Transcription
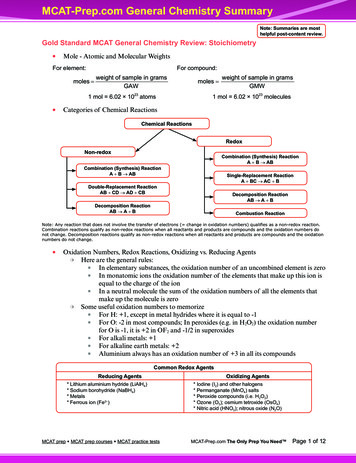
MCAT-Prep.com General Chemistry SummaryNote: Summaries are mosthelpful post-content review.Gold Standard MCAT General Chemistry Review: StoichiometrylMole - Atomic and Molecular WeightsFor element:For compound:moles weight of sample in gramsweight of sample in gramsmoles GAWGMW1 mol 6.02 1023 atoms 1 mol 6.02 1023 moleculeslCategories of Chemical ReactionsChemical ReactionsRedoxNon-redoxCombination (Synthesis) ReactionA B ABCombination (Synthesis) ReactionA B ABSingle-Replacement ReactionA BC AC BDouble-Replacement ReactionAB CD AD CBDecomposition ReactionAB A BDecomposition ReactionAB A BCombustion ReactionNote: Any reaction that does not involve the transfer of electrons ( change in oxidation numbers) qualifies as a non-redox reaction.Combination reactions qualify as non-redox reactions when all reactants and products are compounds and the oxidation numbers donot change. Decomposition reactions qualify as non-redox reactions when all reactants and products are compounds and the oxidationnumbers do not change.lOxidation Numbers, Redox Reactions, Oxidizing vs. Reducing AgentsmHere are the general rules:nIn elementary substances, the oxidation number of an uncombined element is zeronIn monatomic ions the oxidation number of the elements that make up this ion isequal to the charge of the ionnIn a neutral molecule the sum of the oxidation numbers of all the elements thatmake up the molecule is zeromSome useful oxidation numbers to memorizenFor H: 1, except in metal hydrides where it is equal to -1nFor O: -2 in most compounds; In peroxides (e.g. in H2O2) the oxidation numberfor O is -1, it is 2 in OF2 and -1/2 in superoxidesnFor alkali metals: 1nFor alkaline earth metals: 2nAluminium always has an oxidation number of 3 in all its compoundsCommon Redox AgentsReducing Agents* Lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4)* Sodium borohydride (NaBH4)* Metals* Ferrous ion (Fe2 )MCAT prep MCAT prep courses MCAT practice testsOxidizing Agents* Iodine (I2) and other halogens* Permanganate (MnO4) salts* Peroxide compounds (i.e. H2O2)* Ozone (O3); osmium tetroxide (OsO4)* Nitric acid (HNO3); nitrous oxide (N2O)MCAT-Prep.com The Only Prep You Need Page 1 of 12
MCAT-Prep.com General Chemistry SummarylMixturesGold Standard MCAT General Chemistry Review: Electronic Structure & ThePeriodic TablelConventional Notation for ElectronicStructurelMetals, Nonmetals and Metalloids*General Characteristics of metals, nonmetals andmetalloidsThe order for filling atomic orbitals: Follow thedirection of successive arrows moving from topto bottom.MetalsNonmetalsMetalloidsHard andshinyGases or dull,brittle solidsAppearancewill vary3 or lessvalenceelectrons5 or morevalenceelectrons3 to 7 valenceelectronsForm ionsby losing e Form ionsby gaining e Form and/or ionsGoodconductorsof heat andelectricityPoorconductorsof heat andelectricityConductbetter thannonmetals,but not aswell as metals*These are general characteristics. There are exceptionsbeyond the scope of the exam.Gold Standard MCAT General Chemistry Review: BondinglPartial Ionic CharactermThis polar bond will also have a dipole moment given by:D q d.F :.: F:where q is the charge and d is the distance between these two atoms. .:lF :Lewis Acids and Lewis Bases.B.::FB.F. F3. .Noticem. the green arrows. .follow theFthatThe Lewis acid BF3 and the Lewis base NH.flow of electron pairs. {Mnemonic: lEwis Acids: Electron pair Acceptors} : F :. F :: F:H. . :F : N.BH.:FBF :.HHHN. F .HF. .H: F:H. .12Page 2 ofNHHHHMCAT GENERAL CHEMISTRY SUMMARYHHN H
MCAT-Prep.com General Chemistry SummaryValence Shell Electronic Pair Repulsions (VSEPR Models)mGeometry of simple molecules in which the central atom A has one or more lone pairsof electrons ( e-)lTotalnumber ofe- pairsNumber oflone pairsNumber ofbondingpairsElectron Geometry,Arrangement ofe- pairsMolecular Geometry(Hybridization sp3)NH3422Bent(sp3)H 2O514Seesaw(sp3d)SF4523T-shaped(sp3d)ClF3Note: dotted lines only represent the overall molecular shape and not molecular bonds. In brackets under “MolecularGeometry” is the hybridization.Molecular arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom A. Dotted lines only represent the overallmolecular shape and not molecular bonds.MCAT-Prep.com The Only Prep You Need Page 3 of 12
