NOT BE DETECTED ANDWILL NOT HAVE TO BE TAGGED.ADDING ALT TEXT TO IMAGES AND OBJECTS (WORD 2013)1.2.3.Right click the image or object, and then click Format Picture.Click Alt Text.Enter a description of the image or object into the Title and Description text boxes.TIP USE CLEAR, BUT CONCISEDESCRIPTIONS. FOR EXAMPLE, “A REDFERRARI” TELLS THE READER MOREABOUT THE IMAGE THAN “A CAR.”4.Click Close.p. 3Creating Accessible Documents using Microsoft OfficePublished: 11/14/2016
DIVISION OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYCalifornia State University, Dominguez HillsLONG DESCRIPTION FOR CHARTS AND GRAPHSCharts and graphs are primary examples of an image too complex to describe in a few words. Although there doesnot appear to be any limit to the length of text in an “alt” attribute, “alt text” is meant to be relatively brief and tothe point.By including the long description in the graphic you will add information that can be used by all readers, not justthose with disabilities. See how this is accomplished with an image of a graph:Description:The above bar graph shows thepercentage of total U.S. noninstitutionalized population age 16-64declaring one or more disabilities. Thepercentage value for each category is asfollows:Total declaring one or more disabilities:18.6 percentSensory (visual and hearing): 2.3 percentPhysical: 6.2 percentMental: 3.8 percentSelf-care: 1.8 percentDifficulty going outside the home: 6.4percentEmployment disability: 11.9 percent(Data retrieved from 2000 U.S. Census external link)p. 4Creating Accessible Documents using Microsoft OfficePublished: 11/14/2016
DIVISION OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYCalifornia State University, Dominguez Hills3. SPECIFY COLUMN HEADER ROWS IN TABLESMicrosoft Word does not provide an easy method for creating accessible tables. If you have complex tables it ishighly recommended that a description or explanation of the table contents be included in the text of thedocument.NOTE: CONSTRUCT A SIMPLE TABLE THAT WILL READ LOGICALLY FROM LEFT TO RIGHT, TOP TO BOTTOM ORDER.SET A TABLE HEADERNOTE: TABLES WITH COLUMN HEADINGS IN THE TOP ROW MUST HAVE THE TOP ROW FORMATTED AS A HEADERROW.To specify a header row in a table, do the following:1.Select the Insert tab on the ribbon, then select Table Insert Table.2.To add table headers to the first row, select Table Tools Layout on the ribbon, then choose the RepeatHeader Rows option in the Data section.SIMPLE TABLE STRUCTUREBy not using nested tables, or merged or split cells inside of tables, you can make the data predictable and easy tonavigate. For example: When you are designing a form, the entire document is often based on a heavily formattedtable, which makes it very difficult for users to navigate it with a screen reader, and requires them to piecetogether the content of each cell, read to them in an unpredictable order, to get an idea of the form’s content.To test and simplify the table structure, do the following:p. 5Creating Accessible Documents using Microsoft OfficePublished: 11/14/2016
DIVISION OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYCalifornia State University, Dominguez Hills1.2.3.Select the first cell of the table.Press the Tab key repeatedly to make sure that the focus moves across the row and then down to thefirst cell of the next row.If you need to merge or split cells to simplify the table, on the Table Tools Layout tab, inthe Merge group, click Merge Cells or Split Cells as appropriate.READING ORDER FOR EASY TABLE NAVIGATIONIf you use a layout table (table with Table Normal style), check the reading order to be sure that it makes sense(for English: left to right, top to bottom). Verify the table reading order by tabbing through the cells to check that the information is presented in alogical order.AVOID BLANK CELLS IN FORMATTINGUsing blank cells to format your table could mislead someone using a screen reader that there is nothing more inthe table. You can fix this by deleting unnecessary blank cells or, if your table is used specifically to layout contentwithin your document, you can clear all table styles by doing the following:1.2.3.Select the entire table.On the Table ToolsDesign tab, in the TableStyles group, click thearrow next to the stylegallery to expand thegallery of table styles.On the menu below thegallery, click Clear.p. 6Creating Accessible Documents using Microsoft OfficePublished: 11/14/2016
