Transcription
PATIENT CATEGORISATION TOOL(PCAT)SELF-SERVICE TRAINING SLIDESUK ROC & NCASRIProfessor Lynne Turner-Stokes DM FRCPRegional Hyper-acute Rehabilitation UnitNorthwick Park HospitalWatford Road, Harrow, Middx. HA1 3UJLynne.turner-stokes@doctors.org.uk
Glossary NCASRI – National Clinical Audit Specialist Rehabilitation for patientswith complex needs following major injury PCAT – Patient Categorisation Assessment Tool TARN – Trauma Audit and Research Network UK ROC – United Kingdom Rehabilitation Outcome Collaborative
CONTENT Background Structure of tool Tool completion Decision making process Psychometric properties
Background The Patient Categorisation Tool (PCAT) was developed from thedescriptions within the NHSE Standard Contract for specialisedrehabilitation for patients with highly complex needs -ServiceSpecification /04/d02-rehab-pat-high-needs-0414.pdf)for identification of patients with Category A or B needs requiringon-going specialist rehabilitation It is primarily a checklist of rehabilitation needs It has an ordinal tool scoring system ranging from 17-50
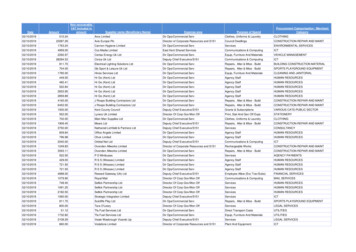
Structure of PCAT –Table 1 The tool provides a checklist to assist clinical decision reasoning to identifypatients with Category A or B needs The PCAT tool contains 2 tables Table 1 contains 4 columns Column 1 – lists 16 domains(each rated on a score of 1-3) subdivided into Specialist medical or neuropsychiatric needs & intensity Clinical needs - physical, tracheostomy/ventilatory, swallowing/nutrition,communication, cognitive, behavioural, mood/emotion, complex disabilitymanagement, social/discharge planning, family support, emotional load on staff Additional needs – Vocational rehabilitation, Medico-legal issues and specialistequipment Column 2 – contains the descriptions of types of need for Category A needs Column 3 – contains the descriptions of types of need for Category B needs Column 4 – contains the descriptions of types of need for Category C needs
Structure of PCAT –Table 2 The second table is on page 2 and contains Service level required Category Expected duration of admission Funding source Purchase type Name of assessor Date of assessment
Interpretation of PCAT Descriptors Throughout the tool the following terms are used: Complex, unstable, severe needs - requiring expertise of aspecialist rehabilitation unit with appropriate staffing/facilitiessuch as provided by a Level 1 tertiary service Routine, stable, moderate needs - requiring expertise of aspecialist rehabilitation unit with appropriate staffing/facilitiessuch as provided by a Level 2 specialist rehabilitation service Normal, higher function, stable or no problem – needs can bemanaged in a Level 3 rehabilitation service
Completion of PCAT From April 2013 full itemised scoring of the tool has been amandatory requirement for Level1/2 services The tool should be completed by a Consultant in RehabilitationMedicine/Neuropsychiatry /- input from the therapy team It is completed: Prior to referral to a specialist rehabilitation unit by a Major TraumaCentre (MTC) AND/OR Following admission to a Level 1/2 specialist rehabilitation unit All sections of the tool should be completed and then entered into TARN (patients assessed in the Major Trauma Centre)/ ORION AND/OR UK ROC database (patients admitted to rehabilitation unit)
Item Selection Tool completion requires indication (by use of the tick boxes) of themost appropriate descriptor/s for each domain Some domains are mutually exclusive whilst others may have relevantdescriptors in both Category A and B columns E.g Intensity – patient may need 5 therapy disciplines (Category A) for 2025 hours total therapy time per week (Category B) All relevant descriptors can be indicated, if the patient does not haveCategory A or B needs for a domain this can be left blank or forcompleteness of the tool Category C option may be selected E.g Tracheostomy – the patient does not have a tracheostomy – either leavedomain blank or tick “no tracheostomy” in Category C column For consistency and comparability only the descriptors provided shouldbe used and no additional descriptors added
