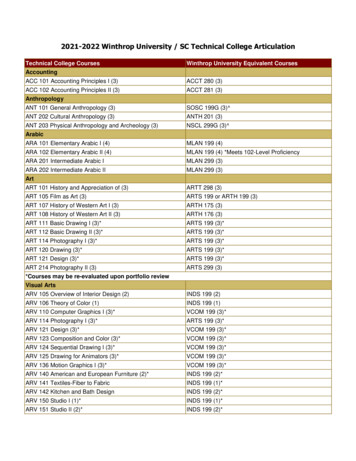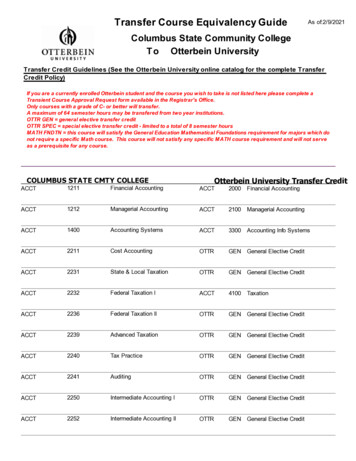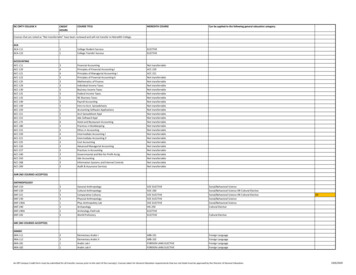
Transcription
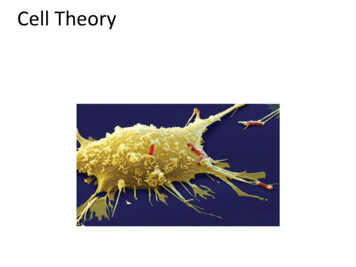
Cell Theory
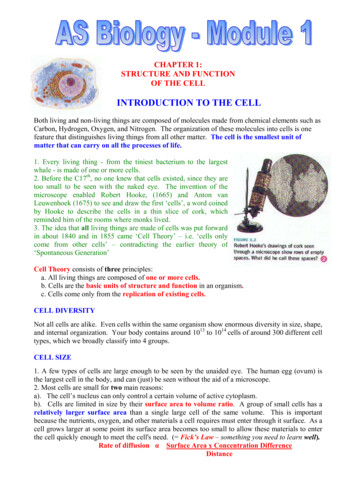
The cell theory grew out of the work ofmany scientists and improvements in themicroscope.Many scientists contributed to the cell theory.More was learned about cellsas microscopes improved.The cell theory is a unifyingconcept of biology.
3.1 CellTheoryThe cell theory has three principles. All organisms are made of cells. All existing cells areproduced by otherliving cells. The cell is the mostbasic unit of life.
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleusand membrane-bound organelles;prokaryotic cells do not.All cells share certain characteristics. Cells tend to be microscopic.cell membrane All cells are enclosed by amembrane. All cells are filled withcytoplasm. All cells have DNAcytoplasmBacterium(colored SEM; magnification 8800x)
There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells andprokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells have anucleus.nucleus Eukaryotic cells havemembrane-boundorganelles.organellescell membrane
There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells andprokaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells do nothave a nucleus.nucleus Prokaryotic cells do nothave membrane-boundorganelles.organellescell membranecytoplasm
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONCHARTPLANT CELLANIMAL CELL
1. Cell Wall (Plants only) inflexible barrier “protecting” thecell and giving it support. Is not selectivelypermeable. It is a rigid structure.
2. Cell Membrane Boundary (“wall”) between the cell and theenvironment. Allows nutrients/ regulatesmovement in and out of the cell. (“SelectivelyPermeable”).
3. Microtubules Part of cell skeleton that act as a scaffold tomaintain the shape of a cell. (“SupportingFramework”)
4. Nucleus Central leader of the cell. Surrounded bynuclear envelope. Contains directions to makeproteins and genetic information, DNA orRNA. (“Control Center of Cell”); inside is thenucleolus which makes ribosomes.
5. Nuclear Membrane The outer lining or wall of the nucleus.(Sometimes this is called the nuclearenvelope.)
6. Chromatin Master set of directions for making proteins.Contents are in the form of Genes & DNA.
7. Vacuole Membrane-bound “compartment” used fortemporary material “storage”. (In plants it isfound in the center of cell, in animals it is offto the side)
8. Mitochondria Membrane-bound organelle that transforms(“generates”) energy from the cell.(“Powerhouse of cell”)
9. Lysosome Contain enzymes which digest excessorganelles, food particles, viruses, andbacteria. The “vacuum cleaner” of a cell. Theybreak down organelles not needed.
10. Rough EndoplasmicReticulum The site of cellular chemical reactions. RoughER means ribosomes are attached and aresynthesizing/making proteins.(“Transportation system with workers”)
11. Smooth EndoplasmicReticulum The site of a cellular chemical reaction.Smooth ER has no ribosomes present.(“Transportation system with no workers”)
12. Ribosomes Site where the cell produces proteinsaccording to the DNA instructions, whichcomes from the nucleus. (“Workers of cell”)– Bound Ribosomes: make proteins for use outsidecell– Free Ribosomes: make proteins for use inside cell
13. Golgi Apparatus Flattens and packages proteins to be sent totheir appropriate destination (The“UPS/FedEx” of the cell)
14. Chloroplast (Found in green plants and some protists only)– converts light energy (SUN) to chemicalenergy (SUGAR). - Contains Chlorophyll
15. Cytoplasm Clear, gelatinous fluid inside a cell whichsuspends and holds a cell’s organelles, such asthe nucleus.
16. Centrioles (Animal Cells Only) Play a role in cell division
CytoskeletonNetwork of fine tubesand threads. Providesinternal structuralsupport.
Cilia, Pilli, and FlagellaStructures used to enablemovement of cells or sometimes topropel substances across outersurface of the cell. Predominantlyprotein in composition.
Quiz of the cell Know all organelles found in a prokaryotic cell Know all organelles found in a eukaryotic cell
basic unit of life. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles; prokaryotic cells do not. All cells share certain characteristics. Cells tend to be microscopic. All cells are enclosed by a membrane. All cells are filled with cytoplasm.