DIVISION OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYCalifornia State University, Dominguez Hills4. USE MEANINGFUL HYPERLINKS IN DOCUMENTSHyperlinks should be active (they turn blue) when they are copied into the document. If the links are not activethey may be made active by using the “Insert Hyperlink” command. Hyperlink text should provide a cleardescription of the link destination, rather than only providing the URL.TO ADD A HYPERLINK TO YOUR DOCUMENT:1.2.3.4.5.Place your cursor where you want the hyperlink.On the Insert tab, in the Links group, click Hyperlink to open the hyperlink dialog box.In the Text to display box, type in the name or phrase that will briefly describe the link destination.In the Address box, type the link URL.Click OK.To change the text of a hyperlink, do the following:1.2.3.Select the link and then, on the Insert tab in the Links group, click Hyperlink to openthe Hyperlink dialog box.In the Text to display box, make any necessary changes to the text.Click OK.Additionally, you can include ScreenTip text that appears when your cursor hovers over a hyperlink, and can beused in a similar way to alt text. To add ScreenTip text, do the following:1.2.3.4.5.Place your cursor in the hyperlink you want to add ScreenTip text to.On the Insert tab, in the Links group, click Hyperlink to open the hyperlink dialog box.Click ScreenTipType in your text in the ScreenTip text box.Click OK.p. 7Creating Accessible Documents using Microsoft OfficePublished: 11/14/2016
DIVISION OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYCalifornia State University, Dominguez Hills5. SET DOCUMENT PROPERTIESSETTING DOCUMENT PROPERTIES: TITLE, SUBJECT, KEYWORDS, AUTHOR,COMPANY & LANGUAGEThe Title, Subject, Author, Keywords and Language are important elements of any document. They are used bysearch engines and screen readers to find and identify content in documents.The document properties form may be displayed by:1.2.Clicking on File; InfoProperties, Advanced Propertiesa. If Properties is not visible, clickon the arrows to expand thepull down menu;3. Select the Summary tab to complete theform as follows:Title:The title of the documentSubject: Brief identification of thesubject of the documentAuthor: Your Name, or DivisionManager: OptionalCompany:Set to “CSUDH”Category:OptionalKeywords: The keywords are associated with thedocument during a search and will effectively rank thedocument for relevance. The closer your keywords areto the search words the user enters, the higher yourdocument will be rated in the search. When usingmultiple keywords, separate them with a comma. Besure to choose words that are relevant to the content.Comments: Optional; if included they should beappropriate and meaningful for your audience.p. 8Creating Accessible Documents using Microsoft OfficePublished: 11/14/2016
DIVISION OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYCalifornia State University, Dominguez HillsHyperlink Base:OptionalUnfortunately, MS Word does not set a default language. You need tospecify the primary language used to create each document.1.2.3.4.Click on the “Custom” Tab to add language. The followingwindow will be displayed:In the Name field, use drop down menu to select languagefrom the list.In the Value field, type the language used (typically“English”).Click the Add button; finish by clicking OK.AVOID IMAGE WATERMARKSImages used as watermarks may not be understood by people with vision or cognitive disabilities. If you must use awatermark, make sure that the information it contains is also included elsewhere in your document.6. CHECK ACCESSIBILITY IN OFFICE 2013The Accessibility Checker in Word, Excel, and PowerPoint points out possible accessibility issues in your Office fileso you can fix these issues. Each issue is classified as an Error, Warning, or Tip. Error - An error is for content that makes a file very difficult or impossible for people with disabilitiesto understand.Warning - A warning is for content that in most, but not all, cases makes a file difficult for people withdisabilities to understand.Tip - A tip is for content that people with disabilities can understand, but that might be betterorganized or presented in a way that would improve their experience.o Fixing some issues might require you to change, reformat, or update your content.p. 9Creating Accessible Documents using Microsoft OfficePublished: 11/14/2016
