Transcription
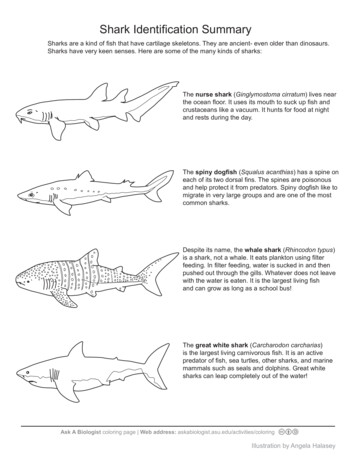
Shark Identification SummarySharks are a kind of fish that have cartilage skeletons. They are ancient- even older than dinosaurs.Sharks have very keen senses. Here are some of the many kinds of sharks:The nurse shark (Ginglymostoma cirratum) lives nearthe ocean floor. It uses its mouth to suck up fish andcrustaceans like a vacuum. It hunts for food at nightand rests during the day.The spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias) has a spine oneach of its two dorsal fins. The spines are poisonousand help protect it from predators. Spiny dogfish like tomigrate in very large groups and are one of the mostcommon sharks.Despite its name, the whale shark (Rhincodon typus)is a shark, not a whale. It eats plankton using filterfeeding. In filter feeding, water is sucked in and thenpushed out through the gills. Whatever does not leavewith the water is eaten. It is the largest living fishand can grow as long as a school bus!The great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias)is the largest living carnivorous fish. It is an activepredator of fish, sea turtles, other sharks, and marinemammals such as seals and dolphins. Great whitesharks can leap completely out of the water!Ask A Biologist coloring page Web address: ion by Angela Halasey
Shark Identification SummaryThe blacktip reef shark (Carcharhinusmelanopterus) is found in shallow, tropicalwaters. It preys on fish and invertibratesfound in reefs. Most sharks live in saltwater,but the blacktip reef shark has been knownto leave the ocean to swim up rivers.The tiger shark (Galeocerdo cuvier) is namedfor its stripes. It eats a wide variety of foodsfrom squid to sea birds. Sometimes it even eatstrash. It is dangerous to humans because it isn’tpicky about what it eats.The scalloped hammerhead (Sphyrnalewini) is found in coastal waters. Like othersharks, it has electroreceptors to senseelectric fields. The unique shape of its headallows it to have more electroreceptorsspread over a larger area. This makesit an effective predator of fish, squid, andeven smaller sharks!The caudal (tail) fin of the common threshershark (Alopias vulpinus) is its most prominentfeature. It is used to hit and stun prey. Thethresher shark eats mainly fish and is shyaround humans.Ask A Biologist coloring page Web address: ion by Angela Halasey
Shark Matching GameDraw a line from each shark to its matching name. Watch out, not all of the names match!Mako SharkNurse SharkSpiny DogfishTiger SharkLeopard SharkBlacktip Reef Shark5 ftAsk A Biologist coloring page Web address: ion by Angela Halasey
Shark Matching GameDraw a line from each shark to its matching name. Watch out, not all of the names match!Great White SharkScalloped HammerheadLemon SharkZebra SharkWhale SharkCommon Thresher Shark5 ftAsk A Biologist coloring page Web address: ion by Angela Halasey
Shark Matching Game KeySpiny DogfishBlacktip Reef SharkNurse SharkTiger Shark5 ftScalloped HammerheadCommon Thresher SharkGreat White SharkWhale Shark5 ftAsk A Biologist coloring page Web address: ion by Angela Halasey
from squid to sea birds. Sometimes it even eats trash. It is dangerous to humans because it isn't picky about what it eats. The caudal (tail) fin of the common thresher shark (Alopias vulpinus) is its most prominent feature. It is used to hit and stun prey. The thresher shark eats mainly fish and is shy around humans. The scalloped hammerhead .