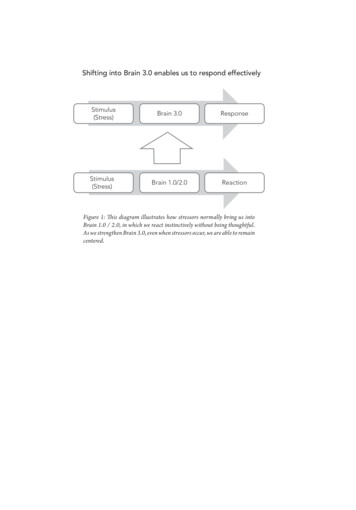
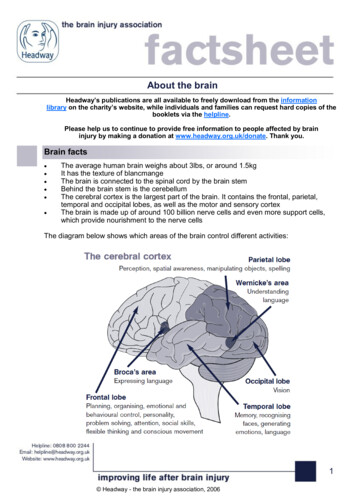
Transcription
Concussion and Traumatic Brain InjurySecondary to Domestic, Intimate Partner andFamily ViolenceEdie E. Zusman, MD, MBA, FACS, FAANSNeurosurgeonDirector, TBI and Concussion ResearchPiedmont Neuroscience CenterCEO SafeLivingSpace.org
Piedmont Neuroscience CenterEdie Zusman, MD, MBAJoshua Kuluva, MDErica Dellenbach, BSSLS Board of DirectorsPiedmontNeuroscienceCenterandSafe Living SpaceEdie Zusman, MD, MBAJudy RobinsonCatherine Ndungo-CaseAdam PrattStacie Buchanan, MSWSLS Advisory BoardJahmal Miller, MHAJessica Almgren-Bell, BSElliott Block, DOJordan Glassman, BSSuzannah Henderson, BSRebecca Hendrickson, RNGretchen Hess, MA, MSKasey Holbert, BSKatherine Kaffka, MSWJonathan KarpaWendy Wood-Kjelvik, RNJoshua Kuluva, MDSaint-Aaron Morris, MDLoc Nguyen, MDJane A. Petro, MDRachel Plouse, BSAndrew Reisner, MDBecky K Reiter, RNHeather Theaux, RNNanci Tucker, MDYuriy Vinokur, MDJerrod Woo, BSErica Dellenbach, BS
Concussion and Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Sudden trauma causing damage to the brainClassified as mild, moderate, or severe - ContinuumEvent can be associated with or without loss ofconsciousness - Anterograde AmnesiaImmediate symptoms may include: Confusion/ disorientation - CompetencyMemory difficultyBehavioral/mood changesBlurred hargyLong term - Alzheimer’s, dementia, Parkinson’s, and CTECDC HEADS UP, 2019
Case 1: Motor Vehicle AccidentPatient demographic: Age: 46Gender: Cis maleEthnicity: WhiteOccupation: Former CFO“Sends wife into Starbucks while he waitsin the car as he feels he may hit someone ifthey get in front of him in the line.”Injury: Motor Vehicle AccidentSymptoms: Headaches Neck pain Memory problems Balance issues Emotional lability
Case 2: Intimate Partner ViolencePatient demographic: Age: 27Gender: Cis femaleEthnicity: LatinxOccupation: Pole Dancer“Signs and symptoms of concussion oftenexist with no evidence of external injury Invisible.”Injury: Pushed out of moving car by boyfriendLeft orbital & maxillary sinus fracturesConcussionSymptoms: Headaches Memory problems Balance issues Anxiety Depressed mood Difficulty sleeping
TBI and Concussion ClinicMayo Clinic Network Affiliate - NorthBayMen wearing sunglasses in clinic are diagnosed with “photophobia/ light sensitivity.”Women wearing sunglasses in clinic are described as “embarrassed.”Example of cognitive bias in healthcare and a social justice issue in our culture
Concussion in Domestic andIntimate Partner ViolenceThe current landscape of the literature
Concussion/TBI in DV/IPV/FVLiterature Review - Safe Living Space Research TeamMethods: Literature review identified 55 primary researchpapers that evaluated concussion and/or TBI within domestic,intimate partner, and family violence populations
Concussion/TBI in DV/IPV/FVLiterature Review - Safe Living Space Research TeamResults:In the 55 papers identified 100% of studies found patients had sustained concussion and/or TBIIncidence of concussion and/or TBI among DV/IPV/FV victims ranged from18.8% - 100% Mean incidence: 58.8%Studies that evaluated patients with concussion and/or TBI: history of multipleconcussions (3 ) in 75% - 88% of patients
Paucity of Research into TBI from DV/IPV/FVLiterature Review - Safe Living Space Research TeamResults: 0.55% of over 16,000studies included evaluation ofconcussion and/or TBI.
