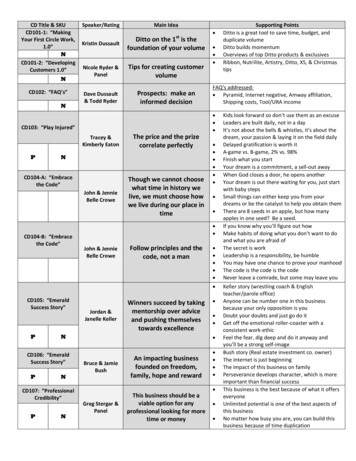
Transcription
6/7/21ArtificialIntelligence (AI)and telemedicineLeo Semes 2021Speaker Bureau, Consultant - Maculogix66414-PDDisclosures Leo Semes, OD , FAAO Professor Emeritus of Optometry and VisionScience, UABSpeaker Bureau - RegeneronScientific Advisory Board - EyePromiseStock options - Eye Promise ( 0.01%ownership), HPO ( 0.01% ownership)Utah Optometric Association 2021212Everydayexamples ofAIWhat isAI?“inspired by your browsing”“Based on your zip code”Google translateVoice-generated textAuto-fill textSports-related applications (“analytics”)JFGIArtificial Intelligence or Always ificial intelligence. Accessed August 8, 201945Impact of AIMonday October 14, 2019WSJSome relevant headlines . . Many jobs will disappear andwon’t be replaced.A brief history of AI We’ll be healthier and live a lotlonger. AI will be a constant companion.One of the aims of AI is to save time and labor;Think of ”A world without work.”15171
6/7/21Turing machinesFirst described by Alan Turing 1936–7, are simpleabstract computational devices intended to helpinvestigate the extent and limitations of what can becomputed.Turing’s ‘automatic machines’, as he termed them in1936, were specifically devised for the computing of realnumbers. They were first named ‘Turing machines’ byAlonzo Church (1937). Today, they are considered to beone of the foundational models of computability andcomputer achine/1819The early history of AIThe early history of AIØ1956 – “Artificial intelligence”coined by John McCarthy on thepremise that every aspect oflearning or any feature ofintelligence can be soprecisely described that amachine can be made tosimulate it.201959 – “Machine learning”created by Arthur Samuel focuses on the learning feature ofintelligence by developing algorithmsthat extract generalized principles fromdata. ML differs from other automatedapproaches that required that thedescriptive rules be defined byhuman experts and implementedby programmers21Ahh, the ‘70sRemote AI applications (telemedicinearound us)Regression analysis of“big data” to produceWho has had a Zoom visit as a patient orprovider?THE AlgorithmAnother aspect“Analytics”22272
6/7/21When was thisstatementmade?The year was 2012“Machines will replace 80% of doctors in ahealthcare future that will be driven byentrepreneurs, not medical professionals.”-Vinod Khosla, co-founder of Sun Microsystems 2012 2014 2016 2018Five years later (2017), he made the following statement,"The role of the radiologist will be obsolete in five la-radiologists-obsolete-five-years.html. Accessed May 30,2017.Do we need doctors or algorithms? Posted Jan 10, 2012 by Vinod -algorithms/. Accessed May 30, ed-with-machines Accessed May 30, 2017.343522 WMHow wouldyou as aclinicianmanage thispatient? presents with 2day history of aunilateral floater 22 WM presents with 2-day history of a unilateralfloater non-contributory medical, allergy, familyhistories non-contributorymedical, allergy,family histories UCVA 20/20 VCVA 20/203637Machine learning aids in diagnosisDeep learning may make the diagnosisRequires human intervention Further history Fundus photo features Order additional agnosticconclusionSchm idt-Erfurth U, Sadeghipour A , G erendas BS, W aldstein SM , Bogunović H .Artificial intelligence in retina. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2018 Nov;67:1-29.38Schm idt-Erfurth U, Sadeghipour A , G erendas BS, W aldstein SM , Bogunović H .Artificial intelligence in retina. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2018 Nov;67:1-29.393
6/7/21Paging Dr. AIPaging Dr. AIPromisesPromises AI can make diagnoses (BC, DR,AMD, glaucoma) Algorithms can guide roboticsurgery AI may reduce medical errors AI can make diagnoses (DR,AMD, glaucoma) Algorithms can guiderobotic surgery AI may reduce medicalerrorsConcerns Algorithms depend onaccurate data input. will machine learningexacerbate human biases? are data from one populationextrapolatable to others? TMI What if algorithmscontinue to generateslightly erroneousrecommendations?4142Demands of AI for healthcareDemands of AI for healthcare Decrease costs without increasing burden onproviders (like EHRs) Decrease costs without increasing burden onproviders (like EHRs) Improve quality without imparting bias or violatingprivacy4344Durability & LongevityWith cautions (Peterson , ED. Machine Learning, Predictive Analytics, and ClinicalMachine learning focuseson the featureextraction of AI.These and deep learningmethods have beenapplied to retinal imagingfor classification,segmentation andprediction(CFP and OCT, e.g.,)Practice: Can the Past Inform the Present? 