Transcription
Air Bag and Belt Restraint Performance in FrontalCrashes - Real World and Test ExperienceSAESAEGovernmentGovernment IndustryIndustry MeetingMeetingWashington,Washington, DCDC20032003John Kindelberger & Augustus “Chip” ChidesterAloke Prasad & Matthew R. MalteseNationalNational HighwayHighway TrafficTraffic SafetySafety AdministrationAdministrationU.S.U.S. DepartmentDepartment ofof TransportationTransportationPresentation Overview Real World Crash InvestigationsChildren Fatally Injured by Air Bagsz Sled-Certified Air Bag Restraint Performance inModerate to Severe Crashesz Laboratory Testing of Sled-CertifiedVehiclesLow-Risk Deployment (OOP) Air Bag Testingz Frontal Crash Testingz1
Presentation Overview Real World Crash InvestigationsChildren Fatally Injured by Air Bagsz Sled-Certified Air Bag Restraint Performance inModerate to Severe Crashesz Laboratory Testing of Sled-CertifiedVehiclesLow-Risk Deployment (OOP) Air Bag Testingz Frontal Crash TestingzNomenclature FMVSS 208 – Rulemaking Summary“Sled Certified” or “Redesigned” Air Bags arefrom vehicles that have certified to the March1997, FMVSS 208 – Optional Sled TestRulemaking.z “Advanced” Air Bags are from vehicles thathave certified to the May 2000 – Advanced AirBag Final Rulez2
SCI and Air Bag Crashes The Special Crash Investigations (SCI) programis a component of the the National Center forStatistics and Analysis (NCSA) in the NationalHighway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)SCI researchers perform special, intensiveinvestigations of crashes selected for highinterestAirbag-related fatal and serious injury cases areof particularly high interestSCI and Air Bag Crashes Cases of interest located through: Fatality Analysis Reporting System (FARS)National Automotive Sampling System (NASS)Other DOT and NHTSA research components, regionaloffices, and hotlinesPolice and fire/rescue personnelAuto manufacturersÆSCI files are believed to contain a near-census ofairbag-related fatalities in crashes of minor tomoderate severity (delta-v 25 mph) .3
Air Bags Enter the FleetNumber of dual air bag-equipped cars/lighttrucks in fleet grew from:600,000 in 1992to40,000,000 in 1997(Source: R.L. Polk registration data)The air bags saved lives BUT in some casescaused fatal injuries, particularly to children:70 air bag related child fatalities during the years1993-1997Responses to Air Bag Injuries Public educationz 1996:Safety campaigns launched byNHTSA and its partners –manufacturers, insurance companies,and other organizationszEmphasized child and adult safety practices4
Responses to Air Bag Injuries RulemakingMarch 1997: NHTSA rule allowsmanufacturers to reduce force at which airbags deployΓRedesigned Air Bags”More accurately called “Sled-Certified Air Bags”zOptional sled test vs. previously required barrier testVehicles certified to new standard enter fleetthroughout 1998 model year May 2000: Final Rule, Advanced Air BagsResponses to Air Bag InjuriesWere the measures effective?To answer, compare counts across years:Align fatality counts into Sept-Aug productionyearsz Divide by “Million Registered Vehicle Years”(MRVY):Estimated number of (driver/pass.) airbagequipped vehicles on road during productionyear (in millions)-adjusted for attrition and gradual releasez5
Air Bag Fatalities AmongChild PassengersChildren Fatally Injured by a Passenger Air BagNormalized by Million Registered Vehicle -9595-9696-9797-9898-9999-0000-0101-0212-Month Period (Sept-Aug)Source: NCSA, NHTSAAir Bag Fatalities AmongChild PassengersChildren Fatally Injured by a Passenger Air BagBarrierBarrier-Certified Air Bags vs. SledSled-Certified Air 101-0212-Month Period (Sept-Aug)Source: NCSA, NHTSA6