Scoring guidelinesMedical/surgical needsCategory DescriptorGuidelinesComplex specialist investigation/interventionRequires neurosurgical intervention and/or investigationsat specialist centreAMedically/surgically unstablee.g uncontrolled seizures/diabetes or sympatheticstorming/sepsis– may need emergency access to HDU/ITUintervention. Must have access to Acute CareAComplex on-going needs for coordinatedtrauma careSevere traumatic injury requiring surgical/vascular/orthopaedic/neurosurgical on-going interventionBRoutine ion can be completed in SpecialistRehabilitation settingCurrently well but potentially unstablePeriods of instability e.g pyrexia, seizures etc. but largelycontrolledBActive on-going trauma care managementMay require surgical/vascular/orthopaedic review whilston specialist rehabilitation unitCNo investigation/interventionRoutine bloods/X-Rays may be required infrequentlyCMedically stableNo immediate medical issuesCTrauma Care largely complete – review onlyOn-going trauma care can be managed on an out-patientor phone call basisAB
Scoring guidelinesNeuropsychiatric needsCategory DescriptorGuidelinesAComplex/unstable psychiatric needsSevere psychiatric problems, suicidal ideation – needs expertiseof a cognitive/behavioural unit and 1-1 interventionAHigh Risk ManagementRequires expertise of cognitive/behavioural unit – needs 1-1supervisionATreatment under section of the MHACurrently sectioned under MHA for own/other safetyBPsychiatric condition stable but needsmonitoringPsychiatric condition well managed with therapyinput/medication but requires regular intervention frompsychiatrist/psychologistMedium Risk ManagementSome concerns with psychiatric problems but can be managedwith advice from psychiatrist on a ad hoc basis or input from apsychologistCNo psychiatric conditionNo history/symptoms of psychiatric conditionCLow or no riskMay or may not have some psychiatric condition but can bemanaged in any environmentB
Scoring guidelinesIntensityCategory DescriptorGuidelinesA 5 therapy disciplinesRequires daily therapy intervention from the inter-disciplinaryteam. At least 5 unit funded therapy disciplines involved eachweek e.g. Physiotherapy, Occupational therapy, SpeechTherapy, Dietitian, Psychology and/or social workerA 25 hours total therapy time per weekHigh therapy input – approximately 6 hours per dayARequires 1-1 supervisionCan not be left unsupervised at any time due to concerns forsafety/abscondingA 2 trained therapists to treat at onetimeRequires either joint sessions (2 or more disciplines involved)or 2 trained therapists from same discipline (e.g 2/3 Physio’sfor all sessions)4 therapy disciplinesRequires weekly therapy intervention from 4 different therapydisciplines (funded establishment)B20-25 hours total therapy time per weekStandard therapy input, approximately 4-5 hours per dayC1-3 therapy disciplinesRequires weekly therapy intervention from 1-3 differenttherapy disciplines (funded establishment)C 20 hours total therapy time per weekLow therapy input, less than 4 hours dailyB
Scoring guidelinesPhysical NeedsCategory DescriptorGuidelinesAComplex postural tone/contracture management24 hour postural management programme in place/regular tilttabling. Complex spasticity management. Bespoke splintingA 2 to handleRequires 3 or more staff for all physical needsAHighly complex musculoskeletal/trauma/pain managementissuesReferral to on-site pain management team. Regular analgesia/painassessmentAComplex amputee needs (Multi-limb, high tech etc)Management of phantom pain. Bespoke prosthesisBRoutine physical issuesRegular physiotherapy intervention – strength training etcB1 to handleAssistance of 1 for most physical needs. E.g. transfers/mobilityBModerately complex musculoskeletal/trauma/painmanagement issuesPain management programme in place with regular reviewBStandard specialist amputee needsRegular prosthetic review. Management of artificial limbCHigher function problemsAble to walk independently with walking aid/prostheisCStandard musculoskeletal/trauma/ pain management issuesPain managed with regular exercises and analgesiaCNo physical issues
Scoring guidelinesTracheostomy/Ventilatory NeedsCategoryDescriptorGuidelinesAUnstable tracheostomy requiring intensive suctionExcessive secretions and/or recurrent mucousplugging of tracheostomy, fluctuating saturation levelsAOxygen saturation monitoring programmeConstant oxygen saturation recording. CPAP may berequiredAActive weaning programmeCuff deflated for periods during the day, capping oftracheostomyAAssisted ventilationPortable ventilatory support e.g. NIPPYBTracheostomy in situ but stableMaintained with regular suctioning/tube changesCNo tracheostomyMay need tracheostomy dressings followingtracheostomy removal only.