Concussion from DV/IPV and footballBrain injuries from DV/IPV: 1.6 million in the US per year (Valera)Concussion/brain injury from football:NFL: 187 in 2021 (preseason regular season)College football: 166 in 2015Hillstrom, 2022NFL, 2022Bella, 2015
No difference in sports concussion metricsConcussion from domesticand intimate partner violence Concussion from sports injury
TBI is occurring inDV/IPV/FV situationsPutting it alltogetherPresentation is thesame as TBI by otherinjury mechanismsThere is no currentprotocol forconcussion screening,evaluation and care
Increasing awareness
Symptoms and Sequelae of Injuriesto the Head and NeckConcussion and Strangulation
Symptoms of ConcussionIn addition to commonly recognized symptoms Amnesia surrounding event difficult to take statement Memory difficulty could forget appointments Difficulty multitasking and maintaining attention losing job Impaired decision making contributes to difficulty finding safe housing
Immediate Risks Associated with Concussion Second Impact Syndrome Second concussion before complete recovery from first Risk of permanent brain injury and deathReturn to play guidelines in sports Player is removed from the game to prevent second impact syndrome/ repeatconcussionPrevention of long-term risks for multiple concussions (3-4 or more lifetime)Should concussed victims be removed from a risky environment to minimizelikelihood of sustaining second impact syndrome/ repeat concussion?
Signs/Symptoms of StrangulationThose who experience DV/IPV also at risk forstrangulation Physical Symptoms: Petechiae in the skin, conjunctive, and/ormucosal surfacesContusionsLigature marks from use of an objectLoss of consciousnessLoss of bowel or bladder controlSwelling of the airway or neckDifficulty breathing or swallowingNeurologic effects due to anoxia, or lack ofoxygen, may not be distinguishable fromthose due to concussion.Neck, throat, and neurologic injuriesintensify with repeat episodes ofstrangulation.Armstrong & Strack, 2016
Strangulation as a precursor to DV Homicide In 43% of homicides in DV/IPV, therewas prior history of strangulationDV/IPV with history of strangulation high risk factor for death Women who had been strangledeven once were 7.5x more likelyto become a homicide victimMost do not have physical injuries uponexamination by police officerUnknown whether concussion, whiplash,and traumatic brain injury precedestrangulation events and/or are alsoassociated with homicide.Glass et al., 2008Strack et al., 2003
Identifying Victims of Concussion and StrangulationConcussion: Contusions - marks on the skinNeurologic effects: Loss of consciousness Loss of memory Headaches DizzinessNausea/vomitingDifficulties with balance and/or coordinationDouble vision/blurred visionNO VISIBLE SYMPTOMS Mechanism of injury Concussion screeningStrangulation: Contusions - marks on the skinNeurologic effects: Loss of consciousness Loss of memory Headaches DizzinessVomitingPetechiaeScratch/ligature marksDifficulty breathing or swallowingSore throat and/or hoarse voiceNO VISIBLE SYMPTOMS Mechanism of injury Concussion/ strangulation screeningStrangulation Training Institute, 2017
Importance of Early Identification and DiagnosisRepetitive injury to the head/neck short term effects and increasedrisk of long term sequelaeDecrease risk of sustaining multiple injuries to the head and neck throughsafe placement when possible Screening and early identification Who: DV shelter workers, advocates, public health officers, law enforcement, firstresponders, clinicians/emergency departments/women’s health/primary care
Concussion Treatment and CareThe pathway of care after diagnosis1.Identification/diagnosis of concussion2.Concussion treatment (modeled after return to play guidelines)Medical carePsychological careSocial supportEducationMedical care for concussion in addition to other services that arecurrently provided
Thinking back to Case 2 Used sports concussion protocols asframework for discussion“If you had sustained this injury in a soccermatch, we would remove you from the game.” Patient stayed with her mother toavoid additional injury and reducerisk of second impact syndrome andmultiple concussions
Case 2 continued Pathway of CareInterventions/treatments Initial decrease in activity levels followed bystepwise increase once other symptoms improved Medications prescribed to assist with sleep andheadachesPhysical therapy and psychiatry Outcomes: Progress was seen on each TBI and concussion metric over time with treatment. Whileshe initially considered returning to her partner, patient reported that her decision changed as her“head cleared”.