Sled-Certified Air BagsFatal injuries confirmed to have beencaused by a deploying sled-certifiedpassenger air bag were sustained by:8 children ages 2-8 – 4 head, 4 neckAll unbeltedz 3 on lap of right front passengerz Pre-impact braking in 7 of the 8z1 male age 85, hgt/wgt unk - headSled-Certified Air BagsFatal injuries confirmed to have been causedby a deploying sled-certified driver air bagwere sustained by:1 female age 48 5’ 5” – belted - head1 female age 80 5’ 7” – not belted - chest1 male age 70 hgt/wgt unk. – not belted- chest1 infant on lap of driver – on-lap - head7
Presentation Overview Real World Crash InvestigationsChildren Fatally Injured by Air Bagsz Sled-Certified Air Bag Restraint Performance inModerate to Severe Crashesz Laboratory Testing of Sled-CertifiedVehiclesLow-Risk Deployment (OOP) Air Bag Testingz Frontal Crash TestingzSled-Certified Air Bags In FY1999 (October 1998) NHTSA initiated aRedesigned Air Bag Special Study (RABSS)Target: cases of high interest located by the SCIteams and the National Automotive SamplingSystem (NASS) teams.ÎRABSS is NOT a random samplez Emphasis on the protective benefit of sledcertified air bagsz8
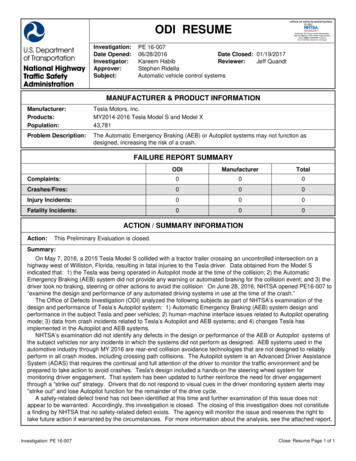
RABSS Criteria Minimum Criteria:z Vehicle with a sled-certified air bag in frontal impact,towed, with occupant in position where air bagdeployedCases of Highest Interest:zzzzChildren in front of deploying bag (injured or not)Fatals (any age)Injuries requiring transport to medical facilityDelta V 25RABSS Special Evaluations NHTSA contracted for an Air Bag AnalysiszTwo engineers independently reviewed over 400cases from RABSSz 447 driversz 143 adult front passengersz 31 child right/other front passengersTotal 621 assessments9
RABSS Special EvaluationsThe evaluators judged whether there was steering wheel orinstrument panel deformation related to occupant loadingsubsequent to an air bag deployment. Their assessment was “yes” for 30 driversz 9 fatalities among the 30z Other 21 had at least moderate (AIS at least 2) injuriesTheir assessment was “no” for 387 driversz 5 fatalities among the 387z 85 moderate to severe injuryz 297 none/minorRight front passengers were also examined, but assessmentwas “no” for all right front occupants where assessmentmade.RABSS Special EvaluationsDriver air bag deployment with steering wheel rim/columndeformation related to occupant loading cases:Selected variable means by injury severityInjurySeverityCountDelta V (mph)Weight (lbs) BMIBeltedAIS 0/10----AIS 2623.5186.727.717 %AIS 31026.6181.927.430 %AIS 4/5535.2193.828.280 %Fatal934.5262.139.00%Î8 of 9 fatalities were maleÎall 9 were in smaller passenger carsÎ2 head, 7 chest10
RABSS Special EvaluationsDriver air bag deployment with little or no steering wheelrim/column deformation related to occupant loading cases:Selected variable means by injury severityInjurySeverityCountDelta V (mph)Weight (lbs) BMIBeltedAIS 0/129715.7164.925.483.1 %AIS 25419.8174.825.277.8 %AIS 32726.7172.125.755.6 %AIS 4/5422.7125.720.4100 %Fatal534.4178.228.280.0 %Special Crash InvestigationsAdvanced Air Bags Caveat - RABSS cases were purposelyselected for their high interest value:means and rates can not be generalized to thegeneral population11
