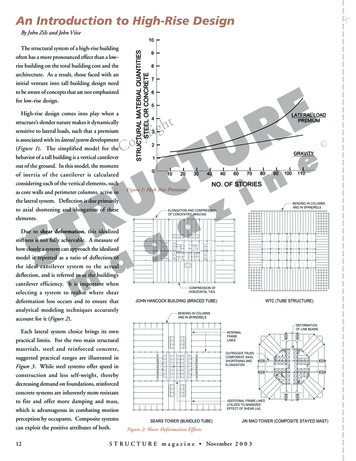
Transcription
Perimeter, Circumference,and Area1-91-91. PlanGO for HelpWhat You’ll LearnCheck Skills You’ll Need To find perimeters ofSimplify each absolute value.rectangles and squares, andcircumferences of circles To find areas of rectangles,squares, and circles. . . And WhyTo find the amount of fencingmaterial needed to build afence, as in Example 111. u4 - 8u 42. u10 - (-5)u 15Skills Handbook page 757and Lesson 1-83. u-2 - 6u 82To find perimeters ofrectangles and squares, andcircumferences of circlesTo find areas of rectangles,squares, and circles4. A(2, 3), B(5, 9) 6.75. K(-1, -3), L(0, 0) 3.2Examples6. W(4, -7), Z(10, -2) 7.87. C(-5, 2), D(-7, 6) 4.58. M(-1, -10), P(-12, -3) 13.09. Q(-8, -4), R(-3, -10) 7.8123456Real-World ConnectionFinding CircumferenceFinding Perimeter in theCoordinate PlaneFinding Area of a RectangleFinding Area of a CircleFinding Area of an IrregularShapeMath BackgroundHands-On Activity: Finding Perimeter and AreaStrictly speaking, a polygon hasno area because it is composedonly of segments. A polygonalregion is the union of a polygonand its interior. You can useEuclidean geometry to deriveformulas for the areas ofpolygonal regions, but you needcalculus to find the areas ofsome nonpolygonal regions.Draw each figure on centimeter grid paper. a rectangle with length 5 cm and width 3 cmYou can think of theperimeter of a polygon asthe distance around it andthe area as the number ofsquare units it encloses.1Find the distance between the points to the nearest tenth.Finding Perimeter and CircumferenceVocabulary TipObjectives a rectangle with length 8 cm and height 2 cm a rectangle with each side 4 cm1. To find the perimeter of each rectangle, find the sum of the lengths ofthe sides. Record the perimeter of each rectangle. 1–2. See margin.2. To find the area of each rectangle, count the number of squarecentimeters in its interior. Record the area of each rectangle.More Math Background: p. 2D3. Do rectangles with equal perimeters have the same area? no4. Do rectangles with the same area have the same perimeter? noLesson Planning andResources5. Use a piece of string and make a loop. Tie a slip knot. Adjust the loopand fix its total length at 36 cm. Use the loop to approximate differentrectangles on your grid paper. Record their lengths, widths,perimeters, and areas. What do you notice? Check students’ work.See p. 2E for a list of theresources that support this lesson.PowerPointThe perimeter P of a polygon is the sum of the lengths of its sides. The area A of apolygon is the number of square units it encloses. For special figures such as squares,rectangles, and circles, you can use formulas for perimeter (called circumference incircles) and area.For: Perimeter/Area ActivityUse: Interactive Textbook, 1-9Some formulas for perimeter and area are given in the chart at the top of the nextpage. You will also find the chart on pages 764 and 765 to be useful at times.Lesson 1-9 Perimeter, Circumference, and AreaSpecial NeedsBelow LevelL1In Example 3, encourage students to first estimate theperimeter. Ask: What is the size of a square unit onthe coordinate grid? one square unit Students thencheck that the solution is reasonable.learning style: visual61L2Review the difference between rational and irrationalnumbers before discussing why p is irrational.learning style: verbalBell Ringer PracticeCheck Skills You’ll NeedFor intervention, direct students to:Skills Handbook, p. 757Finding DistanceLesson 1–6: Example 1Extra Skills, Word Problems,Proof Practice, Ch. 1Activity1. 5 cm by8 cm by4 cm by2. 5 cm by8 cm by4 cm by16 cm23 cm S 16 cm2 cm S 20 cm4 cm S 16 cm3 cm S 15 cm22 cm S 16 cm24 cm S61
