Transcription
Piping codes, valve standardsandball valve selectionRon Manson, March 2015
Valve Requirements for Piping Codes ASME B31.1-Power Piping, 2014ASME B31.3-Process Piping, 2012ASME B31.4-Pipeline Transportation Systems for Liquids and Slurries, 2012ASME B31.8-Gas Transmission and Distribution Piping Systems, 2012All the above codes list valves as a piping component.See sections 101.1.1, 300.2, 400.1 & 803.2 respectively2ENGINEERED & PROCESS VALVES
ASME B31.1-Power Piping, 2014Listed valves (table 126.1) ASME B16.34 - Valves – Flanged, Threaded and Weld EndMSS SP67- Butterfly ValvesMSS SP68- High Pressure Butterfly Valves with Offset DesignNote: the list excludes cast iron and bronze valves107 VALVES107.1 General(A) Valves complying with the standards and specifications listed in Table 126.1 shall be usedwithin the specified pressure–temperature ratings. Unless otherwise required in the individualstandards and specifications listed in Table 126.1, such steel valves shall be pressure testedin accordance with MSS SP-61.(B) Valves not complying with (A) above shall be of a design, or equal to the design, that themanufacturer recommends for the service as stipulated in para. 102.2.2. Such valves shallbe pressure tested in accordance with MSS SP-61.
ASME B31.3-Process Piping, 2012Listed valves (table 326.1) ASME B16.34 - Valves – Flanged, Threaded and Weld EndMSS SP72- Ball Valves with Flanged or Butt-Welding Endsfor General ServiceAPI 608- Metal Ball Valves-Flanged, Threaded and Welding EndsNote: the list excludes cast iron and bronze valves307 VALVES AND SPECIALTY COMPONENTSThe following requirements for valves shall also be met as applicable by other pressurecontaining piping components, such as traps, strainers, and separators. See also Appendix F,paras. F301.4 and F307.307.1 General307.1.1 Listed Valves. A listed valve is suitable for use in Normal Fluid Service, except asstated in para. 307.2.307.1.2 Unlisted Valves. Unlisted valves may be used only in accordance with para. 302.2.3.Unless pressure–temperature ratings are established by the method set forth in ASMEB16.34, pressure design shall be qualified as required by para. 304.7.2
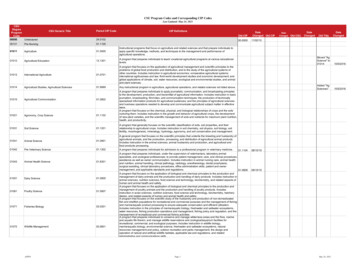
ASME B31.4-Pipeline Transportation Systemsfor Liquids and Slurries, 2012Listed valves (table 423.1.1) ASME B16.34 - Valves – Flanged, Threaded and Weld EndMSS SP68- High Pressure Butterfly Valves with Offset DesignMSS SP72- Ball Valves with Flanged or Butt-Welding Endsfor General ServiceAPI 600- Steel Gate Valves - Flanged and Butt-welding Ends,Bolted Bonnets, Twelfth EditionAPI 602- Steel Gate, Globe and Check Valves for Sizes DN 100 andSmaller for the Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries, 9th EdAPI 603- Corrosion-resistant, Bolted Bonnet Gate Valves-Flangedand Butt-welding Ends, Eighth EditionAPI 6D- Specification for Pipeline and Piping Valves, 24th EdAPI 6A- Specification for Wellhead and Christmas Tree EquipmentNote: the list excludes cast iron and bronze valves
ASME B31.4-Pipeline Transportation Systemsfor Liquids and Slurries, 2012404.5 Valves404.5.1 General. Steel valves conforming to standardsand specifications listed in Tables 423.1-1 and 426.1-1 may be used. These valvesmay contain certain cast, malleable, or wrought iron parts as provided for in API 6D.Cast iron valves conforming to standards and specifications listed in Tables 423.1-1and 426.1-1 may be used for pressures not to exceed 250 psi (17 bar). Care shall beexercised to prevent excessive mechanical loading (see para. 404.4.8.3).Working pressure ratings of the steel parts of steel valves are applicable with thetemperature limitations of -20 F (-30 C) to 250 F (120 C) (see para. 401.2.2.4).Where resilient, rubber-like, or plastic materials are used for sealing, they shall becapable of withstanding the fluid, pressure, and temperature specified for the pipingsystem.404.5.2 Special Valves. Special valves not listed in Tables 423.1-1 and 426.1-1 shall bepermitted, provided that their design is of at least equal strength and tightness andthey are capable of withstanding the same test requirements as covered in thesestandards, and structural features satisfy the material specification and test proceduresof valves in similar service set forth in the listed standards.