Special Crash InvestigationsAdvanced Air Bags The SCI teams have begun data collection oncrashes with air bags certified to the new advancedstandardSCI is not aware of any cases where an advancedcertified air bag failed to protect an occupant from afatal or life-threatening injury nor any cases witha fatal or lifethreatening injuryrelated to a deployingadvanced air bag.Data AvailabilityWWW Case Viewing Preliminary Case ViewerzIn 2002, NCSA began making clinical observations of theNASS CDS cases available via the disclaimer.htmlNASS CDS Casesz1997 EXE/SETFILTERSCI CaseszzzAll confirmed casesAll RABSS irmislogon12
Presentation Overview Real World Crash InvestigationsChildren Fatally Injured by Air Bagsz Sled-Certified Air Bag Restraint Performance inModerate to Severe Crashesz Laboratory Testing of Sled-CertifiedVehiclesLow-Risk Deployment (OOP) Air Bag Testingz Frontal Crash TestingzAir Bag Inflator and LocationTime gap betw een Inflator Stages (msec)DriverSeatInflatorM ode2001 HondaAccord2001 ChevyImpala2001 DodgeCaravan2001 ToyotaEcho2001 FordEscape2001 FordF150LowH igh200Primary StageOnlyPrimary StageOnlyPassengerBag LocationPassenger40LowH igh300Top4M id0M AFrontN/AN/AN/AN/AM id13
Hybrid III 6yo - Position 1H ybrid III 6YO Position 1 Normalized Injury CriteriaChest on Instrument PanelH EADCH EST15ms3ms Clip 51.0940.004VehicleH ICAccel.2001 Toyota Echo0.0010.5480.722001 Ford Escape0.420.4772001 Ford F1500.0972001 HondaAccord (low )2001 DodgeCaravan (low )2001 DodgeCaravan (high)2001 ChevroletImpala (low )NIJHybrid III 6yo - Position 2Hybrid III 6YO Position 2 Normalized Injury CriteriaHead on Instrument PanelH EADCH EST15ms3ms Clip 61.0040.004VehicleHICAccel.2001 Toyota Echo0.0590.2210.062001 Ford Escape0.5060.5952001 Ford F1500.3292001 HondaAccord (low)2001 DodgeCaravan (low)2001 DodgeCaravan (high)2001 ChevroletImpala (low)NIJ14
Hybrid III 5th Female - Position 1Hybrid III 5th Female Position 1 Normalized Injury CriteriaVehicleChin on Air Bag Module2001 ToyotaEcho2001 FordEscape2001 FordF1502001 HondaAccord (low)2001 DodgeCaravan (low)2001 DodgeCaravan (high)2001 ChevroletImpala (low)2001 ChevroletImpala (high)HEADCH EST15ms3ms Clip 10.2470.2470.0390.2810.03NIJHybrid III 5th Female - Position 2Hybrid III 5th Female Position 2 Normalized Injury CriteriaVehicleChin on Steering WheelRim2001 ToyotaEcho2001 FordEscape2001 FordF1502001 HondaAccord (low)2001 DodgeCaravan (low)2001 DodgeCaravan (high)2001 ChevroletImpala (low)2001 ChevroletImpala (high)HEADCH EST15ms3ms Clip 480.5530.0360.6640.027NIJ15
Presentation Overview Real World Crash InvestigationsChildren Fatally Injured by Air Bagsz Sled-Certified Air Bag Restraint Performance inModerate to Severe Crashesz Laboratory Testing of Sled-CertifiedVehiclesLow-Risk Deployment (OOP) Air Bag Testingz Frontal Crash TestingzTest Program 40 and 48 Km/H Rigid Barrier TestsUnbelted 50th percentile dummyz Unbelted 5th percentile dummyz 56 Km/H Rigid Barrier TestszBelted 5th percentile dummy16
Test Matrix – MY2001 RigidBarrier Frontal Crash TestsVehicleChevy ImpalaDodge CaravanFord EscapeFord F-150 PickupHonda AccordToyota EchoNissan MaximaDodge DurangoNissan SentraFord W indstarHonda CivicOccupant Restraint Speed (kmph) MassClass(kg)Medium Pass. Car1566Minivan1761SUV1391Pickup Truck2122Medium Pass. Car1399Light Pass. Car982Medium Pass. Car1470SUV2140Compact Pass. Car1255Minivan1875Compact Pass. Car11465th FemaleUnbeltedBelted40485650th Driver’s Side: 15ms HIC1.2Normalized HIC151CHEV ROLET IMPA LA0.8DODGE GRA ND CA RA V A NFORD ESCA PE0.6FORD F150 PICKUPHONDA A CCORD0.4TOY OTA ECHO0.2040 kmph48 kmph56 kmph5th Female 5th Female 5th FemaleUnbeltedUnbeltedBeltedDriv erDriv erDriv er40 kmph50th MaleUnbeltedDriv er48 kmph50th MaleUnbeltedDriv erT e s t Co n ditio n17
