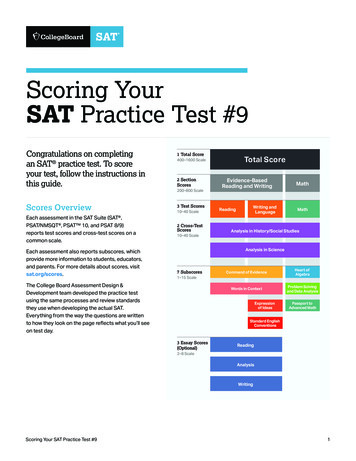
Transcription
SAT PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2TEST 2Your responses to the Physics Subject Test questions should be filledin on Test 2 of your answer sheet (at the back of the book).
SAT Online Physics Practice Tests:http://www.cracksat.net/sat2/physics/SAT Physics Practice Test: KinematicsSAT Physics Practice Test: Newton's LawsSAT Physics Practice Test: Work, Energy, and PowerSAT Physics Practice Test: Linear MomentumSAT Physics Practice Test: Curved and Rotational MotionSAT Physics Practice Test: OscillationsSAT Physics Practice Test: Electric Forces and FieldsSAT Physics Practice Test: Electric Potential and CapacitanceSAT Physics Practice Test: Direct Current CircuitsSAT Physics Practice Test: Magnetic Forces and FieldsSAT Physics Practice Test: Electromagnetic InductionSAT Physics Practice Test: WavesSAT Physics Practice Test: OpticsSAT Physics Practice Test: Thermal PhysicsSAT Physics Practice Test: Modern PhysicsSAT Physics Subject Test: Full-length Practice Test 1SAT Physics Subject Test: Full-length Practice Test 2
Useful Links:SAT Online Practice Tests: http://www.cracksat.net/tests/SAT Subjects Tests: http://www.cracksat.net/sat2/SAT Downloads: http://www.cracksat.net/sat-downloads/For more SAT information, please visit http://www.cracksat.netSAT Downloads:SAT real tests -real-tests.htmlSAT official guide tests -official-guide-tests.htmlSAT online course tests -online-course-tests.htmlSAT subject tests -subject-tests.htmlPSAT real tests 0 College Admission Essay essays/
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 275 Questions Time limit 1 hour You may NOT use a calculator.Part ADirections: Each set of lettered choices below refers to the numbered questions immediately following it. Selectthe one letter choice that best answers each question or best fits each statement, and then fill in the correspondingoval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set.Questions 1-5Questions 6-9fixed supportspringverticaloscillationsmA block of mass m undergoing simple harmonicmotion. Frictional forces are negligible and canbe ignored. Questions 1-5 relate to the ncyPeriodPosition of blockTotal mechanical energy of theblock(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)Alpha decayβ– decayβ decayElectron captureGamma decay6. Which type of decay would cause the number ofneutrons in the nucleus to decrease by 1 ?7. In which type of decay is the identity of thenucleus unchanged?8. Which type of decay ejects the heaviest particle?9. Which type of decay would cause the atomicnumber of the nucleus to increase?1. Once the motion is underway, which quantitydoes NOT remain constant?2. Which quantity is inversely proportional to thesquare root of the block’s mass?3. Which quantity would always be greater if theblock oscillated with a smaller force constant?4. The maximum speed of the block is proportionalto what quantity?5. The graph of which quantity (versus time) wouldlook like a sine wave?462 Cracking the SAT Physics Subject TestGO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2—ContinuedQuestions 10-1210. Which graph best depicts the electric fieldmagnitude along the x axis, from x –a to x a ?y11. Which graph best illustrates the electric potentialalong the x axis, from x –a to x a ? Qa–ax12. If a negative charge, –q, were moved along thex axis from x –a to x a, which graph bestdepicts the magnitude of the electric force itwould feel during this motion?–QAn electric dipole, a pair of equal but oppositecharges. Two isolated point charges are fixed in thepositions shown on the y axis; the positive charge islocated at the point (0, b) and the negative charge islocated at the point (0, –b). Questions 10-12 relate tothe graphs labeled (A) through (E) that appear below.(A)(C)(E)–aa–aa–a(B)–ax (D)–axaaaxxxGO ON TO THE NEXT PAGEThe Princeton Review Practice SAT Physics Subject Test 2 463
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2—ContinuedPart BDirections: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answersor completions. Select the one that is best in each case and then fill in the corresponding oval on theanswer sheet.13. Two people, one of mass 100 kg and the other ofmass 50 kg, stand facing each other on an icecovered (essentially frictionless) pond. If theheavier person pushes on the lighter one with aforce F, then1(A) the force felt by the heavier person is – F2(B) the force felt by the heavier person is –2F(C) the magnitude of the acceleration of the1lighter person will be of the magnitude2of the acceleration of the heavier person(D) the magnitude of the acceleration of thelighter person will be twice the magnitudeof the acceleration of the heavier person(E) None of the above14. Each of the following particles is projectedwith the same speed into a uniform magneticfield B such that the particle’s initial velocity isperpendicular to B. Which one would move in acircular path with the largest radius?