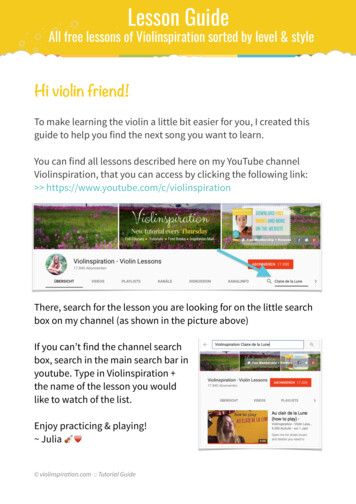
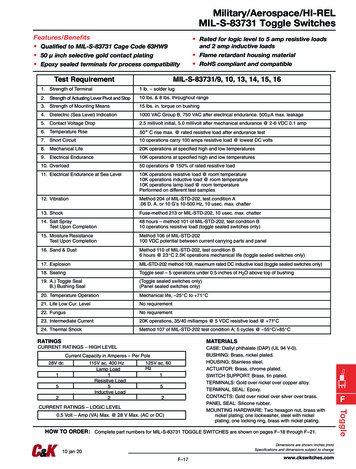
Transcription
QualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsA new test method to evaluate hydraulic fluids forvane pumpsDr. Ir. Dirk Drees, Dr. Ir. Emmanuel Georgiou, Michel De BildeFalex Tribology Belgium – Falex Application Center TribologyTribology is the science and technology related to friction, wear and lubrication
Schedule of presentation1.Objectives2.Existing methodology and its limitations3.Challenges4.Alternative method5.Pre-screening and evaluation tests6.Other possibilities7.Conclusions8.Follow-up actionsQualityKnowledgePartner Solutions2
1. ObjectivesQualityKnowledgePartner Solutions Establishing a new methodology to simulate vane pumptests Efficient and accurate evaluation of friction and wear Matching in-field conditions to a lab tests3
QualityKnowledgePartner Solutions1. Objectivescorrelationcosttime4after Czichos, ASM Metals Handbook Vol 18
2. Existing methodology& their limitationsQualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsConestoga Vickers Vane Pump: ASTM D7043 - DIN 51389 - ISO 20763Pump assemblyTest ParametersSpeed (rpm)1500Load (lbf)250Time (h)Loading rate (lbf/s)50Oil volume (L)Flow rate (LPM)Limitations: Time consuming tests (1 test takes 250 hrs) Large quantity of oil No data on friction Temperature of oil in not well controlled5
3. ChallengesQualityKnowledgePartner Solutions Simulate actual in-field conditions Accelerated wear to minimize testing time Accelerate wear without changing wear mechanisms In-situ monitoring of friction, wear of the tribosystem andoil temperature near contact interface.6
4. Alternative methodQualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsStep 1: identifying wear mechanisms of actual components (Conestoga) Actual components (ring and vane) after testing7
4. Alternative methodQualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsStep 1: identifying wear mechanisms of actual components (Conestoga)RingVane Mild abrasion (smoothening) of vanes Mild abrasion and oxidative wear (oxide layer in contact) Formation of debris particles8
4. Alternative methodQualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsStep 2: calculating centrifugal forceWhere:M : massω : angular speedr : radiusCentrifugal force of a vane in a pump is 65 – 75 N or 15 – 17 lbf9
4. Alternative methodQualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsStep 3: Multispecimen testing protocolTest ParametersSpeed (rpm)1500Load (lbf)800Time (h)25Loading rate (lbf/s)20-30Oil volume (L)3Flow rate (LPM)2For more information on the procedure look into protocol developed by Falex US (April 8th 1997)Starting point of updated protocol: Loading conditions are significantly higher than the ones met in actualconditions definine test conditions to have accelerated wear loss withoutchanging the wear mechanisms* From our previous experience weight gain was observed. This does notcorresponds to reality10
4. Alternative methodQualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsStep 3: Multispecimen testing protocol Test samples (disks) were developed. Grooves simulate pressure variation.Three vanes are tested per experiment11
5. Pre-screening& evaluation testsQualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsLoad (lbf)Step 4: accelerating wear and defining the working limits (failure map)1500 rpm, 3 LPM, 2.5 L, 45 C12
5. Pre-screening & evaluation testsQualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsLoad (lbf)Step 4: accelerating wear and defining the working limits (failure map)1500 rpm, 3 LPM, 2.5 L, 45 C13