Scoring guidelinesSwallowing/NutritionCategory DescriptorGuidelinesAComplex swallowing evaluation (e.g. FEES)At high risk of aspiration/ silent aspiration. Undergoing investigation such as FEESAComplex nutritional requirements requiringintensive dietary support/interventionEnteral/Parenteral feeding, frequent monitoring ofelectrolytesBEnteral feeding programmeOn an established enteral feeding regime – requiresregular reviewBModerate monitoring – e.g progressiveconsistency, dietary contentPuree/soft/normal diet/thickened fluids /supplements. Changing consistency/textureBDietary education (e.g. healthy eating, weightreduction)Weekly weight recording/ dietary advice for patientand familyCNormal or stable modified dietEstablished dietary intake.CAble to eat independently or with supervisionfrom care staffMay need help to open packs/cut up food or needmonitoring for speed of eating/drinking to ensuresafe eating/drinkingCStandard dietary/weight monitoring only
Scoring sAComplex communication needs requiring specialistevaluationLocked-in syndrome assessment – eye gaze etc.Severe expressive/receptive dysphasiaAComplex communication needs requiring complexcommunication aid set-up provisionAlternative and Augmentative communicationrequiredBModerate communication issues with some listenerburden, but able to communicate basic needs & ideasPicture charts, alphabet chart or light-writer toassist with communicationCHigher function problems onlyOccasional word finding difficulties/someclarification may be required for effectivecommunicationCNo problems with communication
Scoring guidelinesCognitive needsCategoryDescriptorGuidelinesASevere cognitive problems requiring intensivesupport for carryover/orientation etcOn day-to-day basis requires prompting/guidancewith all basic needs e.g washing & dressingsequencingASevere cognitive problems requiring complexcognitive/neuropsychological assessmentBModerate cognitive problems requiring structuredenvironment, strategiesOrientation board. Day to day timetable. Visualprompts/clues/remindersBRoutine cognitive assessment e.g. by OTDay-to-day functional table top assessmentsCHigher function problems onlyFunctions independently for most of the time butmay need some occasional help e.g forcommunity navigation or extended activities ofdaily livingCNo cognitive problems
Scoring guidelinesBehavioural needs & Mood/EmotionCategory Descriptor for Behavioural needsGuidelinesAHighly challenging behaviours e.g. physical and/orverbal aggression, requiring interactive behaviouralmanagement programmeNormally managed in a unit specifically able tomeet the needs of cognitive/behavioural issueswith intensive input from neuro-psychiatry/neuropyschologistBMild/moderate behavioural issues controlled in astructured environmentManaged with routine psychology sessions andbehavioural management guidelinesCNo significant behavioural problemsCategory Descriptor for Mood/EmotionGuidelinesASevere anxiety/depression/emotional labilityrequiring specialist evaluationAssessment and at least daily sessions requiredfrom psychiatrist/psychologistASevere anxiety/depression/emotional labilityrequiring active management and frequent crisisinterventionRegular and emergency psychiatric/ psychologyinterventions. Use of medication/behaviouralmanagement programmeBMood disorder/adjustment issues under activemanagement with planned programmeMood assessments – BDI, HADS – therapysession/CBT/medication as appropriateCNo significant mood/adjustment issues
Scoring guidelinesComplex disability managementDescriptor for Complex disabilitymanagementGuidelinesAComplex disability management – evaluation oflow awareness stateRequires SMART/WHIM /CRS-R assessment forformal diagnosisAComplex disability management – neuropalliative rehabilitation/end of life careBest interest/ceiling of care assessments/meetings.Decision on Resuscitation statusBStandard disability management e.g. set-up ofcare programme, care booklet, carer trainingBed board guidelines for family/staff. Carebooklets/daily timetable of careCNone requiredCategory