ASME B31.8-Gas Transmission and DistributionPiping Systems, 2012Listed valves (table 423.1.1) ASME B16.33- Manually Operated Metallic Gas Valves for Use in Gas PipingSystems up to 175 psi (Sizes NPS1/2 Through NPS 2)ASME B16.34- Valves — Flanged, Threaded, and Welding EndASME B16.38- Large Metallic Valves for Gas Distribution: ManuallyOperated, NPS 21 .2 (DN 65) to NPS 12 (DN 300),125 psig (8.6 bar) MaximumAPI 6D- Specification for Pipeline and Piping Valves, 24th EdAPI 6A- Specification for Wellhead and Christmas Tree EquipmentNote: the list excludes cast iron and bronze valves
ASME B31.8-Gas Transmission and DistributionPiping Systems, 2012831.1 Valves and Pressure-Reducing Devices831.1.1 Valves Without Threads. Valves shall conform to standards andspecifications referenced in this Code and shall be used only in accordancewith the service recommendations of the manufacturer.(a) Valves manufactured in accordance with the following standards may beused: see previous list.(b) Valves having shell (body, bonnet, cover, and/or end flange) componentsmade of cast ductile iron in compliance with ASTM A395 and havingdimensions conforming to ASME B16.1, ASME B16.33, ASME B16.34,ASME B16.38, ASME B16.40, or API 6D/ISO 14313 may be used at pressuresnot exceeding 80% of the pressure ratings for comparable steel valves at theirlisted temperature, provided the pressure does not exceed 1,000 psig (6 900kPa), and welding is not employed on any ductile iron component in thefabrication of the valve shells or their assembly as part of the piping system.(c) Valves having shell components made of cast iron shall not be used in gaspiping components for compressor stations.
Federal Codes for Transportation ofNatural and Other Gas by Pipeline§192.145 Valves.Link to an amendment published at 80 FR 181, Jan. 5, 2015.(a) Except for cast iron and plastic valves, each valve must meet the minimumrequirements of API 6D (incorporated by reference, see §192.7), or to a national orinternational standard that provides an equivalent performance level. A valvemay not be used under operating conditions that exceed the applicable pressuretemperature ratings contained in those requirements.(b) Each cast iron and plastic valve must comply with the following:(1) The valve must have a maximum service pressure rating for temperatures thatequal or exceed the maximum service temperature.(2) The valve must be tested as part of the manufacturing, as follows:(i) With the valve in the fully open position, the shell must be tested with noleakage to a pressure at least 1.5 times the maximum service rating.(ii) After the shell test, the seat must be tested to a pressure not less than 1.5times the maximum service pressure rating. Except for swing check valves, testpressure during the seat test must be applied successively on each side of theclosed valve with the opposite side open. No visible leakage is permitted.
Federal Codes for Transportation ofNatural and Other Gas by Pipeline(iii) After the last pressure test is completed, the valve must be operated through itsfull travel to demonstrate freedom from interference.(c) Each valve must be able to meet the anticipated operating conditions.(d) No valve having shell (body, bonnet, cover, and/or end flange) componentsmade of ductile iron may be used at pressures exceeding 80 percent of thepressure ratings for comparable steel valves at their listed temperature. However, avalve having shell components made of ductile iron may be used at pressures up to80 percent of the pressure ratings for comparable steel valves at their listedtemperature, if:(1) The temperature-adjusted service pressure does not exceed 1,000 p.s.i. (7 Mpa)gage; and(2) Welding is not used on any ductile iron component in the fabrication of the valveshells or their assembly.(e) No valve having shell (body, bonnet, cover, and/or end flange) componentsmade of cast iron, malleable iron, or ductile iron may be used in the gas pipecomponents of compressor stations.[35 FR 13257, Aug. 19, 1970, as amended by Amdt. 192-62, 54 FR 5628, Feb. 6,1989; Amdt. 192-85, 63 FR 37502, July 13, 1998; Amdt. 192-94, 69 FR 32894, June14, 2004; Amdt. 192-114, 75 FR 48603, Aug. 11, 2010]
Federal Codes for Transportationof Hazardous Liquids by Pipeline§195.116 Valves.Link to an amendment published at 80 FR 186, Jan. 5, 2015.Each valve installed in a pipeline system must comply with the following:(a) The valve must be of a sound engineering design.(b) Materials subject to the internal pressure of the pipeline system, includingwelded and flanged ends, must be compatible with the pipe or fittings to whichthe valve is attached.(c) Each part of the valve that will be in contact with the carbon dioxide orhazardous liquid stream must be made of materials that are compatible withcarbon dioxide or each hazardous liquid that it is anticipated will flow throughthe pipeline system.(d) Each valve must be both hydrostatically shell tested and hydrostatically seattested without leakage to at least the requirements set forth in Section 11 of APIStandard 6D (incorporated by reference, see §195.3).(e) Each valve other than a check valve must be equipped with a means forclearly indicating the position of the valve (open, closed, etc.).(f) Each valve must be marked on the body or the nameplate, with at least thefollowing: Not shown in this presentation