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)ProtonBeta particleAlpha particleElectronPositron15. Which of the following best describes themagnetic field lines created by a long, straight,current-carrying wire?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)Rays that emanate from the wireCircles centered on the wireLines parallel to the wireLines perpendicular to the wireNoncircular ellipses centered on the wirestringθrod16. If the rod is uniform and has mass m, what is thetension in the supporting string?(mg sin θ )2(B) mg sin2(mgcos θ )(C)2mg(D)2(A)(E) mg17. A lightweight toy car crashes head-on intoa heavier toy truck. Which of the followingstatements is true as a result of the collision?I. The car will experience a greater impulsethan the truck.II. The car will experience a greater change inmomentum than the truck.III. The magnitude of the accelerationexperienced by the car will be greaterthan that experienced by the truck.(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)I and II onlyII onlyIII onlyII and III onlyI, II, and IIIGO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE464 Cracking the SAT Physics Subject Test
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2—ContinuedQuestions 18-19θmaxθA simple pendulum, composed of a bob of mass mconnected to the end of a massless rod, executessimple harmonic motion as it swings through smallangles of oscillation. The largest angle the pendulummakes with the vertical is denoted by θ max. Frictionaleffects are negligible and can be ignored, and thependulum is near the surface of the earth, whereg 9.8 m/s2.18. Which one of the following statements is true?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)AtAtAtAtAtθθθθθ 0, the tangential acceleration is 0. θ max, the tangential acceleration is 0. 0, the speed is 0. 0, the restoring force is maximized. θ max, the speed is maximized.19. Knowing which one of the following wouldenable you to calculate the length of thependulum?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)The mass of the bobThe period of the oscillationsThe tangential acceleration at θ 0The maximum speed of the bobThe acceleration at θ θ max20. A block is moving counter-clockwise in acircular path on a flat table. If the speed of theblock is increasing at the moment it is at theposition shown, which one of the five arrows bestillustrates the direction of the acceleration on theblock?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)ABCDE21. If a particle of charge –0.2 mC were placed at acertain location within an electric field, themagnitude of the electric force it would feel is1 N. What is the magnitude of the electric field atthis location? (1 mC 10–3 C)(A) 2,000 N/C(B)5,000 N/C(C) 20,000 N/C(D) 50,000 N/C(E) 500,000 N/CGO ON TO THE NEXT PAGEThe Princeton Review Practice SAT Physics Subject Test 2 465
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2—Continued22. Traveling at an initial speed of 1.5 106 m/s, aproton enters a region of constant magnetic field,B, of magnitude 1.0 tesla. If the proton’s initialvelocity vector makes an angle of 30 with thedirection of B, compute the proton’s speed 4seconds after entering the magnetic field.(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)5.0 10 m/s7.5 105 m/s1.5 106 m/s3.0 106 m/s6.0 106 m/s523. An object of mass 2 kg increases in speed from2 m/s to 4 m/s in 3 s. What was the total workperformed on the object during this timeinterval?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)4J6J12 J24 J36 J(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)2 cm A 10 cmA 5 cmA 10 cm10 cm A 12 cm12 cm A 24 cm26. A uniform bar is lying on a flat table. Besides thegravitational and normal forces (which cancel),the bar is acted upon by exactly two other forces,F1 and F2 , which are parallel to the surface ofthe table. If the net force on the rod is zero, thenwhich one of the following is true?(A) The net torque on the bar must also be zero.(B) The bar can accelerate translationally if F1and F2 are not applied at the same point.(C) The net torque will be zero if F1 and F2 areapplied at the same point.(D) The bar cannot accelerate translationally orrotationally.(E) None of the above3N2N25. Two traveling waves of equal frequency, one ofamplitude 4 cm and the other of amplitude 6 cm,superimpose in a single medium. Which of thefollowing best describes the amplitude, A, of theresultant wave?6N2 kg24. The figure above shows the forces acting onan object of mass 2 kg. What is the object’sacceleration?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)2 m/s22.5 m/s23 m/s23.5 m/s24 m/s2GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE466 Cracking the SAT Physics Subject Test