DIVISION OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYCalifornia State University, Dominguez Hillso1.2.3.Accessibility Checker also lets you know about Office features you can use to make yourcontent more accessible.Click File Info Check for Issues CheckAccessibility.Your file reappears, and the AccessibilityChecker task pane shows the inspection results.Click a specific issue to see AdditionalInformation and steps you can take to change thecontent.p. 10Creating Accessible Documents using Microsoft OfficePublished: 11/14/2016
DIVISION OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYCalifornia State University, Dominguez Hills7. SAVE OFFICE 2013 FILES AS A TAGGED PDFTagging adds a layer of information called “semantics” to a PDF document, indicating what types of objects areincluded in a file, for example: headings, paragraphs, images and tables.Assistive technologies, such as screen readers and magnifiers are then able to access the tagging and use it topresent the information to disabled users. If you do not tag your file, assistive technologies may not be able tounderstand what certain parts of your file are, in context, and may present the user with a confusing interpretationof the file. In some cases, some items may not be presented at all.IMPORTANT:Including tags in a PDF file will increase the file size.SAVE A WORD DOCUMENT AS A TAGGED PDFAfter you have created a Word document, you can save your file as a tagged PDF by following these steps:1.2.3.4.5.6.7.Click the File tab, and then click Save As.Under Choose a Location, choose where you want the file to be saved.Under Choose a Folder, choose a folder that you have already used or click Browse for Additional Foldersto choose a different folder.In the Save As dialog box, click the arrow in the Save as type list, and then click PDF.Click Options.Make sure that the Document structure tags for accessibility check box is selected, and then click OK.Click Save.NOTE: If you have Adobe Acrobat installed on your computer, you will be able to go to File, Save As Adobe PDFdirectly.SAVE AN EXCEL WORKBOOK AS A TAGGED PDFAfter you have created an Excel workbook, you can save your file as a tagged PDF by following these steps:1.2.3.4.5.6.7.Click the File tab, and then click Save As.Under Choose a Location, choose where you want the file to be saved.Under Choose a Folder, choose a folder that you have already used or click Browse for Additional Foldersto choose a different folder.In the Save As dialog box, click the arrow in the Save as type list, and then click PDF.Click Options.Make sure that the Document structure tags for accessibility check box is selected, and then click OK.Click Save.SAVE A POWERPOINT PRESENTATION AS A TAGGED PDFAfter you have created a PowerPoint presentation, you can save your file as a tagged PDF by following these steps:1.2.Click the File tab, and then click Save As.Under Choose a Location, choose where you want the file to be saved.p. 11Creating Accessible Documents using Microsoft OfficePublished: 11/14/2016
DIVISION OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYCalifornia State University, Dominguez Hills3.4.5.6.7.Under Choose a Folder, choose a folder that you have already used or click Browse for Additional Foldersto choose a different folder.In the Save As dialog box, click the arrow in the Save as type list, and click PDF.Click Options.Make sure that the Document structure tags for accessibility check box is selected, and then click OK.Click Save.SAVE A PUBLISHER PUBLICATION AS A TAGGED PDFAfter you have created a Publisher publication, you can save your file as a tagged PDF by following these steps:1.2.3.4.5.6.7.Click the File tab, and then click Save As.Under Choose a Location, choose where you want the file to be saved.Under Choose a Folder, choose a folder that you have already used or click Browse for Additional Foldersto choose a different folder.In the Save As dialog box, click the arrow in the Save as type list, and click PDF.Click Options.Make sure that the Document structure tags for accessibility check box is selected, and then click OK.Click Save.p. 12Creating Accessible Documents using Microsoft OfficePublished: 11/14/2016
Microsoft Office Creating Accessible Documents With Office 2013 – Updated 10-2016 . CONTENTS . Save Office 2013 Files as a Tagged PDF . 1. USE STYLES TO ADD APPROPRIATE FONT STYLE, SIZE AND COLOR . Heading and paragraph styles, as well as tables of conten