First Responder Concussion Screening ToolSafe Living SpaceAbout the tool: 10 questions Mixed cognitive and symptomatic assessment withphysical exam Administered by a third party (first responder, policeofficer, social worker, DV shelter, etc.) Medical care advised based on scoreAccess the tool:
Questions 1-5
Questions 6-10
First Responder Concussion Screening ToolSafe Living SpaceHow to access Tool is free on SafeLivingSpace.orgOther resources availableFeel free to use, modify, and customizeour tool—we appreciate all feedbackand would be happy to feature yourmodified version on our siteComing soon QR code to digitize this and similarresources
ConclusionAll people who have experienced domestic, intimate partner, and familyviolence should be screened for concussion and strangulation. Concussion is prevalent in DV/IPV, causes serious short- and long-termsequelae, and is clinically the same as concussion from other causesRisk for concussion in DV/IPV is understudied and under-recognized, leading toa gap in screening and appropriate pathways to care for this patient populationStrangulation in DV/IPV has recognized association with homicide and furtherstudy will determine whether TBI/concussion is a predictor of escalationDetection of concussion and/or strangulation requires providers, officers, andprofessionals across multiple fields be trained in proper screening andresponse
Contact: Edie E. Zusman, MD, MBA, FACS, rtners.org
References1.2.3.4.5.6.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019, February 12). Concussion danger signs. Centers for DiseaseControl and Prevention. Retrieved April 17, 2022, fromhttps://www.cdc.gov/headsup/basics/concussion danger signs.htmlZusman, E. E. 2022, April 29-May 2. Is there a role for concussion screening for patients who have experienced domestic, intimatepartner or family violence? [Video]. AANS, Philadelphia.Hillstrom, C. (2022, March 1). The hidden epidemic of brain injuries from domestic violence. New York Times. Retrieved April 18,2022, from trauma-domestic-violence.htmlBella, T. (2015, December 30). What have we learned from 500 concussions in 3 years of college football? Al Jazeera America.Retrieved April 17, 2022, a-college-football-reporting.htmlNFL. (2022, February 7). Injury data since 2015. NFL.com. Retrieved April 17, 2022, lth-and-wellness/injury-data/injury-dataZusman. E. E. 2021, August 21-15. Use of Sports Concussion Metrics to Assess Traumatic Brain Injury Secondary to DomesticViolence/ Partner Violence [Video]. AANS, Orlando, ram/Eposter?eventid 49140&itemid EPOSTER&propid 53815.
References (continued)7.8.9.10.Armstrong M, Strack GB. Recognition and Documentation of Strangulation Crimes: A Review. JAMAOtolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016;142(9):891–897. doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2016.0293Glass, N., Laughon, K., Campbell, J., Block, C. R., Hanson, G., Sharps, P. W., & Taliaferro, E. (2008).Non-fatal strangulation is an important risk factor for homicide of women. The Journal of emergency medicine, 35(3),329–335. doi.org/10.1016/j.jemermed.2007.02.065Strack, G. B., McClane, G. E., & Hawley, D. (2001). A review of 300 attempted strangulation cases.Part I: criminal legal issues. The Journal of emergency medicine, 21(3), ves, Y. (Ed.). (2017). Signs and symptoms of strangulation. Family Justice Center Alliance Signsand Symptoms of Strangulation Comments. Retrieved April 17, 2022, signs-and-symptoms-of-strangulation/
TBI and Concussion Clinic Mayo Clinic Network Affiliate - NorthBay Men wearing sunglasses in clinic are diagnosed with "photophobia/ light sensitivity." Women wearing sunglasses in clinic are described as "embarrassed." Example of cognitive bias in healthcare and a social justice issue in our culture