2019 JAMA) Published Online: November 22, 2019.doi:10.1001/jama.2019.17831Ø The widespread availability of EHR data and the latest ML analytictechniques offer unique opportunities for achieving better healthoutcomes.Ø Combined, data and ML will likely facilitate the development ofnumerous predictive analytic tools in medicine.Ø However, before such advances can transform how clinical decisionsare made, the challenges of effective application will need to beovercome.45464
6/7/21AI in medicine – “expert systems” 1970s – “MYCIN” a successful automated system torecommend appropriate antibiotics using a series of ifthen rules (think 1’s and 0’s)Some examples of AI in medicine performance was superior to that of infectious diseasespecialists, but failed to gain clinical acceptancebecause the variability and complexities of diseasepresentations were insurmountable to do by hand[recall that the if-then decisions were required to bedefined by experts]4950AI in medicine revisited (1990’s) Enter Machine Learning“rules” learned by algorithms directly from a setof examples instead of being encoded by humansLet’s define some terms Contemporarily AI machine learningrequires a set of biomarkers (e.g., CRT* fromOCT), features, measured from data a training setof features (examples known as labels), a classifierlearns to recognize the correct label from newlyseen featuresmachine learningdeep neural networksconvolutional neural networks*central retinal thickness5152AI progress(1990’s)53 The human brain is a series of neuralnetworks – it’s how we function asclinicians. In machine learning artificial neuralnetworks (ANNs) were recognized asgood classifiers to detect / diagnose /screen for myocardial infarction in patientspresenting with chest pain, renal cancer from ultrasound diabetic retinopathy from fundusimagesas equivalent to the same level as expertclinicians!AI progressmilestone 2012 Development of deep neuralnetworks (DNN’s) whichrepresent a series of ANN’s thatimprove performance outcomes(increased efficiency). Advancements in computationalpower allowed DNN’s to betrained and applied within areasonable time (DNN’s canexceed classic machine learning).Deep learningDNN’s can act as feature extractorsinstead of just classifiers.545
6/7/21Do you recognize this?AI next steps – closerto human visual cortex2015 - Convolutional neural networks(CNN’s) are shown to operate like and performbetter than humans at the task of imageidentification.“The paradigm shift to AI has becomeirreversible.”Scientific-American, 2015. World Changing Ideas 2015. om/magazine/sa/2015/12-01/Accessed November 21, t/uploads/2015/07/ibm-watson 02.jpg59Elementary,my Dear WatsonAn algorithm forpatient careElementary,my Dear WatsonAn algorithm forpatient care(end /watson medical ages/1/15/watson medical algorithm.png61Medscape October 19, 20?16“The Future of TeleretinalImaging in DiabeticRetinopathy Screening”Ophthalmic examples66676
6/7/21Medscape October 19, 2016Some Recent Advances in Diagnosis“The Future of TeleretinalImaging in DiabeticRetinopathy Screening” 7-field fundus photography (Gold Standard - posterior pole) Ultrawide fundus photography (for PredominantlyPeripheral Diabetic Retinopathy PPDR) 2015-2016Silva PS, Horton MB, Clary D, et al. Identification of Diabetic Retinopathy and Ungradable Image Rate with Ultrawide Field Imaging ina National Teleophthalmology Program. Ophthalmology. 2016 Jun;123(6):1360-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2016.01.043. Epub 2016Mar 2.Silva PS, Dela Cruz AJ, Ledesma MG, et al. Diabetic Retinopathy Severity and Peripheral Lesions Are Associated with Nonperfusion onUltrawide Field Angiography. Ophthalmology. 