Scoring guidelinesSocial/discharge planningCategory Descriptor for social/discharge planningGuidelinesAComplex placement/housing/funding issuesrequiring extensive multi-agency negotiationOn-going placement unclear – homeless, continuingcare funding/placement required e.g. SpecialistNursing Home placementBActive discharge planning requiring liaison withcommunity SW/DN/OT to arrange care packageOn-going placement identified – needscommunity/family supportCNo major discharge issues, taken care of by familyand/or allocated social worker
Scoring guidelinesFamily Support & Emotional Load on staffCategory Descriptor for Family SupportGuidelinesAMajor family distress issues requiring frequentsupport or crisis interventionFrequent Consultant and multi-disciplinary inputrequired, unrealistic patient/ familyexpectations/dissatisfaction with careBRoutine family support needs met by plannedmeetingsRoutine family meetings/keyworker sessions /nurse discussions meet family needsCNo significant family problemsCategory Descriptor for Emotional load on staffGuidelinesADemanding situation requiring highly experiencedstaff / extra support for staffStaff need additional support from seniorcolleagues and/or psychologists. Change oftreating team to lessen the loadBSomewhat challenging situation but manageableStaff able to cope with patient /family demandsthrough routine supervision sessionsCMinimal or no emotional load on staff
Scoring guidelinesVocational isciplinary vocationalassessmentWSS assessment. Onward placement for retraining for work.Site visits to assess for suitability of work environment.Assessment for access to workAMulti-agency support for return towork, retraining or work withdrawalMedical retirement from work due to ill health or gradedreturn to work. Employer liaison. Provision of re-training toalternative roleAComplex support in other roles e.g.single parentingSupport to care for child/other relativeBWork visits or employer liaisonLiaison with employer, facilitation/support for return to work,reduction in duties.BSupport for others role e.g. homemaker or parentingAble to care for self and ability to engage with another persone.g play a game with own child or able to cook/cleanCNot of working ageAlready in retirement/receiving pensionCNo significant needs for vocationalsupport
Scoring guidelinesMedico-legal issuesCategory DescriptorGuidelinesAComplex best interest decisionse.g. to include withdrawal of nutrition/hydrationACourt of Protection applicationsFor vulnerable adults or in situations of family conflictADoLs/PoVA applicationsDeprivation of living application for those deemed to becompetent or have mental capacity. Protection ofvulnerable adultsALitigation issuesFollowing road traffic accident/medical issue with on-goinginvestigation/court proceedingsAComplex mental capacity/consent issuesAssess ability to consent to treatment optionsBMental capacity evaluationCapacity assessment for specific questions e.g. choice ofdischarge destinationBStandard consent/best interest decisionsStandard consent for procedures e.g insertion of PEG. Dailycues for best interestBLPoA, advance care planningIncudes end of life care. Decision/capacity to delegateresponsibility to othersCNo significant medico-legal issues
Scoring guidelinesSpecialist espoke Assistive Technologye.g. communication aids.AHighly specialist seating/wheelchair needsCustom contoured seatingABespoke orthoticse.g. Thoraco-lumbar-sacral orthosisAElectronic assistive technologyEnvironmental controlsAAssisted ventilationPortable ventilatory supportBAdapted wheelchair/seatinge.g Jay2 cushion. Adjusted tilt-in-space wheelchairBElectric standing framee.g. QuestBTreadmill/harness trainingBAssisted cycling e.g. motomedBSplinting/castingCNo equipment needsCBasic off the shelf equipment onlyCStandard exercise facilitiese.g. plinth, tilt-table, parallel bars
Clinical decision of Service Level andPatient Category Completion of the PCAT checklist provides a detailed account of theoverall rehabilitation needs, thereby providing sufficient information tofacilitate the clinical decision by the Consultant in RehabilitationMedicine on the rehabilitation service level required and the PatientCategory A, B or C needs (NB. the service level required may not be the same as theservice level the patient has been admitted to. Level 1/2a can be selected) Funding source and purchase type should also be completed.
