Transcription
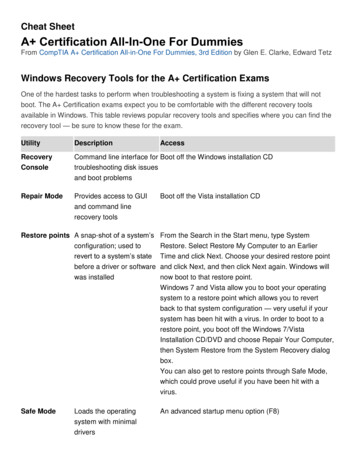
Cheat SheetA Certification All-In-One For DummiesFrom CompTIA A Certification All-in-One For Dummies, 3rd Edition by Glen E. Clarke, Edward TetzWindows Recovery Tools for the A Certification ExamsOne of the hardest tasks to perform when troubleshooting a system is fixing a system that will notboot. The A Certification exams expect you to be comfortable with the different recovery toolsavailable in Windows. This table reviews popular recovery tools and specifies where you can find therecovery tool — be sure to know these for the d line interface for Boot off the Windows installation CDtroubleshooting disk issuesand boot problemsRepair ModeProvides access to GUIand command linerecovery toolsBoot off the Vista installation CDRestore points A snap-shot of a system’sconfiguration; used torevert to a system’s statebefore a driver or softwarewas installedFrom the Search in the Start menu, type SystemRestore. Select Restore My Computer to an EarlierTime and click Next. Choose your desired restore pointand click Next, and then click Next again. Windows willnow boot to that restore point.Windows 7 and Vista allow you to boot your operatingsystem to a restore point which allows you to revertback to that system configuration — very useful if yoursystem has been hit with a virus. In order to boot to arestore point, you boot off the Windows 7/VistaInstallation CD/DVD and choose Repair Your Computer,then System Restore from the System Recovery dialogbox.You can also get to restore points through Safe Mode,which could prove useful if you have been hit with avirus.Safe ModeAn advanced startup menu option (F8)Loads the operatingsystem with minimaldrivers
Last KnownGoodConfigurationLoads the configurationfrom the last time yousuccessfully booted andAn advanced startup menu option (F8)logged onAutomaticSystemRecovery(ASR)An automated installationand restore of WindowsPress F2 during bootupRAID Types for the A Certification ExamsRAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks) is a method of implementing redundancy (duplicatedinformation) on your hard drives — if one disk fails, the other disk(s) can provide the missinginformation. There are many different levels of RAID, but the following are the only RAID levelspertinent to the A exams: RAID 0: Disk striping (striped volume). With RAID level 0, the data is split across drives with nodata redundancy. RAID level 0 improves read and write performance by writing to multipledrives at the same time. You need a minimum of two drives. RAID 1: Disk mirroring/duplexing (mirrored volume). With disk mirroring, the data is written toboth drives involved in the mirror to provide data redundancy. Windows 7 supports diskmirroring. RAID 5: Disk striping with parity (RAID 5 volume). With RAID 5 volumes, the data is written tomultiple drives along with parity information that is used to help recover data if a single drivefails. RAID 5 volumes need a minimum of three disks. RAID 10: Mirrored disk striping. RAID level 10 is also known as RAID 1 0 because it is diskstriping while mirroring the data written in the stripe.