Head Contact Head contact withwindshield, steeringwheel, and other hardinterior pointsoccurred inzzthe unbelted 50th maletests at 40 and 48 kmph,andthe unbelted 5th femaleat 40 kmph, to a lesserextent.Test 3902 50th Male driver occupant showingwindshield glass-to-head contact.Driver’s Side: Nij21.81.6CHEVROLET IMPALA1.4DODGE GRAND CARAVANNij1.2FORD ESCAPE1FORD F150 PICKUP0.8HONDA ACCORD0.6TOYOTA ECHO0.40.2040 kmph48 kmph56 kmph5th Female 5th Female 5th FemaleUnbeltedUnbeltedBeltedDriverDriverDriver40 kmph50th MaleUnbeltedDriver48 kmph50th MaleUnbeltedDriverTest Condition18
Chest Injury5th P e rce ntile Fe m a le Drive r8070706060Deflection (mm)Deflection (mm)50th P e rce ntile M a le Drive r805040302050403020101000020406080020Acce le r atio n (g )40 kmph Unbelted406080Acce le r atio n (g)48 kmph Unbelted40 kmph Unbelted48 kmph Unbelted56 kmph BeltedAbdomen-to-Steering WheelContactC he st/Abdome n Ste e ring Whe e lContact1.4Normalized Deflection1.210.80.60.40.20Test 3805 50th Male driver occupant showingtransfer paint witness marks indicating steeringwheel-to-occupant contact.00.20.40.60.811.2No r m aliz e d A cce le r atio nNo Contac tChes t Contac tA bdomen Contac t19
Femur Injury50th P e rce ntile M a le Drive r5th P e rce ntile Fe m a le Drive r8000Right Femur Force (Newtons)Right Femur Force 03000200010000000200040006000L e ft Fe m u r Fo r ce (Ne w to n s )40 kmph Unbelted1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 80008000 10000 1200048 kmph UnbeltedL e ft Fe m u r Fo r ce (Ne w to n s )40 kmph Unbelted48 kmph Unbelted56 kmph BeltedSummaryReal World: Air bag fatalities down after advent of public safety campaignsand sled-certified air bags, but some unbelted children have stillsustained fatal injuries.Some unbelted heavier drivers in smaller car severe crashesmay have loaded steering wheel or rim subsequent to a sledcertified air bag deployment in extreme cases.Crash Testing: Head contact with the windshield and header was observed inthe unbelted 50th percentile male tests, indicating that the airbag alone was not sufficient to restrain the mid-sized maleoccupant.Abdomen-to-steering wheel contact was observed in this testseries.20
SummaryLow Risk (OOP) Deployment:The first stages of the dual stage inflator air bags were powerfulenough to prevent the 6YO from meeting the Low-RiskDeployment (OOP) Air Bag Testing requirements of the FMVSS208 Advanced Air Bag Rule. Neck Injury Criteria failures were dominant in the 6yo tests. Neck Injury (Nij) and Chest Deflection failures were dominant inthe 5th percentile female tests. There are vehicles whose air bags are not certified to, but canmeet the requirements of, the FMVSS 208 Advanced Air Bag Rulefor the 5th percentile female OOP testing. None of the vehicles chosen could pass both the 5th female andthe 6YO OOP performance requirements. 2003 ESV Publications Kindelberger et al. Air Bag CrashInvestigations Paper No.299-WPrasad et al. Injury Risks from AdvancedAir Bags in Frontal Static Out-of-PositionTests Paper No.427-OMaltese et al. Vehicle Performance In FullFrontal Crash Tests With Small Female AndMid-Sized Male Occupants Paper No.414-O21
Questions ?Restraint Systems DetailsVehicleDual StageAir BagsForce LimitedSeatbeltsPretensioners inSeatbeltsIntegratedSeatbelts2001 Ford Escape2001 Toyota Echo2001 Ford F1502001 Honda Accord2001 Dodge Caravan2001 ChevroletImpala22
2 Real World Crash Investigations zChildren Fatally Injured by Air Bags zSled-Certified Air Bag Restraint Performance in Moderate to Severe Crashes Laboratory Testing of Sled-Certified Vehicles zLow-Risk Deployment (OOP) Air Bag Testing zFrontal Crash Testing Real World Crash Investigations zChildren Fatally Injured by Air Bags zSled-Certified Air Bag Restraint Performance in