Ordinal Score Descriptors for each domain are presented in one of 3 columns. Category A ordinal score 3 Category B ordinal score 2 Category C ordinal score 1 Total scores are automated within the UKROC software If calculating scores manually: Take the highest score from the Medical/surgical & Psychiatric needs – do not include scores fromboth sections For the remaining domains add the highest score (only count one item per domain e.g if 5 therapy disciplines and 25 hours total therapy time per week have been selected in the Intensity domain the score is 3 and not 6) The expected duration of admission scores Long stay – add a score of 2 Medium stay – add a score of 1 Short and assessment/rapid intervention - no additional score added Although the PCAT sensitivity/specificity provides an indication that Category A needs may havea PCAT total score 30, it is also possible that complex needs in just 1 or 2 domains may stillrequire specialist facilities despite a PCAT score 30. Clinical expertise is essential for identifyingrehabilitation needs
Psychometric properties of PCATExploratory and Confirmatory factor analysis suggested that PCAT may be reasonablysummed into a total score but also comprises of two factors one relating principally tocognitive/psychosocial requirements (PCAT-Cog) and the other to physical requirements(PCAT-Phys)PCAT-Cog domains dSocial/discharge planningFamily SupportEmotional load on staffVocational RehabilitationMedico-legal issuesPCAT-Phys. domains Medical/surgicalIntensityPhysical Complex disability managementSocial/discharge planningSpecialist equipment/facilitiesExpected duration of rehabilitation
Psychometric properties of PCAT Inter-rater reliability – percentage absolute agreement ranged from 66-90%and unweighted kappa coefficients from 0.50-0.80 (moderate – substantialagreement) Concurrent Validity – positive correlation with total RCS-E v12 and total NPDSand negative correlation with total UK FIM FAM Sensitivity and specificity - clinical impression of category A, B, C needs vsPCAT total scores suggestedCategory ATotal score 30PCAT Cog score 15PCAT Phys score 16Category BTotal score 24PCAT Cog score 11PCAT Phys score 13
Summary The PCAT tool is a checklist to aid Rehabilitation Consultants decide on theRehabilitation service level and category required by each individual patient The PCAT tool should be completed once by the Consultant in RehabilitationMedicine on admission to the rehabilitation unit All relevant descriptors within each domain should be indicated The rehabilitation service level required to meet the rehabilitation needsshould be selected based on clinical decision The patient category should be selected using the checklist to inform theclinical reasoning
References NHSE Standard Contract for specialised rehabilitation for patients with highly complex needs Service Specification 2014 4/04/d02rehab-pat-high-needs-0414.pdf) Cost efficient service provision in neurorehabilitation: defining needs, costs and outcomes forpeople with long term neurological conditions (awaiting review by funders)
(PCAT) SELF-SERVICE TRAINING SLIDES UK ROC & NCASRI Professor Lynne Turner-Stokes DM FRCP Regional Hyper-acute Rehabilitation Unit Northwick Park Hospital Watford Road, Harrow, Middx. HA1 3UJ Lynne.turner-stokes@doctors.org.uk NCASRI -National Clinical Audit Specialist Rehabilitation for patients