2. TeachKey ConceptsSummaryPerimeter and AreabsGuided InstructionEncourage students to use theterm counterexample in Exercises3 and 4.EXAMPLEError Prevention2EXAMPLE1The calculator value for p is usedfor all the examples and exercisesin this lesson.Circle with radius rand diameter dPerimeter P 4sArea A s2Perimeter P 2b 2hCircumference C pd,Area A bhor C 2prEXAMPLEReal-Worldpr 2Connection3 ftTo find the perimeter of the pool with thedeck, first find the width and length of thepool with the deck.Additional Examplesthe circumference of G in termsof p. Then find the circumferenceto the nearest tenth. 13π; about40.8 cmRectangle with base band height hFencing Your pool is 15 ft wide and 20 ft longwith a 3-ft wide deck surrounding it. You wantto build a fence around the deck. How muchfencing will you need?PowerPoint2 G has a radius of 6.5 cm. FindSquare withside length sThe units of measurement for perimeter and circumference include inches, feet,yards, miles, centimeters, meters, and kilometers. When measuring area, use squareunits such as square inches (in.2), square centimeters (cm2), square meters (m2),and square miles (mi2).Teaching Tip1 Margaret’s garden is a square12 ft on each side. She wants a1-ft-wide path around the entiregarden. What will the outsideperimeter of the path be? 56 ftOCArea Students may think they needto add 3 ft only once to eachdimension. Discuss why 3 ft isadded twice to each dimension.Have students examine a windowframe to help clarify each newlength and width.rdhbHands-On Activity1hs20 ftWidth of pool 15 3 3 21and deckVocabulary TipFor a rectangle,“length” and ”width”are sometimesused in place of”base” and ”height.”15 ftLength of pool 20 3 3 26and deckPerimeter of a rectangle 2b 2hUse the formula for the perimeterof a rectangle.P 2(21) 2(26)Substitute.P 42 52Simplify.P 94You will need 94 ft of fencing.3 Quadrilateral ABCD hasvertices A(0, 0), B(9, 12),C(11, 12), and D(2, 0). Findthe perimeter. 34Quick Check1 Suppose you want to frame a picture that is 6 in. by 7 in. with a 21-in. wide frame.a. Find the perimeter of the picture. 26 in.b. Find the perimeter of the outside edge of the frame. 30 in.Notice that the formulas for a circle involve p. Since the number p is irrational,p 3.1415926. . . ,you cannot write it as a terminating decimal. For an approximate answer, you can22use 3.14 or 227 (3.14 7 ) for p. You can also use the rounded decimal you get bypressingon your calculator. For an exact answer leave the result in terms of p.62Chapter 1 Tools of GeometryAdvanced LearnersEnglish Language Learners ELLL4After students find the perimeter in Example 1, havethem find the area of the deck.62learning style: verbalReview the terms radius, diameter, and circumference.Compare the radius of a bicycle wheel to its diameter.Emphasize that circumference is the distance that thewheel rolls in one revolution.learning style: visual
2Guided InstructionFinding CircumferenceEXAMPLEFind the circumference of A in terms of p. Then findthe circumference to the nearest tenth.Vocabulary TipRead A as “circle A.”AC pdC 12p12125in.Use a calculator.C 37.7The circumference of the circle is 12p in., or about 37.7 in.Quick Check2 a. Find the circumference of a circle with a radius of 18 m in terms of p. 36π mb. Find the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 18 m to the nearest tenth.56.5 m36yEXAMPLEFinding Perimeter in the Coordinate PlaneAlgebra Find the perimeter of #ABC.C(5, 6)Find the length of each side. Add the