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2—ContinuedFQuestions 28-30R27. A uniform cylinder, initially at rest on africtionless, horizontal surface, is pulled by aconstant force F from time t 0 to time t T.From time t T on, this force is removed. Whichof the following graphs best illustrates the speed,v, of the cylinder’s center of mass from t 0 tot 2T ?(A)vtime2RsurfaceRA small box slides down a frictionless track in theshape of a quarter-circle of radius R. The box startsfrom rest at the top of the track, a height equal to 2Rabove a horizontal surface. At the moment the boxleaves the bottom of the track, a ball of the same massas the box is dropped from the same height at thebottom of the track.28. How fast is the box moving when it reaches theend of the track?(B)v(A) v time(B) v (C) v (D) v (C)gR2gRπgR2πgR(E) v π 2gRvtime(D)vtime(E)29. Which of the following quantities must decreaseas the box slides down the track?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)The normal force on the boxThe net force on the boxThe kinetic energy of the boxThe potential energy of the boxThe total mechanical energy (kinetic potential) of the boxvtimeGO ON TO THE NEXT PAGEThe Princeton Review Practice SAT Physics Subject Test 2 467
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2—Continued30. Once the box leaves the bottom of the slide,which of the following statements best describesthe motions of the box and the ball?(A) The ball hits the floor at the same time as thebox.(B) The ball hits the floor before the box does.(C) The ball hits the floor after the box does.(D) The acceleration of the box is greater thanthe acceleration of the ball.(E) The acceleration of the ball is greater thanthe acceleration of the box.31. An ellipsoid-shaped conductor is negativelycharged. Which one of the following diagramsbest illustrates the charge distribution and electricfield lines?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE468 Cracking the SAT Physics Subject Test
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2—Continued40 cm40 cmF35. A student is monitoring the pressure and absolutetemperature in a container of fixed volumefilled with an ideal gas as the gas is heated.Which of the following graphs best illustratesthe relationship between the pressure (P) andabsolute temperature (T) of the gas, assuming thatnone of the gas escapes from the container?(A)32. The figure above shows a square metal plate ofside length 40 cm and uniform density, lyingflat on a table. A force F of magnitude 10 N isapplied at one of the corners, parallel to one ofthe sides, as shown. What’s the torque producedby F relative to the center of the square?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)0 N-m1.0 N-m1.4 N-m2.0 N-m4.0 N-m33. A mover, exerting a steady force of 200 N, pushesa box of mass 50 kg across a flat wooden floor. Ifthe velocity of the box does not change while hepushes, what is the coefficient of kinetic frictionbetween the box and the floor?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)0.20.40.50.60.834. What principle is the basis for the transmission oflight through glass (fiber optic) cables, allowingthe signal to be sent even if the cable is bent?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)Photoelectric effectUncertainty principleLight diffractionLight polarizationTotal internal reflectionPT(B)PT(C)PT(D)PT(E)PTGO ON TO THE NEXT PAGEThe Princeton Review Practice SAT Physics Subject Test 2 469
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2—Continued36. Of the following types of waves, which typetravels at the greatest speed through vacuum?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)Radio wavesMicrowavesUltraviolet lightX-raysNone of the above; all these waves wouldtravel at the same speed.37. What would happen to the electrostatic forcebetween a pair of charged particles if bothcharges were doubled and the distance betweenthem were also doubled?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)It would decrease by a factor of 4.It would decrease by a factor of 2.It would remain unchanged.It would increase by a factor of 2.It would increase by a factor of 4.38. As a bat flies at a constant speed of 0.04 V towarda large tree trunk (where V denotes the speed ofsound), the bat emits an ultrasonic pulse. Thepulse is reflected off the tree and returns to thebat, which can detect and analyze the returningsignal. If the returning signal has a frequency of61 kHz, at approximately what frequency did thebat emit the original ultrasonic pulse?