2015 Dec;122(12):2465-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2015.07.034. Epub 2015 Sep 6.Silva PS, Cavallerano JD, Haddad NM, et al. Peripheral Lesions Identified on Ultrawide Field Imaging Predict Increased Risk of DiabeticRetinopathy Progression over 4 Years. Ophthalmology. 2015 May;122(5):949-56. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2015.01.008. Epub 2015 Feb19 O gunyem i O, G eorge S1, Patty L, Teklehaim anot S, Baker R.Teleretinal screening for diabetic retinopathy in six LosAngeles urban safety-net clinics: final study results. AM IAAnnu Sym p Proc. 2013 Nov 16;2013:1082-8. eCollection2013.68And most recently . . . A u t o m a t e d assessmentof diabetic retinopathy.69Where do we go from here?Where do we go from here?“The era of subclinical diagnosis has begun and a novelapproach to interpretation is required.”“The era of subclinical diagnosis has begun and a novelapproach to interpretation is required.”Schmidt-Erfurth U, Sadeghipour A, Gerendas BS, Waldstein SM, Bogunović H. Artificial intelligence in retina. ProgRetin Eye Res. 2018 Nov;67:1-29.Schmidt-Erfurth U, Sadeghipour A, Gerendas BS, Waldstein SM, Bogunović H. Artificial intelligence in retina. ProgRetin Eye Res. 2018 Nov;67:1-29.Ø If we are to retain control over our future, we willhave to learn to harness output from intelligentalgorithms and apply AI in a constructive manner.7576Another algorithm fordiabetic retinopathystaging (note numerousSolomon SD, Goldberg MF ETDRS Grading of Diabetic Retinopathy: Still the Gold Standard?Ophthalmic Res. 2019 Aug 27:1-6.levels)Standard photographs 1, 2A2B MildModerate,SevereVery SevereProliferative (non-and high risk) 2019 S. Karger AG, Basel77787
6/7/21Automated algorithmfor diabetic retinopathyA closer look Automated algorithmfor diabetic retinopathyTrains machines inimage readingTraining image readingConsider how tedious it would be do do this on each fundus photo of a patient with diabetes.It’s easier to have a machine decide on the 1’s and 0’s7980Why is such anexactingstaging systemsignificant?Conclusions (post-hoc analysisof RIDE and RISE data) 58.6% of patients treated for DME with ranibizumab showedat least a one-step improvement @ 24 months. 40% had no improvement and 3.2% had regression. Patients with stability or improvement (98.6%) hadBSCVA gains of 15.1, 14.2, 11.3 and 11.2 ETDRSletters for 3-, 2-, 1- and No-step improvement.Clinically significant improvement in staging and performance!Ip MS, Zhang J, Ehrlich JS. The Clinical Importance of Changes in Diabetic Retinopathy Severity Score.Ophthalmology. 2017 May;124(5):596-603.8182I Dx-DR is FDA cleared*Ø ClassificationØ SegmentationØPrediction90918
6/7/21Breaking News!FromOptometryTimesyear20199798automated screening forWhat about AMD?AMD Automated OCT segmentation fordrusen, RPE irregularities and analysisof GA areaThe nextfrontiersGlaucoma Digital analysis of RNFL and mRNFL OCT-A correlation of macular andperipapillary vessel densityThe AREDS staging system is established.for early diagnosis and tracking trajectory99100125 u (vein width @ disc margin)The Beckman ClassificationFerris FL 3rd, W ilkinson CP, Bird A, ChakravarthyU, Chew E, Csaky K, Sadda SR; Beckm an Initiative forM acular Research Classification Com m ittee.Clinical classification of age-related m aculardegeneration. O phthalm ology. 2013 Apr;120(4):84451. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.10.036. Epub 2013 Jan16.Automated segmentation(OCT) for AMD125 u (vein width @ disc margin)101Why we need it1049
6/7/21Underdiagnosis of early AMDa) no AMDb) early AMDc) Intermediate AMDd) advanced AMD with GAe) advanced AMD with CNVVenhuizen FG , et al. Autom ated Staging of Age-Related M acularDegeneration U sing O ptical Coherence Tom ography. Invest O phthalm ol VisSci. 