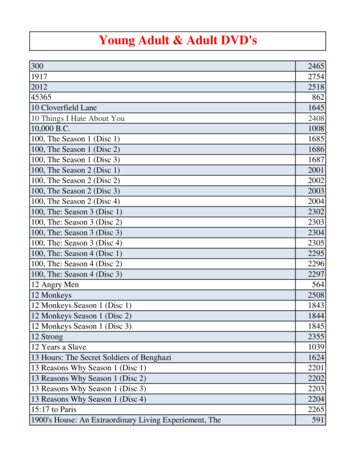
Transcription
About Everything DiSC:Theory and Research
Everything DiSC is a personal development learningexperience that measures an individual’s preferencesand tendencies based on the DiSC model. But, whatis the DiSC model?The DiSC Model is a simple yet powerful model thatdescribes four basic behavioral styles: D, i, S, and C,and serves as the foundation for each distinctEverything DiSC application.D: Dominancei: InfluenceS: SteadinessC: ConscientiousnessEveryone is a blend of all four DiSC styles—usuallyone, two, or even three styles stand out. Each personhas a unique behavioral profile with different stylesand priorities—no one style better or worse thanthe next. We believe that these differences in stylecan be extremely valuable. Once you assess thesedifferences and harness their value, better workplacecommunication AND healthier organizationsbecome possible.iSSeems simple, right? It is. But it’s not simplistic.Here’s why:We’ve been researching and analyzing DiSC for over 40years. In fact, our DiSC Classic Paper Profile was thefirst DiSC assessment ever! (You’ll always know it’s ourDiSC by our signature lower-cased “i” in DiSC.)As technology has evolved, DiSC has too. Our onlineDiSC assessments use the most advanced assessmentmethod (adaptive testing) and sophisticated algorithmsto quickly analyze a person’s responses and deliver themost precise feedback possible. The profile translatesthese assessment results into a personalized narrativethat’s both actionable and memorable.All of our Everything DiSC personality assessmentsare application-focused, so the feedback is presentedto you as a leader, manager, individual contributor, orsales person.2John Wiley & Sons, Inc or its associated companies, are the authorized users or owners of DiSC andEVERYTHING DiSC and associated trademarks within this document.Loves achallengeDCThrives oncollaboration
DiSC Theory Two Dimensions of Human BehaviorAlthough DiSC describes four styles, the model is, at its core, two-dimensional. These two dimensions reflectfundamental aspects of human nature and can be viewed as independent constructs.3VERTICAL DIMENSION:CAUTIOUS-BOLDHORIZONTAL DIMENSION:QUESTIONING-ACCEPTINGEverything DiSC Vertical DimensionEverything DiSC Horizontal DimensionThe vertical dimension is best described as level ofactivity, ranging from active to thoughtful. People withDiSC styles at the top of the circle tend to be fast-pacedand are often described as assertive, dynamic, and bold.Traditional explanations of the model suggest that thesepeople perceive themselves as more powerful than theenvironment. Because of this perception, they tend toexert effort to change their circumstances. Conversely,people with styles that fall toward the bottom of thecircle tend to be more moderate paced and are oftendescribed as calm, methodical, and careful. Traditionally,these people are thought to perceive themselves as lesspowerful than the environment, and thus they are moreinclined to adapt to existing circumstances.The horizontal dimension runs from questioning toaccepting. People with DiSC styles that fall towardthe left side of the circle are naturally more skepticalin nature and are often described as logic-focused,objective, and challenging. A traditional explanationof these characteristics is that these people see theenvironment as antagonistic. In other words, theyinstinctively withhold trust from people and ideas untilthose outside elements can be thoroughly vetted. Onthe other hand, people with styles on the right side ofthe circle are naturally more receptive in nature andare often described as people-focused, empathizing,and agreeable. Traditionally, they are said to see theenvironment as being aligned with their interests. Inessence, they are biased to see the people and ideasaround them as favorable and are thus inclined totrust them.John Wiley & Sons, Inc or its associated companies, are the authorized users or owners of DiSC andEVERYTHING DiSC and associated trademarks within this document.