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)39. During practice, an athlete runs in a straight linefrom point X to point Y, and then back along thesame path from Y to X. If she runs at a constantspeed of 3 m/s from X to Y, and then at aconstant speed of 6 m/s from Y to X, what is heraverage speed for the entire run?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)3.5 m/s4 m/s4.5 m/s5 m/s5.5 m/s40. A sky diver jumps from an airplane. After “freefalling” for a while, she opens her parachute andher descent speed begins to decrease. Whileher descent speed decreases, let F denote themagnitude of the gravitational force on the skydiver and let D denote the magnitude of theupward force of air resistance (drag). Which ofthe following is then true?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)F DF DF D weight of the sky diverF – D weight of the sky diverF–D 056 kHz62 kHz68 kHz74 kHz78 kHzGO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE470 Cracking the SAT Physics Subject Test
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2—ContinuedcationQuestions 43-4541. The figure above shows a cation (a positiveion—that is, an atom that has lost one or moreelectrons) entering a mass spectrometer, whichcontains a region with a uniform magnetic field,B. Once in the magnetic field, the cation movesin a semicircular path in the direction indicated.What is the direction of B ?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)Upward in the plane of the pageTo the left in the plane of the pageTo the right in the plane of the pageOut of the plane of the pageInto the plane of the page42. A traveling wave has a frequency of 6.0 Hz, anamplitude of 0.2 m, and a wavelength of 0.5 m.What is its wave speed?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)0.1 m/s0.6 m/s1.2 m/s2.4 m/s3.0 m/sV2V1region ofmagnetic field12R12R2RRS1S2XYThe circuit shown contains two switches: S1, whichcan connect to point X, and S2, which can connect topoint Y.43. If switch S1 is left in the position shown in thefigure but switch S2 is connected to point Y, whatis the current through the resistor R ?V23RV(B) 2R3V2(C)2R(A)V1 V23RV V2(E) 1R(D)GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGEThe Princeton Review Practice SAT Physics Subject Test 2 471
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2—Continued44. If switch S2 is left in the position shown in thediagram, but switch S1 is connected to point X,what is the current through the resistor R ?(A)V14RV(B) 12R4V1(C)5R(D) 5V14R(E) (V1 V2 )2R45. If both switches are left in the positions shownin the diagram, what is the current through theresistor R ?(A) 02(V1 V2 )(B)11R4(V1 V2 )13 R2(V1 V2 )(D)5R(C)(E)6(V1 V2 )7R46. What does the second law of thermodynamics sayshould happen to an isolated, ordered system?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)Heat will flow into the system.Heat will flow out of the system.Work will be done by the system.Work will be done on the system.The entropy within the system will increase.47. The potential difference between the plates ofa charged, parallel-plate capacitor is equal to Xvolts. If the amount of charge on the POSITIVEplate is equal to Y coulombs, what is thecapacitance (in farads)?(A)X2YY2XY(C)X(B)(D)(E)2YX2XY48. A car, starting from rest, accelerates uniformlyat 4 m/s2 along a straight track. How far will ittravel in 6 s ?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)24 m48 m64 m72 m144 m49. An object is executing uniform circular motion.Which of the following quantities remain(s)constant during the object’s motion?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)Velocity and accelerationSpeed and velocitySpeed and accelerationAcceleration onlySpeed onlyGO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE472 Cracking the SAT Physics Subject Test
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2—ContinuedQuestions 50-53In the diagram accompanying each question,representative light rays from an illuminated object(labeled “O” in the diagrams) interact with an opticaldevice (or devices): a mirror, a lens, or a combinationof both. In each case, identify the optical device(s)—from among the choices below—that is/are most likelyin the dotted box.(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)Plane mirrorConverging lensDiverging lensPlane mirror and a converging lensPlane mirror and a diverging lens50.54. A superconductor is(A) a device used to study the collisions ofsubatomic particles that have beenaccelerated to near light speeds(B) a hollow, doughnut-shaped device containinga strong magnetic field for confinement ofvery high temperature plasmas(C) an element used to generate high-energycoherent laser light(D) an element whose supercooled vapor fillsa cloud chamber to detect the tracksof charged particles when they initiatecondensation of the vapor(E) an element or alloy whose electricalresistivity vanishes when cooled toextremely low temperaturesOy Qr51.–QO52.OOxr55. Two equal but opposite point charges are fixedin position on the x and y axes, as shown in thefigure above. Which of the following arrows bestillustrates the direction of the resulting electricfield at the origin, O ?(A)(B)(C)53.O(D)(E)GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGEThe Princeton Review Practice SAT Physics Subject Test 2 473
