Transcription
Skilled Documentationto Support PDPMCo-Presented by:Terry Raser, RN, RAC-CT, DNS-CT, QCPPANAC Board MemberKay P. Hashagen, PT, MBA, RAC-CTSenior Consultant
Contact Hours 1.5 Contact hours will be awarded for this continuing nursingeducation activity. Criteria for successful completion includeattendance for the entire event and submission of the evaluation form. The Pennsylvania Association of Nurse Assessment CoordinatorsPlanning Committee has determined there are no conflicts of interestof the planning committee or the speakers in the presentation of thisprogram. This nursing continuing professional development activity wasapproved by the Ohio Nurses Association, an accredited approver bythe American Nurses Credentialing Center’s Commission onAccreditation. (OBN-001-91)PANAC ANNUAL CONFERENCE 20202
Your PresentersTerry Raser, RN, RAC-CT, DNS-CT, QCPPANAC Board MemberKay P. Hashagen, PT, MBA, RAC-CTLW Consulting, Inc.Senior ConsultantPANAC ANNUAL CONFERENCE 20203
AboutTerry Raser, RN, RAC-CT, DNS-CT, QCPTerry has more than 39 years of experience in the healthcare industry. As a consultant for 19 years, she dedicates her careerto compliance, quality improvement, MDS education and improvement in the long-term care nursing profession. Terryprovides RNAC support and education and performs audits to assist facilities with regulatory compliance and surveyperformance. She has PDPM expertise as well as Pennsylvania and Maryland Medicaid Case-Mix expertise. She has beentraining skilled nursing staff on PDPM and Medicare Basics.Kay P. Hashagen, PT, MBA, RAC-CTKay is a seasoned Senior Consultant for LW Consulting, Inc. with more than thirty-five years of healthcare industryexperience, specializing in geriatric rehabilitation in skilled nursing and outpatient rehabilitation across the continuum ofcare. She has a proven record of accomplishing excellent customer service, managing operations with strong performancemetrics, and developing creative programs while maintaining appropriate compliance monitoring for Medicare andregulatory requirements. She regularly joins the nurses to teach about the MDS components and how therapy and nursingshould work together for optimal performance. Over the past several years she has presented on “The F-309 Tag Related toDementia and the Importance of a Collaborative Nursing and Therapy Approach,” “Improving Your 5-Star CMS Rating,”“Critical Therapy Performance Indicators,” “Nursing and Therapy Collaboration for Quality Measures and CMI,” and“Optimizing Your EHR to Support Clinical Care.” Kay has also conducted many webinars related to therapy documentation tomeet CMS requirements.PANAC ANNUAL CONFERENCE 20204
Objectives: Demonstrate an understanding of the regulations in the MBPMChapter 8, for both nursing and therapy, to meet Medicare Part Arequirements and how documentation must support theserequirements. Know how to analyze nursing and therapy documentation to identify ifit meets coding on the MDS and skilled requirements. Identify systems to facilitate proper coding and support CMSregulations.PANAC ANNUAL CONFERENCE 20205
SNF Documentation Challenges #1 reason for Medicare Dollar Loss (Repayment) mentation”Focus Areas:Re-educating staffPainting a pictureSupporting the MDS and skilled careSupporting Diagnosis6
Reimbursable MDS Sections for PDPM BIMS- Brief Interview for Mental StatusPHQ-9 Patient Healthcare QuestionnaireSection GG Functional AbilitiesSection I- DiagnosisSection J- Surgical ProceduresSection K- DietarySection M- Skin and WoundsSection O- Special Treatments and Procedures, andRestorative Nursing Program7
PDPM Documentation Team Support MDS Items We don’t know what we don’t know Nursing Education What are the Medicare regulations? Nursing Education Cost of Not Documenting Skilled Services Nursing Education Physician Education Social Service*Dietary*Therapy*Restorative Nursing8
Supportive Documentation for PDPM
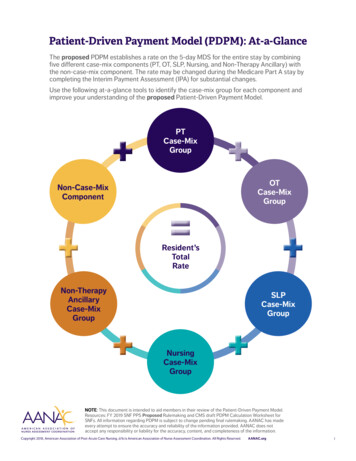
PDPM Snapshot10
PT & OT Components: PDPM PDPM Two classifications are used to obtain patientcharacteristics for PT and OT components under PDPM: Clinical Category- Primary Diagnosis Functional Status- Section GG No therapy minutes required11
The physician’s role in documentation of theprimary diagnosisWHAT IS THE REASON FOR THE SNFADMISSION? This is the question that drives the choice ofthe primary diagnosis code The code will be entered into the MDS in Item“I0020B”The reason for the hospitalizationmay not be the reason for the SNF admission!12
