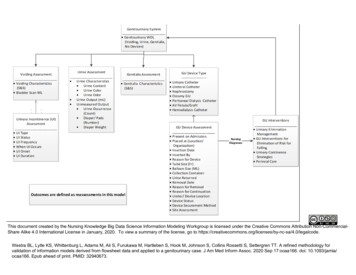
Transcription
Urosepsis and Other CatheterRelated DisordersPaul R TophillConsultant Urological SurgeonPrincess Royal Spinal Injuries CentreNorthern General Hospital, SheffieldUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
What is Sepsis?SepsisSIRST:HR:RR:pCO2:WCC:2 of 38⁰C 36⁰C 90 20 4.3kPa 12,000 4,0002 SIRS Confirmedor suspectedinfectionSevereSepsisSepsis Signs of endorgan damageHypotensionSBP 90mmHgLactate 2mmolSIRS: Severe inflammatory response syndromeUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR TophillSepticShockSevere sepsiswith persistenthypotension
Incidence of SepsisIncidence: 100,000 pa UKMortality: 37,000 pa UKLikely source of infection (STH) Urinary tractRespiratory tractG.I. tractUnknown sourceHepatobiliaryOther sourceSkin/soft tissue42%18%10%10%8%8%4%Urosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Sterile UrineColonised UrineHealthyNormal anatomy/physiologySystemic factorAnatomical/functional abnormalityIncreasedbacterial loadInoculation withcommensalSymptomaticUrinary nSepsisUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR TophillPressure
Impact of ColonisationSterile UrineColonised UrineUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Impact of ColonisationSTD, TBSterile UrineColonised UrineSTD, TBSTD, TBUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Impact of ColonisationSterile UrineColonised UrineSTD, TBSTD, TBSTD, TBInoculationUTI? Female post coitalUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Impact of ColonisationSterile UrineColonised UrineSTD, TBSTD, TBSTD, TBInoculationUTI? Female post coitalRaised pressure Ureteric stonePainUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Impact of ColonisationSterile UrineColonised UrineSTD, TBSTD, TBSTD, TBInoculationUTI?PainSepsis Female post coitalRaised pressure Ureteric stoneUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Impact of ColonisationSterile UrineColonised UrineSTD, TBSTD, TBSTD, TBInoculationUTI? Ureteric stonePainSepsisRaised pressure ImmunosuppressionPain Female post coitalRaised pressureUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Impact of ColonisationSterile UrineColonised UrineSTD, TBSTD, TBSTD, TBInoculationUTI? Ureteric stonePainSepsisRaised pressure ImmunosuppressionPainSevere sepsis Female post coitalRaised pressureUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
ManagementDiagnosis Sepsis screening toolTreatment The sepsis 6 Cardiovascular resuscitation Antibiotics Manage systemic factors E.g. diabetes, immune system support Relieve pressure Drainage; catheter, nephrostomyUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Urosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
The Sepsis Six1.Give high-flow oxygenvia non-rebreathe bag2.Take blood culturesand consider source control3.Give IV antibioticsaccording to local protocol4.Start IV fluid resuscitationHartmann’s or equivalent5.Check lactate6.Monitor hourly urine outputconsider catheterisationwithin one hour.plus Critical Care support to complete EGDTEGDT – Early Goal Directed TherapyUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Soft Tissue InfectionFournier's Gangrene Necrotising fasciitis synergistic gangrene Combination of aerobicanaerobic & microaerophilic Spreading toxin preventsantibiotic penetration Diabetic Urgent debridementUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Scarpa’s and Colle’s FasciaUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Urosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Gas in Bladder Gas forming organisms Not always serious Needs a catheterUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Gas in Bladder Wall Emphysematous cystitis Serious (Catheter in situ)Urosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Left ureteric stone Sterile urine Pain Colonised urine Sepsis NephrostomyUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Intra-Renal RefluxUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Pelvi-ureteric junction obstruction Sterile urine Pain with diuresis Colonised urine Sepsis NephrostomyUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Paraplegic Septic ? cause Reduced renal function ? UrineColonisedClinical History :AKI post-op?hydronephrosis[US Kidney Both]The right kidney demonstrates moderatehydronephrosis.The left kidney also demonstratesmoderate hydronephrosis with a loss ofthe renal cortex mid pole.Kidneys unchanged from previousexamination.Thick walled urinary bladder.Urinary catheter noted in situ. End of Report .Urosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Stone in PUJ NephrostomyUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Perinephric abscess Xanthogranulomatouspyelonephritis (XPN)with fistulaUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Emphysematouspyelonephritis Diabetic May be obstructed May need emergencynephrectomyUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Managing the Dysfunctional BladderTreatment Obstruction e.g. prostate, urethral strictureManagement Dysfunction that cannot be curedUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Problems in Neuropathic BladderManagementIncontinence Neurogenic detrusor overactivity(Reflex bladder contractions) Stress incontinenceInfections, bladder stones Residual urineUpper tract injury Infection – chronically colonised Pressure – hypocomplianceUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Goals in Neuropathic Bladder Management?Protect the kidneysReduce complicationsManage continencePromote independencePreserve body image and sexualityUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Empirical Bladder ManagementEmptying?RU tTreatAnti muscAUSBot A s and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