lengths to find the perimeter.4AB u5 - (-1)u 62 2 O24A( 1, 2)6AC #(5 2 (21)) 2 1 (6 2 (22)) 2xEXAMPLEUse the Distance Formula.AB BC AC 6 8 10 24Use the figure from Example 6to remind students that Postulate1-10, The area of a region isthe sum of the areas of itsnonoverlapping parts, does notapply to perimeter.PowerPointAdditional ExamplesThe perimeter of #ABC is 24 units.Quick Check21Math TipHave students discuss ways toremember the formulas in thislesson. Encourage suggestionsfrom the class. "62 1 82 "100 10B(5, 2)6Auditory LearnersUse the Ruler Postulate.BC u6 - (-2)u 8Teaching TipStudents may think that findingarea in terms of p is less accuratethan using an approximation forp, when the opposite is true. Atthis point, encourage students tofind area both in terms of p andby using an approximation for p.This is the exact answer.37.699112EXAMPLE3 Graph quadrilateral KLMN with vertices K(-3, -3), L(1, -3), M(1, 4), andN(-3, 1). Find the perimeter of KLMN. See margin.4 To make a project, you needa rectangular piece of fabric 36in. wide and 4 ft long. How manysquare feet of fabric do youneed? 12 ft 2Finding AreaQuick CheckTo find area, you should use the same unit for both dimensions.3.nline4EXAMPLEYou are designing a rectangular banner for the front ofthe museum. The banner will be 4 ft wide and 7 yd high.How much material do you need?7 yd 21 ftArea bhVisit: PHSchool.comWeb Code: aue-0775A 4(21)4Finding Area of a Rectangley M (1, 4)2N ( 3, 1)O 4 224x 2Change yards to feet using 1 yd 3 ft.K ( 3, 3)Use the formula for area of a rectangle. 4L (1, 3)Substitute 4 for b and 21 for h.A 8420 unitsThe area of the banner is 84 square feet (ft2). You need at least 84 ft2 of material.Quick Check4 Find the area of the banner in Example 4 by first changing all units to yards.Compare your answer to the one in Example 4. How do they compare?9 31 yd2; 9 13 is one-ninth of 84.Lesson 1-9 Perimeter, Circumference, and Area6363
PowerPoint5Additional ExamplesFinding Area of a CircleEXAMPLEThe diameter of a circle is 10 in. Find the area in terms of p.5 Find the area of B in termsradius 102 or 5Area pr 2of p.A p(5)2B1.5 ydr d2Use the formula for area of a circle.Substitute 5 for r.A 25pThe area of the circle is 25p in.2.Quick Check2.25π yd26 Find the area of the figurebelow.5 The diameter of a circle is 5 ft.2a. Find the area in terms of p. 254 π ftb. Find the area to the nearest tenth. 19.6 ft215 ftThe following postulates are useful in finding areas of figures with irregular shapes.5 ft10 ft10 ftKey Concepts5 ft5 ft5 ftPostulate 1-9If two figures are congruent, then their areas are equal.5 ftPostulate 1-10125 ft 2The area of a region is the sum of the areas of its nonoverlapping parts.Resources Daily Notetaking Guide 1-9 L3 Daily Notetaking Guide 1-9—L1Adapted InstructionExample 6 applies Postulate 1-10 by summing the areas of the parts of a figure.6ClosureMultiple Choice What is the area of thefigure at the right?12 cm224 cm230 cm236 cm245ABEEDDCC2 cmEDB8 cmDEETest-Taking Tip6 cm8 cmsquare: 64 cm2; 32 cm; circle:32π cm2; 8"2π cm4cMarking diagrams on atest can help youunderstand theproblem. If you cannotmark on the test, makea sketch of the diagramon scratch paper.A2A12cm8 cmEDCB6 cmmADCBA3CBA2CBA12cmFind the area and perimeter ofthe square. Find the area andcircumference of the circle interms of p.8 cmFinding Area of an Irregular ShapeEXAMPLESeparate the figure into rectangles.A32 cmArea bhUse the formula for the area of a rectangle.A1 6 ? 2 12Find the area of each rectangle.A2 4 ? 2 8A3 2 ? 2 4Total Area 12 8 4 24The area of the figure is 24Quick Check646.64224442 22 2cm22correct choice is B.6 Copy the figure in Example 6. Separate it in a different way. Find the area.See margin.Chapter 1 Tools of GeometryQuick CheckAdd the areas.cm2. The
