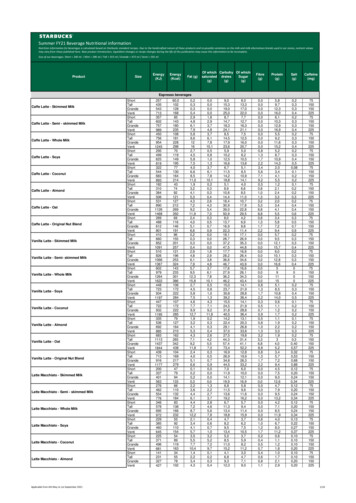
Transcription
Nutritional Properties of Food MaterialsFood materials can be chosen for their nutritional value or contribution to the food product.NutrientProteinStructure Protein is made fromamino acids Amino acids combineto make muscles,hormones, skin,antibodies, nails,enzymes, cellmembranes,haemoglobin In plant and animalprotein there are about20 different amino acids The body can makesome amino acids (nonessential amino acids)The other amino acidshave to be obtainedfrom the food we eat –these are essentialamino acids The human body needsall 20 amino acids Children need 10essential amino acids Adults need 8 essentialamino acidsAlternative proteins forpeople who : want a more varied diet are health consciousFunction For bodygrowth For body repair For energy Formaintenance ofhealthSourcesAnimal source: Cheese, eggs, fish, meat, milk, gelatine, offalProteins from animal sources have a High biological value (HBV) as they containthe essential amino acids.Plant Source: Cereals – Wheat, Oats, Pulses, Rice, Beans, Peas, Pulses, Quorn ‐Mycoprotein, Soya, TVP, Bread, PastaProtein from most plant sources are of Low Biological Value (LBV) as they arelacking in more than one essential amino acids. Soya beans however are of a HighBiological ValueIt is advisable to eat a variety of these foods to help the body obtain all theessential amino acids. For example;Spaghetti bolognaise, Chicken curry and rice ,Cauliflower cheese,Meat topped pizza, baked potato with baked beans and cheese.Deficiency / Too muchA protein deficiency cancause various problems Growth slows or stops inchildren Liver fails to function Muscles become weak Limbs are thin Tummy is soft and maylook distended Enzymes are notproduced so digestivesystem not functioningproperly KWASHIORKOR is adisease where there is ashortage of proteinToo much protein will beconverted to energy and ifunused will be stored as fatin the bodyAlternative Proteins –Meat free proteins1
and want to eat lessanimal foods do not wish to eatanimal foods because ofmoral, religious orethical beliefsAlternative Proteins are:‐ High in protein Low in fat Enriched with Vitaminsand MineralsFood combiningMixing different lowbiological value proteinsto supply all the essentialamino acids.Vegetarians, vegans orother limiting diets relyon combining lowbiological value proteins(LBV) to form proteins ofhigher value. Examplesare:Beans on toast,Hummus with pitta breadDhal and ricelentil pate with FrenchbreadTexturised Vegetable Protein (TVP) is made from soya beans It is an excellentsource of protein and fibre and has a long shelf life if stored correctlyTIVALL is made from Soya & Wheat Proteins with Calcium, Iron & Vitamins A & B.They are low in fat, saturates, salt and contains no cholesterol or artificialpreservatives or colours.QUORN is a MYCOPROTEIN which is extracted from a fungus (similar to themushroom) which is grown in large vatsIt is not a vegan food as egg white is used as a binder. It is a healthy meatalternative, free from animal fats and cholesterol. It has high biological valueprotein and dietary fibre.TOFU and BEAN CURD is made from soya beans, water and a coagulant, orcurdling agent. The curds are pressed into soft white blocks. It is bland, high in2
protein and calcium and has the ability to absorb new flavors through spices andmarinades. Tofu and bean curd products can be bought frozen. Chilled, ready tocook and eatRef to video: http://video.about.com/vegetarian/Tofu.htm (How to cook withTofu with Ben Kurtzman)3
Task:Match the protein type to the correct source using the following words:Gluten, Connective tissue, Lactalbumin, Milk and cheese, EggProtein typeAlbumenSourceMilkCaseinWheatCollagenTask: Alternative proteins can be found in supermarkets.Complete the table below to show which statements are true or false by placing a tick ( ) in the correct columnStatementsAlternative proteins can be bought in different forms and cooked in many different waysQuorn is a mycoprotein and is suitable for vegansTofu can be flavoured with spices, sauces and marinadesAlternative proteins are usually difficult to storeTask:TrueFalseUsing the words from the list below complete the sentences showing the ethical considerations for alternative proteins.Controlled environment lessCheaperquicker,Alternative proteins are . and .to produce than meat and require. land.They are made in a. . which helps to keep pollution to a minimum.4
