Transcription
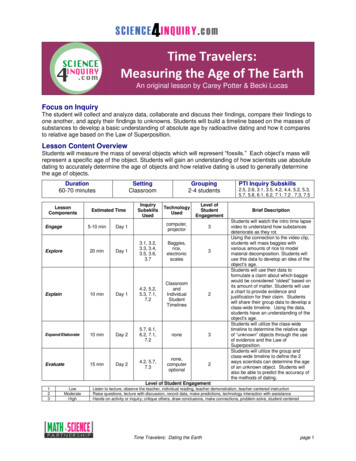
NameCHAPTER 6ClassDateThe Rock and Fossil RecordSECTION3 Absolute Dating: A Measure of TimeNational ScienceEducation StandardsBEFORE YOU READAfter you read this section, you should be able to answerthese questions:ES 2b How can geologists learn the exact age of a rock? What is radiometric dating?What Is Radioactive Decay?Geologists can use the methods of relative dating tolearn whether a rock is older or younger than anotherrock. However, they often also need to know exactly howold a rock is. Finding the exact age of an object is calledabsolute dating. One way to learn the age of a rock is touse unstable atoms.All matter, including rock, is made of atoms. All atomsare made of three kinds of particles: protons, neutrons,and electrons. All of the atoms of an element, such asuranium, have the same number of protons. However,some atoms of an element have different numbers of neutrons. Atoms of an element that have different numbersof neutrons are called isotopes.Many isotopes are stable and are always in the sameform. However, other isotopes are unstable and canbreak down into new isotopes of different elements. Anunstable isotope is also called a radioactive isotope.Radioactive decay happens when a radioactive isotopebreaks down into a new isotope.STUDY TIPLearn New Words As youread, underline words thatyou don’t understand. Whenyou learn what they mean,write the words and theirdefinitions in your notebook.READING CHECK1. Define What are isotopes?ProtonNeutronAfter radioactivedecay, an isotopeof a new elementis left. The newisotope is stable.ElectronThis isotope is unstable,or radioactive.TAKE A LOOK2. Compare How is aradioactive isotope differentfrom a stable isotope?Radioactive isotopes candecay in different ways.During one kind of radioactivedecay, a neutron becomes aproton and an electron.The electron moves to adifferent part of the atom.Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.Interactive Textbook97The Rock and Fossil Record
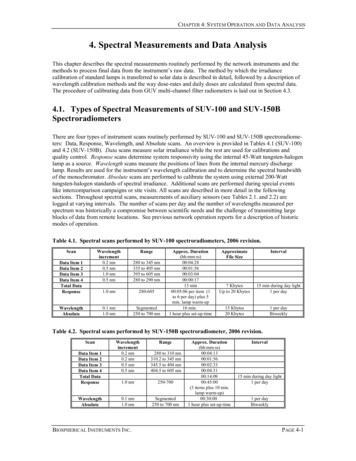
NameSECTION 3ClassDateAbsolute Dating: A Measure of Time continuedCritical Thinking3. Infer What happens tothe amount of parent isotopein a rock with time? Whathappens to the amount ofdaughter isotope?RADIOMETRIC DATINGA radioactive isotope is also called a parent isotope.Parent isotopes break down into daughter isotopes.Because of radioactive decay, the amounts of parent anddaughter isotopes in a rock are always changing. However,they change at a constant, known rate. Therefore, scientists can learn the age of a rock by studying the amounts ofparent and daughter isotopes in it.Radiometric dating is the process of determining theabsolute age of a sample based on the ratio of parent isotope to daughter isotope. In order to use radiometric dating, you need to know the half-life of the parent isotope.The half-life of a radioactive isotope is how long ittakes for half of a sample of the isotope to decay. Forexample, imagine that a parent isotope has a half-life of10,000 years. A sample of this isotope has a mass of 12 mg.After 10,000 years, only one-half, or 6 mg, of the samplewill be left. YEARS0ARENT ISOTOPE MG4HIS SAMPLE CONTAINS MG OF A PARENTISOTOPE 4HE ISOTOPEHAS A HALF LIFE OF YEARS YEARS0ARENT ISOTOPE MG ?!FTER ONE HALF LIFE OF THE ORIGINALMASS OF PARENTISOTOPE IS LEFT YEARS0ARENT ISOTOPE MG ?!FTER TWO HALF LIVES OR OFTHE ORIGINAL MASS OFPARENT ISOTOPE IS LEFT YEARS0ARENT ISOTOPE MG?!FTER THREE HALF LIVES OR OF THE ORIGINAL MASS OFPARENT ISOTOPE IS LEFT Math Focus4. Calculate Fill in the blanklines in the figure with themass of parent isotope that isleft at each step.The half-lives of different isotopes can be very different. Some parent isotopes have half-lives of more than4 billion years. Others have half-lives of only about 6,000years. Very old rocks can be dated only if isotopes withlong half-lives are used. Very young rocks can be datedonly if isotopes with short half-lives are used.How do scientists know which isotope to use to findthe age of a rock? They use information about the relative age of the rock to guess about how old the rock is.Then, they find its age, using an isotope that is useful fordating rocks of that age.Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.Interactive Textbook98The Rock and Fossil Record