Bus Architectures for the A Certification ExamsAnother term for the expansion slots on a computer’s motherboard is bus slots. A number of differentbus architectures have been developed over time. For the A exams, you need to be able to identifythe differences between each of these bus architectures and know which ones are more populartoday.Architecture Bus Width(In Bits)SpeedISA8/168 MHzEISA328 MHzPCI32/6433 MHzAGP3266 MHz (1x), 133 MHz (2x), 266 MHz (4x), 533 MHz (8x)PCMCIA(laptops)1633 MHzPCIeSerialUses multiple lanes, with each lane carrying 250 Mbps. As an example,a PCIe x1 slot can carry data at 250 Mbps, while a PCIe x4 slot cancarry data at 1 Gbps. PCIe version 2 doubles those transfer rates.USB and FireWire Standards for the A Certification ExamsThe most popular ports used today on the system are the USB and FireWire ports — which allow youto connect devices such as flash drives, digital cameras, and digital video cameras. This tablecompares features of USB and FireWire, including the transfer rate and number of devices supported.StandardTransfer RateDevice SupportUSB 1.012 Mbps127 devicesUSB 2.0480 Mbps127 devicesUSB 3.05 Gbps127 devicesIEEE 1394 400 Mbps; also known as FireWire63 devicesIEEE 1394b 800 Mbps; also known as FireWire 800 63 devices
Windows XP Boot Files for the A Certification ExamsWindows XP requires four core files to boot the computer. You will need to understand what they areon your A Certification exam. The four core files are: ntldr: Operating system loader code boot.ini: Builds the operating system selection menu ntdetect.com: Performs hardware detection ntoskrnl.exe: Core kernel code responsible for tasks such as thread managementWindows 7 and Windows Vista Boot Files for the A CertificationExamsWindows 7 and Windows Vista utilize four boot files, and you will need an understanding of all four ofthem for the A Certification exams. The four boot files for Windows 7 and Vista are: bootmgr: Operating system loader code; similar to ntldr in previous versions of Windows Boot Configuration Database (BCD): Builds the operating system selection menu; similar toboot.ini in Windows XP, but data resides in the BCD store. You can edit the boot configurationdata with the bcdedit utility. winload.exe: Loads the Vista operating system if selected from the operating system selectionmenu provided by BCD winresume.exe: Resumes the Vista operating system if the system is started from a hibernatestatePower-On Self-Test Error Codes Categories for the A CertificationExamsEach BIOS manufacturer has its own diagnostic codes that identify specific POST errors. You need toconsult the BIOS documentation for the diagnostic codes for your BIOS, but the general breakdownof the code categories is as follows: 100–199: Motherboard error 200–299: Memory error 300–399: Keyboard error 600–699: Floppy drive error 1400–1499: Printer error 1700–1799: Hard drive error
Windows Troubleshooting Utilities for the A Certification ExamsAs an A Certified Professional you will troubleshoot a number of different problems on the system —this table outlines some of the popular utilities you will use to support or troubleshoot a system. Besure to know these before taking the A Certification exams!FilenameNameDescriptionchkdisk.exeCheck DiskCheck your hard drive for problems with the file system and forbad sectors.regedit.exeRegistry EditorMake changes to Registry values; can be used to make selectivebackups.defrag.exeDiskUsed from the command line, or graphically through the MicrosoftDefragmenterManagement Console (MMC).ntbackup.exe Windows NTbackupBack up files to tape or any writable file system.sfc.exeSystem FileCheckerVerifies that system files have not been modified; or, if they have,replaces them with the original.taskman.exeTask ManagerSee running programs and services, terminate problems, andview rudimentary performance information about the system.perfmon.exePerformanceView detailed performance informationConsolemsconfig.exe SystemConfigurationToolReconfigure the boot process for troubleshooting and diagnosingthe boot process.drwtsn32.exe Dr. WatsonConfigure the level of logging you want to do when applicationscrash.SystemInformationView hardware and configuration information for your computer.Event ViewerLogging component of the operating system; the central locationfor all logging activity.
Windows Network Troubleshooting Utilities for the A CertificationExamsWhen problems arise on a Windows network, you can use the following utilities to do yourtroubleshooting. Having a clear understanding of all of them will help you on the A Certificationexams. ipconfig: Display basic TCP/IP configuration, such as IP address, subnet mask, and defaultgateway. ipconfig /all: Display TCP/IP settings, including your Media Access Control (MAC) address,domain name system (DNS) server, and lease information. ipconfig /release: Release your IP address. ipconfig /renew: Renew your IP address. ping IP address or ping host name : Send four test messages to the IP address or hostname you specify; verify whether the other system is up and running. netstat: Display TCP/IP protocol statistics and connection information. Can be used to see whois connected to your system; what ports are open. nslookup: Troubleshoot DNS problems. For example, you can get a listing of all the records inDNS using nslookup. arp: Troubleshoot ARP. Shows MAC address. For example, you can use arp -a to view yourAddress Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache.