EXERCISESEXERCISESFor more exercises, see Extra Skill, Word Problem, and Proof Practice.3. PracticePractice and Problem SolvingAssignment GuideAPractice by ExampleExample 1GO forHelpFind the perimeter of each figure.1.(page 62)2.22 in.1 A B 1-19, 50, 5536 cm2 A B20-49, 51-54, 56-63C Challenge64-709 cm4 in.7 in.Test PrepMixed ReviewFind the perimeter of each rectangle with the given base and height.3. 21 in., 7 in. 56 in.4. 16 cm, 23 cm 78 cm5. 24 m, 36 m 120 m6. Framing A rectangular certificate 8 in. by 10 in. will have a frame 1 12 in. widesurrounding it. What is the perimeter of the outside edge of the frame? 48 in.7. Fencing A garden that is 5 ft by 6 ft has a walkway 2 ft wide around it. Find theamount of fencing needed to surround the walkway. 38 ftExample 2(page 63)Find the circumference of each circle in terms of π.8.9.10π ft15π cm14mO3.7π in.Find the circumference of the circle to the nearest tenth.Example 3(page 63)351.9 cm12. r 9 in.13. d 7.3 m14. d 12 yd15. r 56 cm56.5 in.22.9 m1.6 yd16–19.Draw each figure in the coordinate plane. Find the perimeter. See back of book.16. X(0, 2), Y(4, -1), Z(-2, -1)Homework Quick CheckTo check students’ understandingof key skills and concepts, go overExercises 6, 37, 41, 46, 51.Visual LearnersExercises 6, 7 Encourage studentsto draw the rectangles, write theapplicable formula next to eachdrawing, and label their drawingswith the appropriate units.m11.O3.7 in.O15 cm12π10.5 ftO71-7576-88Exercises 20–26 Use theseexercises to highlight theimportance of using the sameunits when working withmeasurements.17. A(-4, -1), B(4, 5), C(4, -2)18. L(0, 1), M(3, 5), N(5, 5), P(5, 1)19. S(-5, 3), T(7, -2), U(7, -6), V(-5, -6)Example 4(page 63)Example 5(page 64)Find the area of each rectangle with the given base and height. 20–25. See margin.20. 4 ft, 4 in.21. 30 in., 4 yd22. 2 ft 3 in., 6 in.23. 40 cm, 2 m24. 3 m, 190 cm25. 240 cm, 5 mGPS Guided Problem Solving26. Find the area of a section of road pavement that is 20 ft wide and 100 yd long.6000 ft2 or 666 32 yd2Find the area of each circle in terms of π.27.28.29.20 m400πm216 ft64πL4L2ReteachingL1Adapted PracticePracticeName34 in.ClassPractice 1-7L3DatePerimeter, Circumference, and AreaFind the area of each rectangle with the given base and height.964 πft2L3Enrichment1. base: 3 ftheight: 22 in.in.22. base: 60 in.height: 1.5 yd3. base: 2 mheight: 120 cmFind the circumference of each circle in terms of π.4.5.6.3.91630.31.32.6.3 ft16Find the perimeter and area of each rectangle with the given baseand height.7. b 7 cm, h 6 cm0.1 m10. b 17 ft, h 3 ft8. b 21 cm, h 2 cm11. b 11 m, h 9 m9. b 4 in., h 10.5 in.12. b 13 m, h 7 mFind the perimeter and area of each figure. All angles in the figures areright angles.13.9.9225π ft20.25π m20.01π m2Lesson 1-9 Perimeter, Circumference, and Area2220. 1 13 ft or 192 in.221. 4320 in.2 or 3 13 yd22. 1 18 ft2 or 162 in.223. 8000 cm2 or 0.8 m265714.1515.4419422 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.0.5 m7248Find the area of each circle in terms of π.16.17.18.12.5200p–219. Find the area and perimeter of rectangle ABCD with vertices A(3, 7),B(9, 7), C(9, -1), and D(3, -1).20. Find the perimeter of PQR with vertices P(-2, 9), Q(7, -3), andR(-2, -3).21. The circumference of a circle is 26p. Find the diameter and the radius.24. 5.7 m2 or 57,000 cm225. 120,000 cm2 or 12 m265