How can the dysfunctional bladder be managed?Some preserved sphincter function Void with controlHand function and cognitive function Intermittent self catheterisation (ISC)No hand or cognitive function Suprapubic catheter (urethral) Penile sheath (pads) – effective emptyingUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Continuous Drainage(catheter)Little risk of hydronephrosisBut: catheter related problems Chronic infection, pyelonephritis Bladder and kidney stonesUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Urosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Urosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Catheter StrapABUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Continuous DrainageFacilitationSuprapubic Avoids urethral injuryCatheter valve Maintains bladder capacity and clears debrisStorage Reduce overactivityAntimuscularinicsBot A ToxUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Suprapubic CatheterCatheter valveUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Contained IncontinenceMethods Penile Sheath Collection (EUCD)PadsUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Urosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Urosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
ISC Appliance free continence Lowest risk of catheter related complications When combined with a large capacity lowpressure bladder provides maximum kidneyprotectionUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Facilitating Bladder Management by ISCAble to do ISC?DrugsReconstruction Antimuscarinics BotoxAugmentation Reflex bladder Poor complianceMitrofanoffAbdominal stomaUrethra Not available Not accessible ChoiceStress incontinence AUS Sling Urethral closureUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Intermittent CathetersUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Problems with Bladder ManagementStrategiesCatheterSheathVoid withControlISCISC Surgery - -Bladder stones -Kidney stones -- -IncontinenceInfectionsHydronephrosisUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Colonised UrineCausation Undiagnosed urological disease Untreated urological diseaseComorbidity Bladder abnormality/ dysfunctionNeuropathy, diabetes, bladder reconstruction Systemic factorsImmune suppressionUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Challenge – asymptomatic bacteriuria Normal urine is sterile BUT – asymptomatic bacteriuria becomes increasinglycommon with increasing age and is rarely an indication fortreatmentEXCEPTION – PREGNANCY, CHILDREN Prevalence of bacteriuria in over theterised100%100%Urosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
approx. prevalence (%)Prevalence of asymptomatic bacteriuria1412108642005 10 15 20 25 30 40 50 60 70Age (years)FemaleMaleUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Catheter Associated UTI (CAUTI)Cultures often mixed and difficult to interpretBacteriuria is universal by 30 daysTreatment Increases antibiotic-resistant organisms Only if patient develops fever/signs of bacteraemia Does not sterilise the system/ reduce the number ofbacterial species in the urine or decrease febrileepisodesUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Definite UTI in Patients withColonised UrineDiagnosis ClinicalFever, loin pain, foul urine despite adequate urine outputDip test – pointlessTreatment CSU for sensitivities Commence antibiotics Consider catheter on free drainageUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Sepsis in Patients withColonised Urine High index of suspicion for urosepsisAtypical presentation Use sepsis screening tool Implement sepsis 6Catheter on free drainageCSU for sensitivitiesCommence antibiotics CT abdomen/pelvis Nephrostomy if appropriateUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Recurrent UTI in Patients withColonised UrineDiagnosis Clinical. Dip test – pointless Definite UTIFever, loin pain, foul urine despite adequate outputBeware Foul urine only Increased bladder overactivity due to increasedbacterial loadUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Recurrent UTI in Patients withColonised UrineInvestigate for treatable conditions Upper tract – ultrasound, CTStones, tumours, hydronephrosis Lower tract – cystoscopy (flexible), residual urineStones, tumours, poor emptyingUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Recurrent UTI in Patients withColonised UrineTreatment Review bladder management Adequate throughput (minimum 2L day) Effective emptying ( ideally 4x day) Effective control of overactivity Self help strategies Consider self start antibiotics Consider prophylactic antibioticsPersonal benefit vs personal risk e.g. MRSAvs community riskUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Take Home MessagesUrosepsis Drainage is an important treatment in urosepsisColonised urine Is often a multisystem disorder Does not usually need treating Is a risk factor for urosepsis and presents atypicallyCatheters Always consider a suprapubic catheter and/or cathetervalve in patients requiring long term catheterisation Do not dip test urine in patients with catheters ordoing intermittent self catheterisationUrosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill
Always consider a suprapubic catheter and/or catheter valve in patients requiring long term catheterisation Do not dip test urine in patients with catheters or doing intermittent self catheterisation Urosepsis and Catheter Related Problems. February 2015. PR Tophill . Title: Urosepsis and Catheter Related Problems