Discussion about Primary DiagnosisDays1-8 Physician documented reason for SNFadmission Physician list the primary diagnosis first Physician(s) educated on PDPM Comorbidity diagnoses documented bya physician13
PDPM Clinical Categories for PT and OT14
Physician Documentation Day 1-8 physician documentation imperative AdmittedFridayARDDay 4 5-day MDS pays the entire Medicare A stay!H&P, Progress note, Consults, Hospital RecordsDiagnosis must be specific- laterality, anatomical areaUnspecified codes- most are RTPDr. VisitsEducate to why it is importantonTuesday15
Physician Documented Diagnosis Must be documented to code 60-day lookback physician documented diagnosis 7-day active diagnosis lookback Progress notes must support the primary diagnosis Progress notes must support skilled service(s)16
Nursing Documentation- Primary Diagnosis Know the Primary DiagnosisDocument the skilled conditionState the primary diagnosis in progress notesDocument the need and reason for skilled careDocument the part of the body affected by thecondition Current condition and discharge needs17
Sample Nursing Documentation Left Fractured Hip- Readmitted 09/23/2019NursingNursingDietary18
Sample Doc: Primary Condition is Pneumonia Mr. Jones requires skilled care for his pneumonia.No complaints offered. Slept well during the night.Requires assist of 1 for ADLs.Oxygen via nasal cannula 2L., wheezing as times.Receives PT and OT.19
Improved Doc: Primary Condition is Pneumonia Mr. Jones requires skilled care for his pneumonia. His respiration are labored with an expiratory wheeze andrales bilaterally. O2 saturation is 94% on 2L of O2 via nasalcannula. Lips and nailbeds are pink. The head of bed iselevated 45 degrees. Resident expressed shortness of breathon exertion during am care. BP 146/84, P88, R20. Willcontinue to monitor. IV antibiotic continues as ordered. Resident continues to receive PT and OT daily forstrengthening but has difficulty due to SOB on exertion andtires easily.20
PT/OT Component- Functional Status Section GG Supported by nursing and therapy Days 1-3 on admission/readmission (if out 3 days) Interrupted stay or New stay Interim Payment Assessment (IPA) ARD plus 2 days prior PPS Discharge PPS DC date plus 2 days prior Comprehensive (NC) and Quarterlies (NQ) New October 1st for some states21
Section GG Importance Drives reimbursement for PT/OT and Nursingcomponents Functional Score22
Section GG Documentation Resources Section GG Assessment FormTherapy DocumentationNursing DocumentationADL Documentation Definitions are different, Retiring G in the future How bring utensils to mouth- Eating Sit to lying, lying to sitting on the side of the bed23
Ineffective Nursing GG Documentation Resident requires contact guard of 1 assist with sit tostand and bed to chair transfers or Resident requires moderate assistance of 1 personwith sit to stand and bed to chair transfers or Resident requires maximal assistance of 1 personwith sit to stand and bed to chair transfers24
Speech Language Pathology Component-PDPM 5 Componentssupport SLP forPDPM.SLP ComponentAcute Neurologic clinical classificationDiagnosisCertain SLP related co-morbiditiesDiagnosisPresence of cognitive impairmentBIMSPresence of mechanically altered dietSection KPresence of a swallowing disorderSection K25
Speech Language Pathology Component-PDPM Physician DocumentationDiagnosis26
Cognitive Impairment Component (BIMS) PDPM- Speech ComponentConducted on the ARD or the day beforeResident InterviewRules to Stopping an InterviewStaff InterviewMissed Interviews – Considered Cognitively IntactUnplanned Discharges – Do Staff InterviewAffectsReimbursement Don’t Dash for PPS Assessments27
PDPM Cognitive Measure Classification Methodology: Cognitive Function Scale for PDPM using the BIMS ResidentInterviewA score of mildly impaired, moderately impaired or severely impairedwill support the PDPM SLP component28
PDPM Cognitive Measure Classification Methodology: Cognitive Function Scale for PDPM using the BIMS Staff InterviewA score of mildly impaired, moderately impaired or severely impaired willsupport the PDPM SLP component29
Mechanically Altered Diet Component- PDPM Order from physician Documentation from dietician and nursing Reason for dietResident’s response to dietImprovement on diet or lack ofWeight on dietDoes diet affect activity participation and socialization?30