NutrientCarbohydrates(CHO)SugarsStructureComposed from theelements Carbon,Hydrogen andOxygen (hydratebecause of the sameproportion of H andO as in water H2O )Carbohydrates aredivided intoi. sugars (simplecarbohydrates) andii. starches (complexcarbohydrates)Monosaccharides(simple sugars)Glucose , Fructose(fruit sugar)Function For energy used forbodily functions Provide body withenergy for physicalactivity Sweeten andflavour foods Provide dietaryfibre non‐starchpolysaccharide(NSP) to helpdigestionSourcesUsually plant products which has energy obtained from the sunlight withthe help of chlorophyllCarbon dioxide H2O energy carbohydrates oxygenDeficiency / Too muchToo much CHO will be stored as fat in the body can lead to weight gainand obesity Absorbed quickly bythe body Gives instant energyGlucose is: found in fruits, vegetables such as onions, honey can be manufactured from starch for sweets. not as sweet as cane sugar and can be added to foods and drinks toincrease their energy content but not making them too sweetFructose is found in fruit, honey, plant juicesSugars are also found in drinks, jam, cakes, biscuits.Glucose is often used by athletes in tablet or powder form to provide afast –energy boostToo much sugar causes: tooth decayPlaque sucrose acidAcid tooth decay obesityDisaccharides(double sugars)Lactose (glucose andgalactose),Sucrose (glucose andfructose)Galactose is formedduring digestion oflactose (milk sugar)Lactose: Milk sugar (not as sweet as sucrose), milkSucrose: Sugar cane and sugar beet, fruit, vegetables5
MaltoseA word ending in‘ose’ suggests thepresence of sugarMaltose: Formed from starch in the germination of barley grain. Malt isused in some food production and as a dietary supplementINTRINSIC sugar:contained within theplant cell wall of fruitand vegetables.Intrinsic sugars areless harmfulEXTRINSIC sugars:sugars you can seeand added sucrose toproducts such ascakes, ydrate such asstarch or fibre)Starch must be broken down intosugars by digestion. It is a slowerprocess of releasingenergy Adds bulk to thedietStarch comes from plants which store starch such as potatoes, rice,cereals, and pulses. Other sources are pasta, cakes, biscuits, puddings,breakfast cereals. Flour, cornflourToo much starch will: be converted into fat lead to being over weightand obesityPeople involved in high endurance sports eat starchy carbohydratessuch as pastaDextrin (moresoluble than starch)Dextrin comes from starch which has been changed by cooking e.g. toast,breakfast cereals, crusts of loavesGlycogenGlycogen is an animal carbohydrateActs as roughageCelluloseSkins of fruit, vegetables, cerealsSets jam (pectin)HemicelluloseFruit and vegetables6
Non starchpolysaccharidesNSPNSP is a type of fibrei. Soluble fibreii. Insoluble fibreSoluble fibre Slows down theabsorption of CHO Helps control bloodsugar levels Stops us feelinghungry Reduce bloodcholesterol levels Reduce risk ofheart disease Reduce risk ofdiabetespreventsconstipationSoluble fibre is found in pulses, oats, fruit such as apple, bananas andleafy vegetables, peas, beans, lentilshttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v jajYw8G8ZUY(Good to Know about Dietary Fibre)Too little fibre in the dietcan cause: constipation diverticular disease wherethe lining of the intestinebecomes inflamedhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v QsZML2KQoqg(Importance of Dietary Fibre and How Dietary Fibre Works)Insoluble fibre is found in cereal products such as oats, baked beans,wholemeal flour, wholegrain breakfast cereals, pasta, brown rice, somefruit and vegetablesFact:If the body takes in more carbohydrates than it needs for its energy use, the unused carbohydrates will be stored asfat in the body. This can lead to obesity.Task: Design and make lunch for an athlete which is high in carbohydrates.Use Nutritional software to calculate the percentage carbohydrate in the meal.7
NutrientFatsSaturated fats.Structure Composed from the elementsCarbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen thesame as carbohydrates but indifferent proportions The most concentrated energyfood Fats are solid at roomtemperature Oils are liquid at roomtemperature Fats and oils are made from:‐i. Glycerol or glycerine (sweetsticky liquid)ii. Fatty acids (there are about 25fatty acids) 1 molecule fat 1 glycerol 3 fattyacids Fatty acids may be saturated orunsaturated The type of fatty acids present willdetermine the consistency of the fator oil:‐Lard –soft fat –oleic acidBeef fat – hard fat – palmitic acidSaturated fats.Each carbon atom in the fatty acid iscombined with two hydrogen atoms solid at room temperature too much saturated fat in the dietFunction provide concentrated sourcesof energy form part of the structure ofcells help to insulate the body incold weather. Excess fat in the diet is storedas body fat Vital organs such as kidneysare protected by a layer of fat Fat is a source of fat‐solublevitamins A, D, E, K Fat gives texture and