Comparison of Valve Standards API 6D vs API 608API 6D 24TH EDITION, AUGUST 2014API 6D INDEXScopeConformanceUnits of measurementRoundingConformance with SpecificationProcesses Requiring ValidationDescriptionAPI 608, 4TH EDITION, DECEMBER 2008SecDescriptionThis standard specifies the requirements formetal ball valves suitable for petroleum,petrochemical and industrial applications thathave flanged ends in sizes NPS 1/2 throughThis specification defines the requirements for theNPS 20 (DN 15 through DN500); butt-weldingdesign, manufacturing, assembly, testing, andends in sizes NPS 1/2 through NPS 20 (DN 15documentation of ball, check, gate, and plug valvesthrough DN 500); socket-welding ends in sizesfor application in pipeline and piping systems for theNPS 1/4 through NPS 2 (DN 8 through DN 50);petroleum and natural gas industries.threaded ends in sizes NPS 1/4 through NPS 2This specification is not applicable to valves for(DN 8 through DN 50).1.1pressure ratings exceeding Class 2500.Corresponding to the nominal pipe sizes inIf product is supplied bearing the API MonogramASME B36.10M.This standard applies to metaland manufactured at a facility licensed by API, theball valves with pressure classes as follows;requirements of Annex A applies.flanged ends in Classes 150, 300 and 600 (PNAnnexes B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, and O16, 25, 40 and 100);butt-welding ends inare annexes that are used in order listed.Classes 150, 300 and 600 (PN 16, 25, 40 and100); socket-welding ends in Classes 150, 300,600 and 800 (PN 16, 25, 40 and 100); threadedends in Classes 150, 300, 600 and 800 (PN 16,25, 40 and 100).Sec11.21.2.1 Not addressed1.2.2 Not addressed1.3 Not addressed1.4 Not INEERED & PROCESS VALVES
API 6D 24TH EDITION, AUGUST 2014API 608, 4TH EDITION, DECEMBER 2008API 6D INDEXDescriptionSecDescriptionSecNormative references22Terms, Definitions, Acronyms,Abbreviations, Symbols, andUnits33Terms and Definitions3.1Acronyms and AbbreviationsAddressed3.2 Not addressedSymbols and UnitsAddressed3.3 Not addressedValves types and configurationsValve typesValve configurations4Covers Ball, Gate, Check and Plug Valves. Example4.1 Covers Ball Valves only (No valve Drawings)of covered valve given (Valve Drawing)Full-opening valves shall have an internalminimum cylindrical opening for categorizingbore size as specified in Table 1. Minimum valvebore values given, (NPS 0.5 - NPS 60). Obturatorand seat dimensions shall meet Table 1.For valve not covered in Table 1, the size andbore shall be by agreement and the manufactureshall stamp the size and bore on the nameplate.For Reduced-opening valves:- valves NPS 4 (DN 100) to NPS 12 (DN 300):one size below nominal size of valve with boreaccording to Table 1,- valves NPS 14 (DN 350) to NPS 24 (DN 600):two sizes below nominal size of valve with boreaccording to Table 1.134.21Flow passageway in this standard categorizedas full bore; single reduced bore and5.2double reduced bore.Minimum cylindrical diameter for categorizingbore size given, (NPS 0.25 - NPS 20)ENGINEERED & PROCESS VALVES
API 6D 24TH EDITION, AUGUST 2014API 6D INDEXDesignDesign standards andcalculationsWall ThicknessDescriptionAPI 608, 4TH EDITION, DECEMBER 2008SecDescriptionSec5In accordance with an internationally recognizeddesign code: e.g. ASME BPVC, Section VIII,Meet the requirements of Standard Class valves5.15Division 1 or Division 2; ASME B16.34; EN 12516per ASME B16.341 or EN 12516-2; and EN 13445-3.Referenced from ASME B16.34 orASME Section5.3.5.1 In accordance to requirements of ASME B16.34VIII.1In ASME rating class. Pressure-temperatureratings for class-rated valves is based per ASMEB16.34 and Class 400 valves is based per ASMEB16.5. Covers up to Class 2500 maximum.NOTE: It is not required that identical material ormaterial form be used for body and bonnet orcover parts.Valve rating shall be the lesser of the shell ratingPressure-temperature ratings are based onor seat rating. Valve shell rating shall be the ratingmaterial group of valve's end connection. Wherefor the shell material as listed for Standard Class1.2,Pressure and temperature rating the valve ends are made from material in two5.2 in ASME B16.34. Covers up to Class 600 (Class4different groups, the material with the lower150, 300, and 600) for flange
dimensions conforming to ASME B16.1, ASME B16.33, ASME B16.34, ASME B16.38, ASME B16.40, or API 6D/ISO 14313 may be used at pressures not exceeding 80% of the pressure ratings for comparable steel valves at their listed temperature, provided the pressure does not exceed 1,000 psig (6 900 kPa), and welding is not employed on any ductile iron component in the fabrication of the valve shells or .