Swallowing Disorder Component- PDPM Ask the residentInterview staff membersObserve the resident during meals or medication passReview documentation in the medical record31
SLP Component: Payment GroupsTier 1Tier 232
Nursing Component- PDPM Extensive ServicesSpecial Care HighSpecial Care LowClinically ComplexBehavior/CognitiveReduced Physical Function33
Nursing Components34
Nursing Component Extensive Services Ventilator, respirator Trach Infection Isolation Special Care-High Comatose*COPD w/ SOB lying flatSepticemia*Fever w/PNA, VomitingQuadriplegiatube feed or wt. lossDiabetes with injections *Respiratory TherapyParenteral/IV Feeding35
Nursing Components36
Nursing Component Special Care-Low Cerebral Palsy, MS, Parkinson's2 or more Stage 2 Plus, stage 3 or 4, venous, arterialFeeding Tube, Oxygen, Respiratory failureFoot infection, Diabetic foot ulcer, open foot lesionRadiationDialysis37
Nursing Component Clinically Complex PneumoniaHemiplegia/paresisBurnsChemoOxygenIV MedicationTransfusions38
Nursing Components0.7039
Nursing Components Behavior/Cognitive HallucinationsDelusionsVerbal AbusePhysical Abuse Reduced Physical Function Catch All Category Hierarchical Structure40
NTA Component NTA classification Based on the presence of certain comorbidities or use of certainextensive services Co-morbidities and extensive services for NTA classification Derived from a variety of MDS sources Some co-morbidities identified by ICD-10-CM codes reported in MDSItem I8000 HIV/AIDS reported on the SNF claim, likewise, to RUG-IV 8 points awarded for this one diagnosis CMS lists 50 diagnosis codes and conditions Maximum allowable 12 points41
NTA Comorbidities42
NTA Comorbidities43
NTA Comorbidities44
NTA Component: Payment Groups45
Skilled Documentation
30.2.2 - Principles for Determining Whether aService is Skilled First Understand What a Skilled Service is. If the inherent complexity of a service prescribed for a patient issuch that it can be performed safely and/or effectively only byor under the general supervision of skilled nursing or skilledrehabilitation personnel, the service is a skilled service. Second Determine the Skilled Service(s) Nurses won’t document if they don’t know the Skilled Service.Medicare Benefit Policy Manual- Chapter 847
30.2.2.1 Documentation to Support Skilled Services An 81-year-old woman who is aphasic and confused, suffers from hemiplegia, congestive heart failure, and atrial fibrillation, has suffereda cerebrovascular accident, is incontinent, has a Stage 1 decubitusulcer, and is unable to communicate and make her needs known. No specific service provided is skilled, The patient’s condition requires daily skilled nursing involvement tomanage a plan for the total care needed, To observe the patient’s progress, and To evaluate the need for changes in the treatment plan.The medical condition of the patient must be describedMust be documented to support the goals for the patient and the needfor skilled nursing services.48
Skilled Documentation Documentation needs to allow a reviewer todetermine whether: Services furnished safely and effectively Services are reasonable and necessary Documentation supports duration and quantity49
Skilled Documentation Documentation should include the following The individual’s medical assessment including areas thatare relevant to the services provided to the individual The skilled services provided and the individualsresponse to these services The continued need for these services based on theindividual’s response to the plan The influencing and complicating factors related to theindividual’s illness or injuries The complexity of the service to be performed50
Skilled Documentation When documenting a skilled service it is important toinclude communication between team members: The individual’s medical condition Development of a plan with measurable goals for the skilledstay Changes in the plan of care The individual’s progress toward goals Training provided to the individual and caregivers51
Skilled Documentation The clinical record should be specific and descriptiveto the skilled care of the individual Avoid general statements that do not support thecare provided52
NOT Skilled Documentation The following examples does not sufficientlydescribe the reaction of the patient to his/her skilledcare: Patient tolerated treatment wellActivities of Daily Living (ADLs) need assist of oneContinue with plan of carePatient remains stableContinue to encourage fluidsAll needs anticipated by staffSafety measures in place53