flavourto foods We are advised to lower ourintake of fat by 35% of ourtotal energy intakeFats helps to give a feeling ofbeing full for longer after eating‐satietySourcesFats come from animal andplant sourcesPlant sources:fruits such as olives, avocadopearsnuts – peanuts, walnuts, pulsesseeds – sunflower, soya, sesameDeficiency / Too muchExcess fat in the diet will be stored as body fatcan lead to weight gain andobesityAnimal sources:Meat and meat products such aslard, suetDairy products such as milk,butter, cheese, creamFish particularly oily fish such astuna, sardines, salmon. Animal sources: butter, lard,hard margarine, cheese, wholemilk and anything that containsthese ingredients, such ascakes, chocolate, biscuits, piesand pastries. It's also the whitefat you can see on red meatand underneath poultry skin.8
is associated with Vegetable sources such ascoconut and palm oilsi. high blood cholesterolii. increased risk of heart disease.iii. diabetesiv. obesityCholesterol is produced in the liver transported round the body by theblood deposited on the walls of thearteries, narrowing them andmaking them less efficientUnsaturated fatsSoft or liquid at roomtemperatureNarrowed arteries: a majorcause of heart diseaseThere are two types:i. Monounsaturated fat:A fat molecule with one hydrogenspaceii. Polyunsaturated fatsA fat molecule with more than onehydrogen spaceMonosaturated fatty acids can: Help to lower bloodcholesterol Reduce the risk of diabetes Be linked with a lower rate ofcancerMonosaturated fatty acids arefound in animal and vegetablefats, fish, nuts, olivesVegetable sources: sunfloweroil, soya oil, olive oil, sesame oil,mackerel, sardines, pilchards,salmonThey are very soft /oily at roomTrans fatty acidstemperatureMan‐made molecules producedwhen hydrogen is added tovegetable oils to make them intosolid fats This is known asTrans fatty acids: raise cholesterol levels are bad for thecardiovascular system9
hydrogenation.Essential fatty acidsEFAsEssential fatty acids: cannot be made by the body are important to the healthy andefficient functioning of the bodymay increase risk of breastcancerEssential fatty acids areimportant for regulating body processes blood clotting controlling inflammationTwo examples of EFAs are Omega 3 Rancid fatsOmega 6Hydrolytic fat caused by the glycerolOmega 3 protects the heartOmega 3 is found in oily fish,seeds, green leafy vegetables,walnut oilOmega 6 helps lowercholesterolOmega 6 is found in fruits,grains, seeds, vegetables,chickenRancid buttersplitting from the fatty acidOxidative fat :breakdown of fattyacids in reaction with oxygenFacts A slice of malt loaf contains 0.7g fatA teaspoon of peanut butter contains 5.4g fatA jam doughnut contains 10.9g fatA handful of mixed nuts contains 21.6g fatA pint of whole milk contains 22.8 g fat10
Task: Visit your supermarket and conduct a survey of the types of products that have a lower‐fat version.Record your findings in the following table.Product NameRegular ProductFat content per 100gPriceLower‐fat versionFat content per 100gPriceHow much is the fat reducedper 100g?Task: Compare the fat content of a range of butter, margarines and spreads.Name of fatProduct DescriptionPriceFat content per 100g11
Check food labels The nutrition labels are usually on the back on food packaging can help you to cut down on total fat and saturated fat. This label will tell you how much fat and saturated fat is contained in 100g of the food Some packaging will show nutrition labels on the front, which give at‐a‐glance information on specific nutrients. Packaging may also use traffic lights to show the fat, salt and sugar content, red means 'high'. Beware of eating too many red foods andto eat mainly foods that are green or amber.aimWhat counts as high‐fat and low‐fat?High fat contentMedium fat contentLow fat contentHigh saturated fatLow saturated fat 20g of fat per 100gbetween3g and 20g of fat per 100g3g of fat or less per 100g 5g saturates per 100g1.5g saturates per 100gMay show a red traffic lightMay show an amber traffic lightMay show a green traffic lightFacts: A food packet with the words “lower fat” or "reduced fat" doesn’t necessarily mean it's a healthy choice. The lower‐fat claim means that the food is 30% lower in fat than the standard equivalent. A high fat food such as mayonnaise is high in fat may still be high in
Plant Source: Cereals – Wheat, Oats, Pulses, Rice, Beans, Peas, Pulses, Quorn ‐ . helpThe most concentrated energy food Fats are solid at room temperature Oils are liquid at room temperature Fats and oils are made from:‐ i. Glycerol or glycerine (sweet sticky liquid) ii. Fatty acids (there are about 25 fatty acids) 1 molecule fat 1 glycerol 3 fatty acids .