NameSECTION 3ClassDateAbsolute Dating: A Measure of Time continuedWhat Isotopes Can Be Used forRadiometric Dating?Remember that different parent isotopes have differenthalf-lives. Each parent isotope can be used to date rocks ofdifferent ages.POTASSIUM-ARGON METHODPotassium-40 is one isotope that is often used inradiometric dating. It has a half-life of 1.3 billion years.It decays to produce the daughter isotope argon-40.Scientists usually use the potassium-argon method todate rocks that are older than about 1 million years.URANIUM-LEAD METHODUranium-238 is also used for radiometric dating. Ithas a half-life of 4.5 billion years. It decays to producelead-206. Scientists use the uranium-lead method to daterocks that are older than about 10 million years.READING CHECK5. Explain Using relativedating, a scientist learns thata rock is about 50,000 yearsold. Can the scientist use thepotassium-argon methodto find the exact age of thisrock? Explain your answer.RUBIDIUM-STRONTIUM METHODRubidium-87 is also used for radiometric dating. It hasa half-life of about 48 billion years. It decays to producethe daughter isotope strontium-87. The half-life ofrubidium-87 is very long. Therefore, this method is onlyuseful for dating rocks older than about 10 million years.CARBON-14 METHODCarbon-14 is a radioactive isotope of the element carbon.Carbon-14, along with the other isotopes of carbon, combines with oxygen to form the gas carbon dioxide. Plantsuse carbon dioxide to make food. Therefore, living plantsare always taking in small amounts of carbon-14. Animalsthat eat plants also take in carbon-14 from the plants.When a plant or animal dies, it stops taking in carbon-14.The carbon-14 already in its body starts to decay to producenitrogen-14. Carbon-14 has a short half-life: only 5,730 years.Therefore, this method can be used to date the remains oforganisms that died in the last 50,000 years.Parent isotopeDaughter isotopeHalf-lifePotassium-40READING CHECK6. Describe How do animalstake in carbon-14?TAKE A LOOK7. Identify Fill in the spacesin the chart to show thefeatures of different right by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.Interactive Textbook99The Rock and Fossil Record
NameClassDateSection 3 ReviewNSESES 2bSECTION VOCABULARYabsolute dating any method of measuring theage of an event or object in yearshalf-life the time required for half of a sampleof a radioactive isotope to break down byradioactive decay to form a daughter isotopeisotope an atom that has the same number ofprotons (or the same atomic number) as otheratoms of the same element do but that has adifferent number of neutrons (and thus adifferent atomic mass)radioactive decay the process in which aradioactive isotope tends to break down into astable isotope of the same element or anotherelementradiometric dating a method of determiningthe absolute age of an object by comparing therelative percentages of a radioactive (parent)isotope and a stable (daughter) isotope1. Describe How is radioactive decay related to radiometric dating?2. Calculate A parent isotope has a half-life of 1 million years. If a rock contained20 mg of the parent isotope when it formed, how much parent isotope would beleft after 2 million years? Show your work.3. List What are two radioactive isotopes that are useful for dating rocks that areolder than 10 million years?4. Apply Concepts A geologist uses relative dating methods to guess that a rock isbetween 1 million and 5 million years old. What is one radioactive isotope thegeologist can use to learn the exact age of the rock? Explain your answer.5. Infer Why can’t geologists use the carbon-14 method to date igneous rocks? Whycan’t they use the carbon-14 method to date dinosaur bones?Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.Interactive Textbook100The Rock and Fossil Record