The Four Quadrants of DiSC The D (Dominance) styleis active and questioning.This describes peoplewho are direct, forceful,and outspoken with theiropinions.The i (Influence) style isactive and accepting.This describes people whoare outgoing,enthusiastic, and lively.Although the DiSC dimensions form four distinct styles,it is probably more useful to think of the DiSC circle incontinuous terms. Consider that each of the four stylesblend into their neighboring styles much the same waythat colors blend into one another on the color wheel.Red and yellow are distinct colors, but they both blendto form a new color, orange. In the same way, the Dand i styles are distinct, but the space between themon the circle represents an equally distinct set of traits.For instance, people with a Di style are more likelythan people with the D style to describe themselvesas daring and convincing. A person with an iD style ismore likely than someone with the i style to describehimself as charismatic and dynamic. In both cases,these two styles (Di and iD) share something with theD and i styles, but they also have characteristics thatdifferentiate them from those singular styles.You may also notice that when discussing DiSC, wego out of our way to say “a person with the C style”rather than simply calling someone a “C”. This subtledifference in language is meant to mitigate the naturaltemptation to pigeonhole people. Although a personwith the C style predominantly demonstrates C traits,she has elements of the other four styles in her aswell. For example, it is likely that she is quite capableof patiently listening to a coworker describe his hurtfeelings, even though this is more of an S quality.4The S (Steadiness) style is The C (Conscientiousness)thoughtful and accepting.style is thoughtful andThis describes people who questioning. This describesare gentle, accommodating,people who areand patient with others’analytical, reserved, andmistakes.precise.THE IDEA OF STRETCHThe continuous nature of the DiSC circle also helpspeople understand the idea of “stretch.” It is helpfulto think of your style as your home base or comfortzone. Someone with a C style may be very comfortableworking alone on analytical projects that requireaccuracy. At times, however, this person may be calledon to mingle with strangers at a professional function.In this case, the person is being asked to stretch acrossthe circle toward the i style. Now, someone with the Cstyle who has a dot close to the center of the circle willprobably find this mingling unpleasant, but manageable.On the other hand, someone with a C style whose dotis located on the edge of the circle is more likely to findthis mingling highly stressful. In the second case, theperson has had to travel farther outside their comfortzone, and that will require more energy. So, as a generalrule, people with dots located close to the center usuallyhave a somewhat easier time adopting foreign DiSCstyles when the situation calls for it. People whose dotsare on the edge of the circle may have to stretch more(and experience more stress) if they want to adoptanother style. On the other hand, because these peoplehave more pronounced DiSC styles, those styles areoften accompanied by some very distinct strengths.John Wiley & Sons, Inc or its associated companies, are the authorized users or owners of DiSC andEVERYTHING DiSC and associated trademarks within this document.
DiSC Research Psychological instruments are used to measureabstract qualities that we can’t touch or see. Theseare characteristics like intelligence, extroversion,or honesty. So how do researchers evaluate theseinstruments? How do we know whether such tools areactually providing accurate information about thesecharacteristics or just generating haphazard feedbackthat sounds believable?SCALESA person’s DiSC style is measured by asking them thedegree to which they agree with a series of statementsabout themselves. These responses are used tocalculate a score for that individual on eight scales. Theeight scales are as follows:Simply put, if an instrument is indeed useful andaccurate, it should meet a variety of different standardsthat have been established by the scientific community.Validation is the process through which researchersassess the quality of a psychological instrument bytesting the tool against these different standards.This page is designed to help you understand thesedifferent standards and see how the Everything DiSCassessment performs under examination. For moredetailed information, see the full Everything DiSCResearch Report.Validation asks two fundamental questions:How reliable is the tool? That is, researchers ask if aninstrument measures in a consistent and dependableway. If the results contain a lot of random variation, it isdeemed less reliable.How valid is the tool? That is, researchers ask if aninstrument measures accurately. The more that a toolmeasures what it proposes to measure, the more validthe tool is.Note that no psychometric tool is perfectly reliableor perfectly valid. All psychological instruments aresubject to various sources of error. Reliability andvalidity are seen as matters of degree on continuousscales, rather than reliable/unreliable and valid/invalidon dichotomous scales. Consequently, it is moreappropriate to ask, “How much evidence is there for thereliability of this tool?” than, “Is this tool reliable?”5John Wiley & Sons, Inc or its associated companies, are the authorized users or owners of DiSC andEVERYTHING DiSC and associated trademarks within this document. D measures a direct, dominant disposition usingadjectives such as aggressive, strong-willed, andforceful. Di measures an active, fast-paced disposition usingadjectives such as dynamic, adventurous, and bold. i measures an interactive, influencing dispositionusing adjectives such as sociable, lively, andtalkative. iS measures an agreeable, warm disposition usingadjectives such as trusting, cheerful, and caring. S measures an accommodating, steady dispositionusing adjectives such as considerate, gentle, andsoft-hearted. SC measures a moderate-paced, cautiousdisposition using adjectives such as careful, softspoken, and self-controlled. C measures a private, conscientious dispositionusing adjectives such as analytical, reserved, andunemotional. CD measures a questioning, skeptical dispositionusing adjectives such as cynical, stubborn, andcritical. Although these scales do not show up inthe profile, they are used to determine which stylethe respondent receives.