Alternative MethodFind the area of each circle to the nearest tenth.Exercises 37–38 Each figurecan be separated in several ways.After students find the areas,have them share with a partnerhow they separated the figures.Example 6(page 64)Exercise 58 Once studentsunderstand the question, writex ? 5 (4x2 2 2x) on the boardand have them try to fill-in thebox. Students should recognizethat x ? (4x 2 2) and 4x 2 2 2xare equivalent.DiversityExercise 60 Some students maybe unfamiliar with weatherstripping. Invite a student toexplain its use.Exercise 64 If necessary, reviewthe procedure for making tableson a graphing calculator.33. r 7 ft34. d 8.3 m35. d 24 cm153.9 ft2452.4 cm254.1 m2Find the area of the shaded region. All angles are right angles.237. 310 m38. 80 in.220 m18 m5mApply Your Skills39c. There are 144 squareinches in one squarefoot. A square whosesides are 12 in. longand a square whosesides are 1 ft long arethe same size.4 in.4 in.8 in.10 m5mB36. r 12 in.452.4 in.212 in.39. a. What is the area of a square whose sides are 12 in. long? 144 in.2b. What is the area of a square whose sides are 1 ft long? 1 ft2c. Reasoning How many square inches are in a square foot? Explain.See left.40. a. Count squares to find the area of the1 in.polygon outlined in blue. 30 squaresb. Use a formula to find the area of eachsquare outlined in red. 16; 9; 4; 1c. How does the sum of your results inpart (b) compare to your result inpart (a)? Which postulate does this support? They are . Post. 1-1041. Estimation On a postcard from Mexico, Ky sketched the “footprint” of thepyramid known as El Castillo in the ancient Mayan city Chichen Itza. He saidhe estimated the three different lengths on each side to be 22 m, 6 m, and 11 m.Use those estimates to estimate the area of El Castillo’s footprint. 3289 m242–45. Answers may vary. Check students’ work. Samples are given.Estimation Estimate the perimeter and area of each object.39 in.; 93.5 in.238 in.;42. the front cover of this book43. the front cover of your notebook290 in.44. a classroom bulletin board45. the top of your desk12 ft; 8 ft28 ft; 3.75 ft246. Writing Choose one exercise from Exercises 42–45 and explain why you choseyour unit of length. See margin.il loEl C a stex ic oIt z a , MC h ic h en47. The area of an 11-cm wide rectangle is 176 cm2. What is its length? 16 cm48. The perimeter of a rectangle is 40 cm and the base is 12 cm. What is its area? 296 cm49. A square and a rectangle have equal area. The rectangle is 64 cm by 81 cm.What is the perimeter of the square? 288 cm50. a. Critical Thinking Can you use the formula for the perimeter of a rectangleto find the perimeter of any square? Explain. See margin.b. Can you use the formula for the perimeter of a square to find the perimeterof any rectangle? Explain. See margin.c. Use the formula for the perimeter of a square to write a formula for the area2of a square in terms of its perimeter. A (P4)2 or A P16Real-WorldConnectionPostulate 1-10 can help youestimate the area of the“footprint” of El Castillo.6651. The surface area of a three-dimensional figure is theGPS sum of the areas of all of its surfaces. You can find thesurface area by finding the area of a net for the figure. 4 in.6 in.a. Draw a net for the solid shown. Label8 in.the dimensions. See back of book.b. What is the area of the net? What is the surface area of the solid?208 in.2, 208 in.2Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry46. Answers may vary.Sample: For Exercise 44,you use feet becausethe bulletin board is toobig for inches.6650. a. Yes; every square is arectangle.b. Answers may vary.Sample: No, not allrectangles aresquares.