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2—Continued56. The planet Jupiter is 5 times farther from thesun than the earth, and the mass of Jupiter is 300times the mass of the earth. If FJ is the strengthof the gravitational force exerted by the sun onJupiter, and FE is the strength of the gravitationalforce exerted by the sun on the earth, what’s theFvalue of the ratio J ?FE(A)160(B)112(C)8(D) 12(E) 6057. Consider a double-slit interference experimentusing yellow light of wavelength λ, with theslits labeled S1 and S2. If P is the center of adark fringe on the screen on which the resultingdiffraction pattern is projected, which of thefollowing equations relating S1P and S2P, thedistances from slits S1 and S2, respectively, to thepoint P could be true?1(A) S1P – S2P λ2(B) S1P – S2P λ58. A pair of tuning forks produce sound wavesthat travel through the air. The frequency of thesound waves produced by the first tuning fork is440 Hz, and the frequency of the sound wavesproduced by the second tuning fork is 880 Hz. Ifv1 denotes the speed of the sound waves producedby the first tuning fork and v2 denotes the speed ofthe sound waves produced by the second turningfork, then(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)v1 2v2v1 4v2v1 v2v2 2v1v2 4v159. A block of aluminum and a block of iron eachabsorb the same amount of heat, and both blocksremain solid. The mass of the aluminum block istwice the mass of the iron block. If the specificheat of aluminum is twice the specific heat ofiron, then(A) the increase in temperature of the aluminumblock is twice the increase in temperatureof the iron block(B) the increase in temperature of the aluminumblock is four times the increase intemperature of the iron block(C) the increase in temperature of the aluminumblock is the same as increase intemperature of the iron block(D) the increase in temperature of the iron blockis twice the increase in temperature of thealuminum block(E) the increase in temperature of the iron blockis four times the increase in temperature ofthe aluminum block(C) S1P – S2P 2λ(D) S1P – S2P 3λ(E) S1P S2P474 Cracking the SAT Physics Subject TestGO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2—Continued60. If a container contains a mixture of two idealgases (of different molecular masses) at thermalequilibrium, which of the following is true?(A) The average kinetic energy of the moleculesof the lighter gas is less than the averagekinetic energy of the molecules of theheavier gas.(B) The average kinetic energy of the moleculesof the lighter gas is greater than theaverage kinetic energy of the molecules ofthe heavier gas.(C) The average speed of the molecules of thelighter gas is less than the average speedof the molecules of the heavier gas.(D) The average speed of the molecules of thelighter gas is equal to the average speed ofthe molecules of the heavier gas.(E) The average speed of the molecules of thelighter gas is greater than the averagespeed of the molecules of the heavier gas.61. A vertically polarized plane wave (an AM radiowave) is emitted by a radio antenna and travelsacross flat ground. Which of the followingcould describe the direction of the magnetic fieldcomponent of the wave?(A) Parallel to the ground and perpendicular tothe direction of propagation(B) Perpendicular to the ground and to thedirection of propagation(C) Parallel to the ground and to the direction ofpropagation(D) Perpendicular to the ground and parallel tothe direction of propagation(E) Parallel to the electric field component of thewave62. Which of the following best describes therelationship between the frequency and amplitudeof a sound wave?(A) Frequency is proportional to amplitude.(B) Frequency is proportional to the square ofthe amplitude.(C) Frequency is inversely proportional toamplitude.(D) Frequency is inversely proportional to thesquare of the amplitude.(E) Frequency and amplitude are independent.63. An atom whose nucleus contains 17 protonsand 20 neutrons is a chlorine atom. Which ofthe following describes the composition of thenucleus of an isotope of chlorine?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)20 protons, 17 neutrons19 protons, 18 neutrons18 protons, 18 neutrons17 protons, 19 neutrons16 protons, 20 neutrons64. When a projectile moving in a parabolic pathreaches its highest point above the ground,(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)its velocity is instantaneously zeroits acceleration is instantaneously zeroits weight balances the force of air resistancethe net force it feels is instantaneously zeroNone of the aboveGO ON TO THE NEXT PAGEThe Princeton Review Practice SAT Physics Subject Test 2 475