Windows Security Best Practices for the A Certification ExamsOne of the most important skills to have as an A Certified Professional is the capability of securingWindows systems and networks. And even if you are not working in a networked environment, youcan apply these same skills to your customers with home Internet machines. Harden the operating system: Uninstall any software you are not using and stop any servicesnot being used. The more software that is running, the more potential security holes in thesystem. Patch the systems: Keep the operating systems and devices up to date with Service Packsand security patches. Use a firewall: Ensure that there is a firewall between your system and the Internet. A firewallprevents hackers from connecting to your system Use strong passwords: Ensure that all user accounts use a strong password (at least eightcharacters, and uses a mix of uppercase and lowercase characters, numbers, and symbols). Enable auditing: Log any suspicious activity on the system so you are aware of it. Secure your wireless routers: If you have no need for wireless, disable this functionality onyour wireless router. If you are using wireless, secure it by changing the SSID, disabling SSIDbroadcasting, and encrypting traffic with WEP, WPA, or WPA2 (best option). You should alsosecure the wireless router by setting a strong password for the admin account and disableDHCP on the router. You will then need to configure all your clients with static IP addresses. Use antivirus software: Install antivirus software on all servers and client machines to helpprotect your systems from a virus. Make sure that your virus definition database is frequentlyupdated.
10 or So Things You Might Have Forgotten for the A CertificationExamsWith the massive amount of information you’re required to know for the A Certification exams, thereare bound to be a few things that might slip past you. Here’s a quick list of some things you’ll need toknow for the A Certification exams that you might have easily forgotten or overlooked. Contrast ratio: A value measuring the brightness of different colors such as white versus black.The larger the ratio, the better the picture quality on the display. Native Resolution: The actual resolution of a monitor, as opposed to the display resolutionwhich may be set lower which scales the image to the display area of the monitor. Creation of files: You can create a file in any folder on your hard drive by right-clicking in anempty area and choosing a document type from the New menu. Files can also be created fromapplications by choosing the application’s save feature. Grayware: A term used to describe software that performs unwanted actions. Graywareencompasses malicious software such as adware and spyware. Be sure to have malwareprotection software loaded on your system to protect against forms of grayware. Spam: An unsolicited e-mail message. Today’s e-mail servers are being hit with a wealth ofunsolicited e-mail messages a day from companies that are trying to sell services or products.Be sure to configure spam filters on your e-mail servers and e-mail clients. KVM switch: A device that allows you share a keyboard, video device (monitor), and mousebetween several computers while being able to quickly switch between them. Reset page count: A troubleshooting tip for printers — if you find the printer reports low tonerand you know there is more than enough toner available then it could be that the printer isgauging the toner level by the number of pages printed. Find out how to reset the page count onyour printer to get rid of the low toner error. Avoid trip hazards: You may create trip hazards when doing things like testing a replacementnetwork cable by using a network jack which is further away or laying out tools and computercomponents in a walkway by a desk. Always ensure that you are not needlessly risking thesafety of yourself or others. Heavy devices: Most computer equipment is light enough for a single person to handle whilemany servers and UPSs will require two people to move or place in a server rack. Alwaysensure that you have help for these and other heavy items and bend with your knees to preventinjury. Hot components: As equipment is used, many components will build up heat, which can injureyou. This is especially true of both computer and printer components. When servicingequipment, ensure that you exercise proper care when hot components are present.
Odors: When troubleshooting system components be aware of unexpected odors or smells thatmay lead you to the source of the problem or signal an immediate danger. For example, burnedsmells could identify overheating components or melted connectors. Taskbar: The bar at bottom of the Windows desktop which displays the Start menu, all openapplications and documents, and contains the system tray (systray). Systray: The systray (or system tray) is on the right side of the taskbar and displays manyrunning processes, known as background processes that run in the background but do not havea visual interface until you click on the icon in the system tray. Most of these processes areaccessed by clicking or right-clicking on the icon in the system tray so that you can change thesettings of the running program or terminate the process by choosi
05.08.2014 · Cheat Sheet A Certification All-In-One For Dummies From CompTIA A Certification All-in-One For Dummies, 3rd Edition by Glen E. Clarke, Edward Tetz Windows Recovery Tools for the A Certification Exams One of the hardest tasks to perform when troubleshooting a system is fixing a system that will not boot. The A Certification exams expect you to be comfortable with the different recovery .