52. Tiling The students in the Art Club are tiling a wall that is 8 ft by 16 ft at theentrance to the community center. They are using tiles that are 6 in. by 6 in. tocreate a multi-colored design. How many tiles do the students need? 512 tilesx 2 Algebra Draw each rectangle in the coordinate plane. Find its perimeter and area.4. Assess & ReteachPowerPointLesson Quiz53. A(–3, 2), B(-2, 2), C(-2, -2), D(-3, -2) 53–54. See back of book.Real-WorldConnectionFour 6 in.-by-6 in. tiles willcover 1 ft2.54. A(-2, -6), B(-2, -3), C(3, -3), D(3, -6)A rectangle is 9 ft long and 40 in.wide.Coordinate Geometry On graph paper, draw polygon ABCDEFGH with verticesA(1, 1), B(10, 1), C(10, 8), D(7, 8), E(7, 5), F(4, 5), G(4, 8), and H(1, 8).1. Find the perimeter in inches.296 in.55. Find the perimeter of the polygon. 38 units2. Find the area in square feet.30 ft256. Divide the polygon into rectangles. Find the area of the polygon. 54 units257. Biology In the Pacific Northwest, a red fox has a circular home range with aradius of about 718 meters. To the nearest thousand square meters, what is thearea of the home range of a red fox? 1,620,000 m258. Multiple Choice A rectangle has a base of x units. The area is A4x2 2 2xBsquare units. What is the height of the rectangle in terms of x? D(4 2 x) units(4x3 2 2x2) units(x 2 2) units(4x 2 2) unitsGOnlineHomework HelpVisit: PHSchool.comWeb Code: aue-0109Home Maintenance To determine how much of each item to buy, tell whether youneed to know area or perimeter. Explain your choice. 59–62. See margin.59. wallpaper for a bedroom60. weatherstripping for a door61. fence for a garden62. paint for a basement floor3. The diameter of a circleis 18 cm. Find the area in termsof p. 81π cm24. Find the perimeter of atriangle whose verticesare X(–6, 2), Y(8, 2), and Z(3,14). 42 units5. Find the area of the figurebelow. All angles are rightangles. 256 in.216 in.8 in.8 in.8 in.8 in.8 in.8 in.63. Coordinate Geometry The endpoints of a diameter of a circle are A(2, 1) andB(5, 5). Find the area of the circle in terms of p. 6.25π units2CChallengePHSchool.comFor: Graphing calculatorproceduresWeb Code: aue-212064. Graphing Calculator You want to build a rectangularcorral by using the side of a barn for one side and100 ft of fencing for the other three sides.a. Make a table on your graphing calculatorlisting integer values for the base and thehcorresponding values of the height and area.b. Make a graph using your table values. Graphthe base on the horizontal axis and area on thevertical axis. a–b. See back of book.c. What are the dimensions of the corral with thegreatest area? 25 ft by 50 ftCorralBarn16 in.Alternative AssessmentHave students draw and labela rectangle and a circle, eachhaving an area between 20 and25 in.2 They should includewith each drawing a writtenexplanation of how each areacan be verified.b65. How many circles with the given radius are needed for the sum of their areas toequal the area of a circle with the second given radius?a. 1 in. , 3 in. 9b. 2 in. , 6 in. 9c. 3 in. , 9 in. 9d. Make a Conjecture How many circles with a radius of n in. are needed forthe sum of their areas to equal the area of a circle with a radius of 3n in.? 9x 2 Algebra Find the area of each figure.3a2a266. a rectangle with side lengths of 5bunits and 3b8 units 20 units2267. a square with perimeter 10n units 25n4 units68. a square with side lengths of (3m - 4n) units (9m2 – 24mn 16n2) units2lesson quiz, PHSchool.com, Web Code: aua-010959. Area; the wall is asurface.60. Perimeter;weatherstripping mustfit the edges of the door.Lesson 1-9 Perimeter, Circumference, and Area6761. Perimeter; the fencemust fit the perimeter ofthe garden.62. Area; the floor is asurface.67