Earth Science Answer Key continued2. After 1 million years, there would be (1/2) 8. Possible answers: There was no deposition9.10.11.12.(20 mg) 10 mg of parent isotope remaining.After 2 million years, (1/2) (1/2) (20 mg) 5 mg of parent isotope would remain.3. uranium-238, rubidium-874. Potassium-40, because it can be used to daterocks that are older than about 1 million years.5. C-14 dating can be used only on the remainsof living organisms. Igneous rocks do notcontain these remains. C-14 dating can beused only on remains that are less than50,000 years old. Dinosaur bones are olderthan this.happening at that time; there was a lot oferosion happening at that time.erosion, nondepositiona place where part of a sequence of parallelrocks is missingRocks are pushed up and eroded. Later, sediment is deposited on top of the eroded rock.The rock layers below an angular unconformity are tilted and may be any kind of rock.Review1. An unconformity can form if no sediment is2.3.4.5.deposited for a long time. An unconformity canalso form if layers of rock are eroded away.an angular unconformityThe youngest rock layers are at the top, andthe oldest rock layers are at the bottom.to interpret rock sequences and to identifyrock layersA sequence of rock layers is uplifted anderoded. Then, sediment is deposited on theexposed rock layers. After a while, the sediment turns into rock.SECTION 4 LOOKING AT FOSSILS1. Body fossils are fossilized parts of an2.3.4.5.6.SECTION 3 ABSOLUTE DATING: AMEASURE OF TIME7.1. atoms of an element with different numbers2.3.4.5.6.7.of neutronsRadioactive isotopes can break down. Stableisotopes do not break down.The amount of parent isotope decreases, andthe amount of daughter isotope increases.8 mgNo, because K-Ar dating can be used only forrocks that are older than about 1 million years.by eating plantsParent isotopeDaughterisotope8.9.10.Review1. tracks, burrows, coprolites2. Only a small fraction of the organisms thatHalf-lifePotassium-40argon-401.3 billion yearsUranium-238lead-2064.5 billion yearsRubidium-87strontium-8748 billion yearsCarbon-14nitrogen-145,730 yearsorganism. Trace fossils are signs that anorganism once existed.shells, teeth, boneswhen minerals replace an organism’s tissueThey are not made of parts of an organism,but they show that an organism once existed.an impression left in sedimentthe kinds of organisms that lived in the past;how the environment has changed; howorganisms have changedOrganisms that had hard parts or lived incertain environments were more likely to befossilized when they died.They compare fossils. They also comparefossils to living organisms.Answers include: according to their age, byabsolute and relative dating methodstheir shellshave existed in Earth’s history have beenfossilized. Many fossils have not yet beendiscovered.3. A beetle, because fossils in amber are madewhen an organism gets stuck in tree sap.Smaller organisms that can be found ontrees are more likely than other organismsto become fossils in amber.4. The climate was probably much warmerwhen the plant was alive.5. It must be common throughout the world. Itmust have existed for a relatively short geologic time. It must be easy to identify.Review1. Radiometric dating uses known rates ofradioactive decay to determine the age of arock sample.Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.Interactive Textbook Answer Key40Earth Science
Radiometric dating is the process of determining the absolute age of a sample based on the ratio of parent iso-tope to daughter isotope. In order to use radiometric dat-ing, you need to know the half-life of the parent isoto