2017 Apr 1;58(4):2318-2328. (Netherlands, Sw itzerland)106107Automated segmentation of AMDPerformance of two human readers vs. the algorithmNobody’s perfect. Machine-learningclassification as early AMD, but thered arrows show a patch of GA.Venhuizen FG , et al. Autom ated Staging of Age-Related M acular Degeneration U sing O ptical CoherenceTom ography. Invest O phthalm ol Vis Sci. 2017 Apr 1;58(4):2318-2328.109Venhuizen FG , et al. Autom ated Staging of Age-Related M acular Degeneration U sing O ptical CoherenceTom ography. Invest O phthalm ol Vis Sci. 2017 Apr 1;58(4):2318-2328.110ConclusionsAutomated drusen detectionDrusen area overlaid on en face OCT angiograms.Top and bottom rows – drusen areafrom 2 representative pts.projected on the inner, outer retinaand choriocapillaris to show theabsence of motion artifacts in theproposed protocol.Good agreement between manualand automated grading.inner retinaZhao R, et al. Autom ated drusen detection in dry age-related m acular degeneration by m ultiple-depth, en faceoptical coherence tom ography. Biom ed O pt Express. 2017 O ct 17;8(11):5049-5064.111outer retinachoriocapillarisZhao R, et al. Autom ated drusen detection in dry age-related m acular degeneration by m ultiple-depth, en faceoptical coherence tom ography. Biom ed O pt Express. 2017 O ct 17;8(11):5049-5064.11210
6/7/21From DEEP MIND, Moorfields, LondonDe Fauw J, Ledsam JR, Romera-Paredes B, et al. Clinically applicable deep learning for diagnosis and referral inretinal disease. Nat Med. 2018 Sep;24(9):1342-1350.114116Challenges in glaucoma for AI Six glaucoma experts evaluated 75 optic discphotographs under both viewing conditions. Interobserver agreement in estimating verticalcup-to-disc ratios was moderate (stereoscopicmedian weighted kappa, 0.67); individual expertsdiffered by as much as 0.2 disc diameters (DD)monoscopically and 0.16 DD stereoscopically. Intraobserver agreement in assessingglaucomatous disc damage was substantial(median kappa, 0.76). Interobserver agreement in assessingglaucomatous damage was moderate(stereoscopic median kappa, 0.50).No FDA-approval forglaucoma diagnosis orprogression.Wish listØ Accurate diagnosisØ Trajectory predictionØ Target IOPVarma R1 Steinmann WC, Scott IU. Expert agreement in evaluating the optic disc for glaucoma.Ophthalmology. 1992 Feb;99(2):215-21.118119Correlating macular ganglion-cell thickness andmacular vessel density via AIJune 13, 2020Segmentation free no need to manuallyassess artefacts, e.g. Correlating macular ganglion-cell thickness and macular vessel density via AI Subjects: 100 plus 73 for neural net training.The test group consisted of 32 healthy, 33 early, and 35 advanced glaucoma subject Macular GCIPLT and macular vessel density (MVD) were measured usingSpectralis optical coherence tomography and Topcon swept-source opticalcoherence tomography, respectively.In differentiating normal and early glaucoma, the diagnostic power of macular GCIPLT(AUROC 0.67 to 0.81) was much better than that of macular vessel density (AUROC 0.50 to 0.60). Combining MVD with GCIPLT data using the neural network resultedin significantly enhanced diagnostic performance. (Better than allsectors of MVD or GCIPLT alone (all Ps 0.043).Park K, Kim J, Lee J. Macular Vessel Density and Ganglion Cell/Inner Plexiform Layer Thickness and TheirCombinational Index Using Artificial Intelligence. J Glaucoma. 2018 Sep;27(9):750-760.12012111
6/7/21June 13, 2020And this . . .122123 The fatal flaws in machine learningresearchMIKE REDDY FOR STAT June 3, 2021Every sliverlining has acloud143 Machine learning, a subset of AI driving billions ofdollars of investment in health care, is facing acredibility crisis, Casey reports. A growing list ofstudies rely on limited or low-quality data, fail tospecify their training approach and statisticalmethods, and don’t test whether they will work forpeople of different races, genders, ages, andgeographies. “We should inherently be more skepticalof any claims of long-term generalizability and stabilityof the results over time,” Matthew McDermott, aresearcher at the Massachusetts Institute ofTechnology.144AI will ewill allowtelemetric dataanalysisis here to stay inour daily livesand practices145is making inroadsin the ophthalmicspacewill be astransformative foroptometry as the lastfew decades of scopeof practice expansion14612
6/7/21Thank you,UOAStay safe and be well.14813
“The Future of Teleretinal Imaging in Diabetic Retinopathy Screening” OgunyemiO, George S1, Patty L, TeklehaimanotS, Baker R. Teleretinalscreening for diabetic retinopathy in six Los Angeles urban safety-net clinics: final study results. AMIA AnnuSympProc. 2013 Nov 16;2013:1082-