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2—ContinuedQuestions 65-66u2m2mUbefore thecollision30ºm60ºafter thecollisionmvAn object of mass 2m moving with velocity U strikesan object of mass m initially at rest. After the collision,the objects move away with velocities u and v, asshown.65. Which one of the following equations correctlyrelates u and v ?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)67. The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is1/6 of its value on Earth. If an object weighs20 N on the moon, what is its mass on Earth?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)2 kg7.2 kg12 kg60 kg72 kg68. The electric field strength at a point somedistance away from a source charge does NOTdepend on(A)(B)(C)(D)the magnitude of the source charge.the sign of the source charge.the distance from the source charge.the nature of the medium surrounding thesource charge.(E) None of the above2u cos 30 v cos 60 u cos 30 2v cos 60 2u sin 30 v sin 60 u sin 30 2v sin 60 u sin 30 v cos 60 66. If the collision is elastic, then(A) U2 u2 – 1 v221(B) U2 u2 v221(C) U u – v21(D) U u v21(E) (U – u)2 v22GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE476 Cracking the SAT Physics Subject Test
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2—Continued69. Which of the following equations best statesthe relationship between a material’s coefficientof volume expansion due to heating, β, and itscoefficient of linear expansion, α ?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)β αβ 3αβ α α2β α3β 3α370. The ends of a long, taut tightrope are attached totwo platforms. A tightrope artist walks along thetightrope and, upon reaching the middle, stops.Someone standing on one of the platforms grabsthe rope near one end and sends a transversewave pulse down the rope. When the pulsereaches the tightrope walker, he briefly risesupward, and the wave passes. This illustrates thefact that the wave gthdensityQuestions 71-72incidentbeam35ºairglassNote: The figure is not drawn to scale.The figure above shows a beam of light striking thesurface of a piece of glass from the air.71. If the reflected beam and refracted beam areperpendicular to each other, what is the index ofrefraction of the glass?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)sin 55 1/sin 55 1/sin 35 sin 55 /sin 35 sin 35 /sin 55 72. Let n denote the index of refraction of the glass.If the incident light has a frequency of f whentraveling through the air, what is the wavelengthof the light when it travels through the glass?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)fc/nn/fcc/fnc/fc/nfGO ON TO THE NEXT PAGEThe Princeton Review Practice SAT Physics Subject Test 2 477
PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2—Continued73. An electron that accelerates from a point near acollection of negative source charges toward apoint near a collection of positive source chargesexperiences(A) a decrease in electrical potential energy as itmoves toward a region at a lower electricpotential(B) a decrease in electrical potential energy as itmoves toward a region at a higher electricpotential(C) an increase in electrical potential energy as itmoves toward a region at a lower electricpotential(D) an increase in electrical potential energy as itmoves toward a region at a higher electricpotential(E) no change in electrical potential energy75. Five identical spaceships take off from PlanetX, and each passes by Planet Y at a constantspeed on its way to Planet Z. A science station onPlanet Y observes them passing by. The spaceshiptraveling at which of the following speeds wouldbe observed to have the greatest length?(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)6 107 m/s9 107 m/s1 108 m/s1.5 108 m/s2 108 m/s74. As the air around the base of a candle flame isheated, it rises and is replaced by cooler air. Thisillustrates what type of heat ionDiffractionLatent heatSTOPIf you finish before time is called, you may check your work on this test only.Do not turn to any other test in this book.478 Cracking the SAT Physics Subject Test
Your responses to the Physics Subject Test questions should be filled in on Test 2 of your answer sheet (at the back of the book). SAT PHYSICS SUBJECT TEST 2. . The Princeton Review Practice SAT Physics Subject Test 2 463 GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE Questions 10-12 - a a x Q -Q y An electric dipole, a pair of equal but opposite