Documentation Skilled or Not? Documentation supports the removal of a Foley catheterwith notation that individual will be encouraged to voidevery two hours The next dated shift documentation does not addressvoiding Further documentation supports “voiding pattern every2 hours for 3 days” with no further documentation The next note states “up to BR with 380 cc clear yellowurine. 39 cc after void on bladder scan. No abdominaldiscomfort upon palpation. “54
Skilled Nursing CareTips for documenting to support specific diagnosis codes orsymptoms1. Know the primary diagnosis2. Document on the skilled nursing assessments that take placeon a daily basis3. Capture skilled treatments that are performed and monitoredon a daily basis4. Always try to paint the picture of what skilled care is beingprovided to the patient based on the patient’s diagnosis55
Daily Skilled Documentation Guidelines Pneumonia/Pulmonary Diseases Vital signsLung AssessmentsCoughShortness of breath/endurance levelUse of supplemental oxygen/oxygen saturation resultsSkin colorUse of accessory musclesMedications and responses to these medicationsLab results56
Daily Skilled Documentation Guidelines Pneumonia/Pulmonary Diseases : Skilled nursing required for daily nursing observation forsigns of exacerbation of COPD. Vital Signs- BP-132/80,Pulse 86, Respirations 20. Lung sounds clear. No cough.Resident continues to be short of breath with exertionfrom bed/chair to dining room. Requires O2 at 2 L via nasalcannula continuously. HOB elevated secondary toresident’s experiencing SOB while lying flat.57
Daily Skilled Documentation Guidelines Hip or Knee Replacement/Fracture of Hip Level of pain/response to pain medicationsSurgical site conditionStaples and suturesAny hip precautionsCirculation or sensation assessmentUse of Continuous Passive Motion (CPM) if ordered/responseWeight bearing status and ability to maintain itUse of anticoagulants/adverse reactionsLab results58
Daily Skilled Documentation Guidelines Hip or Knee Replacement/Fracture of Hip MoreSpecific Documentation Patient received from therapy. New pain medicationadministered 30 minutes prior to therapy was effectivetoday. Patient rates pain at 0/10 at this time. Incision at lefthip is intact and well approximated with 19 staples.Redness noted at incision. Slight yellow serous drainage.Nurse Practioner to visit this afternoon. Skilled nursingassessments required daily to assess for complicationsrelated to hip replacement surgery.59
Daily Skilled Documentation Guidelines Anticoagulation Therapy Medication administeredSigns or symptoms of bleedingLab resultsPainPallor or cyanosisEducation to individual or caregiver and responseNew orders60
Daily Skilled Documentation Guidelines Urinary conditions/Urinary Tract Infections Urine color, clarity or odorBurning or pain with urinationFrequency or urgencyChange incontinenceOther painLab resultsMedications administered and the individual’s responseCathetersDialysis61
Nursing Documentation for Training 30.2.3.3 - Teaching and Training Activities Teaching and training activities, which require skillednursing or skilled rehabilitation personnel to teach apatient how to manage their treatment regimen,would constitute skilled services.62
Example of Teaching and Training Teaching self-administration of injectable medications or a complex range of medications;Teaching a newly diagnosed diabetic to administer insulininjections, to prepare and follow a diabetic diet, and toobserve foot-care precautions;Teaching self-administration of medical gases to a patient;Gait training and teaching of prosthesis care for a patient whohas had a recent leg amputation;Teaching patients how to care for a recent colostomy orileostomy63
Documentation for Teaching and Training The documentation must describe all efforts thathave been made to educate the patient/caregiver, The resident’s responses to the training. Can the resident demonstrate back the trainingprovided. The medical record should also describe the reasonfor the failure of any educational attempts, ifapplicable.64
Nursing Documentation Must Support the LOS Under PDPM, since the patient diagnosis will besupporting the reimbursement of the CMI for PT, OTand Nursing, BOTH therapy and nursing mustdemonstrate that skilled care, related to thediagnosis for the reimbursement is still necessary If nursing documentation does not support skilledcare for the diagnosis CMS might say Why didn’t you discharge the patient off Part A services?65