RELIABILITYTo determine if a tool is reliable, researchers look at thestability of the instrument and the internal consistencyof the instrument. Stability is easy to understand. In thiscase, a researcher would simply have a group of peopletake the same assessment twice and correlate theresults. This is called test-retest reliability. InternalAs Table 1 shows, all values were well above the .70cutoff and all but one were above .80. This suggeststhat the measurement of DiSC is both stable andinternally consistent. For more information on thereliability of the DiSC scales, see the more in-depthEverything DiSC Research Report.VALIDITYTABLE 1. SCALE RELIABILITIESTest-RetestAlpha(2 CD.85.87D.86.88N599752There are many different ways to examine the validityof an assessment. We will provide two such exampleshere, but many more are included in the full EverythingDiSC Research Report.The DiSC model proposes that adjacent scales (e.g.,Di and i) will have moderate correlations. That is, thesecorrelations should be considerably smaller than thealpha reliabilities of the individual scales. For example,the correlation between the Di and i scales (.50) shouldbe substantially lower than the Alpha reliability of the Dior i scales (both .90). On the other hand, scales that aretheoretically opposite (e.g., i and C) should have strongnegative correlations. Table 2 shows data obtainedfrom a sample of 752 respondents who completed theEverything DiSC assessment. The correlations amongall eight scales show strong support for the model.That is, moderate positive correlations among adjacentscales and strong negative correlations are observedbetween opposite scales.consistency is more difficult to understand. Here,we have the assumption that all of the questions (oritems) on a given scale are measuring the same trait.As a consequence, all of these items should, in theory,correlate with each other. Internal consistency isrepresented using a metric called alpha.We can use similar standards to evaluate both testretest and alpha. The maximum value is 1.0 and highervalues indicate higher levels of reliability. Althoughnot set in stone, most researchers use the followingguidelines to interpret values: above .9 is consideredexcellent, above .8 is considered good, above .7 isconsidered acceptable, and below .7 is consideredquestionable. The reliability estimates for the eightDiSC scales are shown in Table 1.6John Wiley & Sons, Inc or its associated companies, are the authorized users or owners of DiSC andEVERYTHING DiSC and associated trademarks within this document.
TABLE 2. SCALE -.62-.19.42Cronbach’s Alpha reliabilities are shown in boldalong the diagonal, and the correlation coefficientsamong scales are shown within the body of thetable. Correlation coefficients range from -1 to 1.A correlation of 1 indicates that two variables areperfectly positively correlated such that as one variableincreases, the other variable increases by a proportionalamount. A correlation of -1 indicates that two variablesare perfectly negatively correlated, such that as onevariable increases, the other variable decreases by aproportional amount. A correlation of 0 indicates thattwo variables are completely unrelated; N 752, asshown in Appendix 1 of the Everything DiSCResearch Report.A statistical technique called multidimensional scalingalso adds support to the DiSC model as a circumplex.This technique has two advantages. First, it allows for avisual inspection of relationship among the eight scales.Second, this technique allows researchers to look at allof the scales simultaneously. In Figure 1, scales that arecloser together have a stronger positive relationship.Scales that are farther apart are more dissimilar. Thecircumplex DiSC model predicts that the eight scaleswill be arranged in a circular format at equal intervals.As can be seen in Figure 1, the scales are arranged in away that is expected by the DiSC model. (Keep in mindthat the original MDS rotation is presented below andthis rotation is arbitrary.) Although the eight scales7SD.88FIGURE 1S ScaleiS ScaleSC Scalei ScaleDi ScaleC ScaleCD ScaleD Scaledo not form a perfectly equidistant circle (as predictedby the model), this theoretical ideal is nearly impossibleto obtain with actual data. The actual distance betweenthe scales, however, is roughly equal, providing strongsupport for the model and its assessment.To learn more, visit EverythingDiSC.com.John Wiley & Sons, Inc or its associated companies, are the authorized users or owners of DiSC andEVERYTHING DiSC and associated trademarks within this document.
these assessment results into a personalized narrative that’s both actionable and memorable. All of our Everything DiSC personality assessments . manager, individual contributor, or sales person. John Wiley & Sons, Inc or its associated companies, are the authorized users or owners of