5. Pre-screening& evaluation testsQualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsStep 5: understanding failure (in-situ monitoring of COF & T at interface) Heating up of hydraulic fluid Change in the lubrication regime (metal-metal contact)14
QualityKnowledgePartner Solutions5. Pre-screening& evaluation testsStep 5: understanding failure (analysis of wear mechanisms)VaneDiskAt 400 lbf for 1 h:At 200 lbf for 1 h: Different wear mechanisms At 200 lbf wear mechanisms are closer to reality15
5. Pre-screening& evaluation testsQualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsStep 6: optimization of testing conditions (defining working conditions) Mapping limits of contact pressure (calculated with Hertzwin software)16
5. Pre-screening& evaluation testsQualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsStep 7: matching Multispecimen with Conestoga tests1500 rpm, 200 lbf, 2.5 L, 3 LPM 45 C Wear is measurableRepeatable measurementsRunning-in period observedWeight loss is similar to the one obtained after Conestoga test ( 2 mg/h)17
5. Pre-screening& evaluation testsQualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsStep 7: matching Multispecimen with Conestoga tests Similar coefficient of friction at the steady state conditionsDifferent running-in, possibly due to initial surfaceIncrease of friction is accompanied by increase in temperatureLubrication regime confirmed18
5. Pre-screening& evaluation testsQualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsStep 7: matching Multispecimen with Conestoga testsVane after Multispecimen testingat 200 lbf for 20 hrsVane after Conestoga vane pumptesting for 250 hrs Similar wear mechanisms, namely mild abrasion and oxidative wear(formation of a localized oxide tribo-layer)19
6. Other possibilitiesQualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsInvestigate the effect of T on the performance of hydraulic fluids No potential danger of overshooting temperature ( 10 C) on frictionLubrication regime confirmed and comparedIn-situ monitor of evolution of COF and T near the contactBetter comparison of performance of hydraulic fluids20
6. Other possibilitiesQualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsInvestigate the effect of T on the performance of hydraulic fluids45 CVaneDisk55 CVaneDisk Similar wear mechanisms on both vanes and disks Some difference in weight loss was observed Shorter tests allow to test repeatability21
7. ConclusionsQualityKnowledgePartner Solutions Conestoga Vickers Vane Pump tests can be simulated byMultispecimen tester Similar wear mechanism as in Conestoga Vickers Vane Pump testsfor loads below 300 lbf Above 400 lbf severe abrasion of the disk and oxidative wear of thevanes may occur Higher wear rate during first hour (running-in ) Similar wear loss as in Conestoga Vickers Vane Pump tests In-situ monitoring of coefficient of friction and temperature allow for abetter understanding of occuring phenomena Possibility to change and regulate the contact conditions (speed,load, acceleration etc.), temperature and hydraulic fluid flaw rate22
8. Follow-up actionsQualityKnowledgePartner Solutions Testing of various hydraulic oils that have been alreadytested on the Conestoga Create a ranking based on friction and wear23
QualityKnowledgePartner SolutionsThank you for your attention !24
A new test method to evaluate hydraulic fluids for vane pumps . Conestoga Vickers Vane Pump: ASTM D7043 - DIN 51389 - ISO 20763 Pump assembly . Step 5: understanding failure (analysis of wear mechanisms) At 400 lbf for 1 h: At 200 lbf for 1 h: Vane Disk Different wear mechanisms