Test PrepA sheet of blank grids is availablein the Test-Taking Strategies withTransparencies booklet. Give thissheet to students for practice withfilling in the grids.69. Answers may vary.Sample: one8 in.-by-8 in. square one 5 in.-by-5 in.square two4 in.-by-4 in. squaresResourcesFor additional practice with avariety of test item formats: Standardized Test Prep, p. 75 Test-Taking Strategies, p.70 Test-Taking Strategies withTransparencies69. Open-Ended The area of a 5 in.-by-5 in. square is the same as the sum of theareas of a 3 in.-by-3 in. square and a 4 in.-by-4 in. square. Find two or moresquares whose total area is the same as the area of an 11 in.-by-11 in. square.See left.70. Track An athletic field is a rectangle,10 yd100 yards by 40 yards, with a semicircle100 ydat each of the short sides. A runningtrack 10 yards wide surrounds the40 ydfield. Find the perimeter of the outsideof the running track to the nearesttenth of a yard. 388.5 ydTest PrepGridded ResponseFor Exercises 71 and 72, a rectangular garden has a rectangular walkwayaround it. The width of the walkway is 8 ft.71. How many feet greater than the perimeter of the garden is the outsideperimeter of the walkway? 6472. If the garden is a square with a perimeter of 260 ft, what is the area of thewalkway in square feet? 233673. You need to tile a 12 ft-by-15 ft floor. Thecolor you want allows you the choices foundin the table at the right. How many dollarswould it cost to tile the floor with12 in.-by-12 in. tiles? 54074. How many tiles would cover the 12 ft-by-15 ftfloor if you choose the 10 in.-by-12 in. tiles? 216Size of TilesCost12 12 11 11 10 12 6 8 3/ft2 3/ft2 4/ft2 4.50/ft275. How many dollars would it cost to cover the 12 ft-by-15 ft floor with thetiles that are 6 in. by 8 in.? 810Mixed ReviewGO forHelpLesson 1-876. The midpoint of CD has coordinates (5, 6). Point C has coordinates (-5, -1).Find the coordinates of point D. (15, 13)Find (a) AB to the nearest tenth and (b) the coordinates of the midpoint of AB.Lesson 1-777. A(4, 1), B(7, 9)78. A(0, 3), B(3, 8)5.8 units; (1.5, 5.5)8.5 units; (5.5, 5)80. A(0, 1), B(-4, 6)81. A(4, 10), B(-2, 3)9.2 units; (1, 6.5)* )6.4 units; (–2, 3.5)BG is the perpendicular bisector of WR at point I.79. A(9, 2), B(-3, 9)13.9 units; (3, 5.5)82. A(-1, 1), B(-4, -5)6.7 units; (–2.5, –2)WI O RI84. Name two congruent segments.83. What is m&BIR? 9085. WR has length 124. What is the length of IR? 62 unitsLesson 1-5For the given coordinates, find PQ.86. P: 12, Q: -618 units6868Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry87. P: 3, Q: 96 units88. P: -23, Q: 1033 units
Lesson 1-9 Perimeter, Circumference, and Area 63 Finding Circumference Find the circumference of A in terms of p.Then find the circumference to the nearest tenth. C pd C 12p This is the exact answer. 12 37