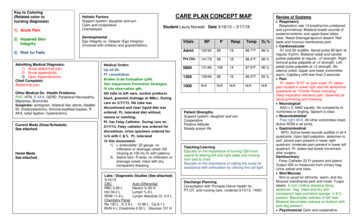
Transcription
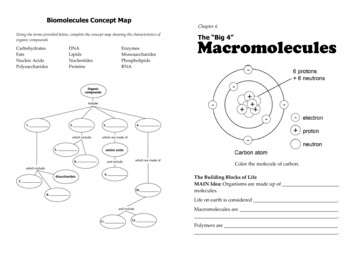
Biomolecules Concept MapChapter 6Using the terms provided below, complete the concept map showing the characteristics oforganic compoundsCarbohydratesFatsNucleic zymesMonosaccharidesPhospholipidsRNAThe “Big 4”Macromolecules- -- Color the molecule of carbon.The Building Blocks of LifeMAIN Idea: Organisms are made up ofmolecules.Life on earth is considered .Macromolecules are.Polymers are.
Biomolecules VocabularyBiological macromolecules are organized into four categories:1.2.3.4.WordBiomoleculeTable 1. Biological Macromolecules ateLipidProteinLipidsNucleic sisAmino AcidNucleic AcidsPeptide BondFatty AcidDefinition
Enzymes(p.156, 159)Chemical ReactionsMAIN Idea: Chemical reactions allow living things to.Color each of the elements below according to the color listed nextto the element's symbol. Then color code the squirrel with thecorrect proportion of each element's color. Now color code thecarrot with the same colors as you used on the squirrel.A is a substance that lowers the activation energyneeded to start a chemical reaction.Special proteins called are the biologicalcatalysts that .18.5%black65%red9.5%yellowCells contain thousands of different enzymes to control thefunctions of the cell. An enzyme’s name describes what it doesand usually ends in the suffix - .Enzymes must physically fit (like a lock and key) a specificsubstrate(s) to work properly.The place where a substrate fits an enzyme to be catalyzed iscalled the active site.Enzyme SubstrateEnzyme-SubstrateComplexmmEnzyme rple
CarbohydratesProteins(p.168)(p.170)A protein is made of .Amino acids are composed of.There are different variable groups.After an amino acid chain is formed,.Label, then color the molecule of glucose (C6H12O6). Color code theamino acid (carbon-black, hydrogen-yellow, and oxygen-red).Carbohydrates are used by the body for energy and structuralsupport in cell walls of plants and exoskeletons of insects andcrustaceans. Composed ofin a ratio.The monosaccharide plays a central role asan energy source.Monosaccharaides (simple sugars) can be linked to formand .In plants, a carbohydrate called providesstructural support for .Draw the diagram for the disaccharide, sucrose, in the spacebelow:Proteins make-up percent of your total body mass.Proteins are made of subunits called amino acids and are used tobuild cells and do much of the work inside organisms. They alsoact as enzymes helping to control metabolic reactions inorganisms. Amino acids contain two functional groups, thecarboxyl group (-COOH) and the amino group (-NH2). Use yourtextbook to circle the amino and carboxyl groups on the diagram.Color code the amino acid (carbon-black, hydrogen-yellow,nitrogen-blue, and oxygen-red).HNHOHCR-GroupCH
Nucleic AcidsLipids(p.171)(p.169)Nucleic acids are .Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules.Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve aswaxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), andsteroids. Lipids are molecules made mostly of.Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms.Nucleic acids are made up of small repetitive units composed of,called .There are two types of nucleic acid and .Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) contains all the instructions formaking every protein needed by a living thing, carrying thegenetic information in the nucleus of a cell. RNA copies andtransfers this genetic information so that proteins can be made.Color and label the parts of a nucleotide: sugar-green,phosphate group-yellow, and nitrogen base-blue.They include .The primary function of a lipid is .One characteristic of a triglyceride is .One characteristic of an oil is .Saturated fatA nucleotide with three phosphate groups is calledor ATP. ATP used for cellular energy is ahigh energy nucleotide with three phosphate groups. Color codethe ATP and label the phosphates.Unsaturated fatDescribe the difference between a saturated and an unsaturatedfat.Phospholipids are responsible for.Hydrophobic means .Hydrophilic means .Steroids include substances such as.
Basics of Biomolecules1.2.3.4.5.6.Carbon is the central atomCarbon will bond covalently because of 4 valence electronsCarbon likes to share electrons with sulfur, phosphorous, oxygen, nitrogen, other carbons, and hydrogenSPONCHAll four are macromolecules (BIG molecules)Polymers-large unit of the macromolecule (made of many monomers); Monomers-small pieces of the polymer (building blocks)BiomoleculeCarbohydrateProteinLipidNucleic AcidElements/Chemical FormulaFunctionMonomer/PolymerExamplesOther
Biomolecules Concept Map Using the terms provided below, complete the concept map showing the characteristics of organic compounds Carbohydrates DNA Enzymes Fats Lipids Monosaccharides Nucleic Acids Nucleotides Phospholipids Polysaccharides Proteins RNA Chapter 6 MacromoleculesThe “Big 4” Color the molecule of carbon.