Skilled Therapy FocusPANAC ANNUAL CONFERENCE 2020
Therapy Requirements to Support Skill MBPM §30.2.1 - Skilled Services Defined Furnished pursuant to physician orders Require the skills of qualified technical or professionalhealth personnel Skilled care may be necessary to improve a patient’s current condition, to maintain the patient’s current condition, or to prevent or slow further deterioration of the patient’scondition.67
30 - Skilled Nursing Facility Level of Care - GeneralCare in a SNF is covered if all the following are met: The patient requires skilled nursing services or skilledrehabilitation services The patient requires these skilled services on a dailybasis The daily skilled services can be provided only on aninpatient basis in a SNF The services delivered are reasonable and necessary forthe treatment of a patient’s illness or injuryPANAC ANNUAL CONFERENCE 202068
How is “daily” basis defined for therapy? A patient whose inpatient stay is based solely on theneed for skilled rehabilitation services would meetthe “daily basis” requirement when they need andreceive those services on at least 5 days a week. If therapy services are provided less than 5 days aweek, the “daily” requirement would not be met Note: if therapy doesn’t meet skilling criteria,nursing mustPANAC ANNUAL CONFERENCE 202069
Considerations for Therapy Delivery Coverage criteria unchanged for intensity Patient care needs is the focus Medical Necessity TypeDurationIntensitySkillPDPM is a reimbursement model change,not a clinical change70
Reduction in Therapy? Underutilization concerns CMS is watching71
Ramifications and Risks Under PDPM Therapy intensity will no longer be used forreimbursement Documentation must support reasonable andnecessary care and demonstrate outcomes CMS will be monitoring changes in intensity Administrators will want to see demonstration ofoutcomes to justify ongoing therapy72
Therapy Metrics
Therapy Frequencyof ServicesModes74
The evaluating therapists should provide input regarding the appropriate clinical minutes the patientcan benefit from.If the evaluating therapist determines the care needsbased on the resident needs, the intensity of therapyshould remain like that under RUGSPANAC ANNUAL CONFERENCE 202075
Frequency is times per week Are the therapists developing plans of care for 5x perweek to meet skilled requirements? Are they providing the plan frequency?NOTE: audits often reveal less therapy than the plan A common tactic is 5x BETWEEN OT and PTPANAC ANNUAL CONFERENCE 202076
The modes of therapy provided, as outlined by CMS include: IndividualGroupCo-treatmentConcurrent CMS originally stated that delivery of therapy should remainmostly individual, with a cap of 25% concurrent and group perdiscipline.Covid has certainly helped this metric!PANAC ANNUAL CONFERENCE 202077
DisciplineInvolvement Your staff mix of Therapists and licensed TherapistAssistants should be monitored. Especially if you have contract therapy, you shouldknow that your Therapist-Assistant requirements arebeing met. Supervisory visits are being documented Progress notes are completed and signed timely Goals are updated to demonstrate progressPANAC ANNUAL CONFERENCE 202078
PDPM Therapy Metrics Monitoring of therapy utilization PDPM compared to current/historical RUGs IV PPS Performance changes Therapy outcomesLength of StayDiagnosis coding supported by therapy documentationDocumentation supports modes79
Specific Therapy Documentation Risks Resident is mostly “skilled” for rehab yet frequencyis less than 5x/week. Coding of minutes includes refusals or non-skilledrepetitive walking and/or exercise (that could bedone by restorative) Documentation does not support reasonable andnecessary care, no progress, extended LOSPANAC ANNUAL CONFERENCE 202080
Systems to Support Defensible Documentation Utilize the entire IDT to review documentationlooking for skill, painting the picture and key words READ the documentation, really Use your Triple Check meeting as a time to catchdocumentation and coding errors Have baseline knowledge regarding root causes oferrors in your building External auditsPANAC ANNUAL CONFERENCE 202081
Thanks for your attention!Please submit to Kay.Hashagen@lw-consult.comOr call (410) 207-8338PANAC ANNUAL CONFERENCE 202082
20 Improved Doc: Primary Condition is Pneumonia Mr. Jones requires skilled care for his pneumonia. His respiration are labored with an expiratory wheeze and rales bilaterally. O2 saturation is 94% o