MCAT-Prep.com General Chemistry SummaryGold Standard MCAT General Chemistry Review: Phases & Phase EquilibriallStandard Temperature and Pressure, Standard Molar Volumem0 C (273.15 K) and 1.00 atm (101.33 kPa 760 mmHg 760 torr); these conditions areknown as the standard temperature and pressure (STP). {Note: the SI unit of pressure isthe pascal (Pa).}mThe volume occupied by one mole of any gas at STP is referred to as the standard molarvolume and is equal to 22.4 L.Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases (A Model for Gases)mThe average kinetic energy of the particles (KE 1/2 mv2) increases in direct proportionto the temperature of the gas (KE 3/2 kT) when the temperature is measured on anabsolute scale (i.e. the Kelvin scale) and k is a constant (the Boltzmann constant).The Maxwell Distribution PlotGraham’s Law (Diffusion and Effusion of Gases)Combined Gas LawPVPV PV1 1 PV 1 k1 2 2 2 2T1 T1 T2 T2 (at constant mass)Charles’ LawV Constant TorIdeal Gas LawV1/V2 T1/T2PV nRTsince m/V is the density (d) of the gas:P Boyle’s LawV Constant 1/Pord RTMPartial Pressure and Dalton’s LawP1V1 P2V2PT P1 P2 PiOf course, the sum of all mole fractions in amixture must equal one:ΣX1 1Avogadro’s LawV/n ConstantPage 4 of 12orV1/n1 V2/n2MCAT GENERAL CHEMISTRY SUMMARYThe partial pressure (Pi) of a component of a gasmixture is equal to:Pi Xi PT
MCAT-Prep.com General Chemistry SummarylLiquid Phase (Intra- and Intermolecular Forces)Van Der Waal's forces (weak) and hydrogen bonding (strong). London forces between Cl2 molecules,dipole-dipole forces between HCl molecules and H-bonding between H2O molecules. Note that a partialnegative charge on an atom is indicated by δ- (delta negative), while a partial positive charge is indicatedby δ (delta positive). Notice that one H2O molecule can potentially form 4 H-bonds with surroundingmolecules which is highly efficient. The preceding is one key reason that the boiling point of water ishigher than that of ammonia, hydrogen fluoride, or methanol.lSurface TensionmPE is directly proportional to the surface area (A)mPE gA; g surface tensionmg F/l; F force of contraction of surface; l length along surface(a) cohesive adhesivelPhase Changes(b) adhesive cohesivelPhase DiagramsMCAT-Prep.com The Only Prep You Need Page 5 of 12
MCAT-Prep.com General Chemistry SummaryGold Standard MCAT General Chemistry Review: Solution ChemistrylVapor-Pressure Lowering(Raoult’s Law)lBoiling-Point Elevation and FreezingPoint DepressionP P Xsolventwhere P vapor pressure of solutionP vapor pressure of pure solvent (at thesame temperature as P)lOsmotic PressureΠ i MRTwhere R gas constant per moleT temperature in degrees K andM concentration of solute (mole/liter)i Van’t Hoff factorlPhase diagram of water demonstrating theeffect of the addition of a soluteΔTB iKbmΔTF iKFmIons in SolutionmIons that are positively charged cations; ions that are negatively charged anionsmMnemonic: anions are negative ionsmThe word “aqueous” simply means containing or dissolved in waterCommon ateCommon CationsNaSodiumH HydrogenLi LithiumCa2 CalciumK PotassiumMg2 MagnesiumNH4AmmoniumFeIron (II)H3O HydroniumFe3 Iron (III) 2 Common Anions and CationsPage 6 of 12MCAT GENERAL CHEMISTRY SUMMARY
MCAT-Prep.com General Chemistry SummaryllUnits of ConcentrationoMolarity (M): moles of solute/liter ofsolution (solution solute solvent)oNormality (N): one equivalent per literoMolality (m): one mole/1000g of solventoMolal concentrations are not temperaturedependent as molar and normalconcentrations areoDensity (ρ): Mass per unit volume at thespecified temperatureoOsmole (Osm): The number of moles ofparticles (molecules or ions) that contributeto the osmotic pressure of a solutionoOsmolarity: osmoles/liter of solutionoOsmolality: osmoles/kilogram of solutionoMole Fraction: amount of solute (in moles)divided by the total amount of solvent andsolute (in moles)oDilution: MiVi MfVflSolubility Product Constant, theEquilibrium ExpressionAgCl (s)Ag (aq) Cl- (aq)Ksp [Ag ][Cl -]Because the Ksp product alwaysholds, precipitation will not takeplace unless the product of [Ag ]and [Cl-] exceeds the Ksp.Solubility Rules1. All salts of alkali metals are soluble.2. All salts of the ammonium ion are soluble.3. All chlorides, bromides and iodides are water soluble, with the exception of Ag , Pb2 ,and Hg22 .4. All salts of the sulfate ion (SO42-) are water soluble with the exception of Ca2 , Sr2 , Ba2 ,and Pb2 .5. All metal oxides are insoluble with the exception of the alkali metals and CaO, SrO andBaO.6. All hydroxides are insoluble with the exception of the alkali metals and Ca2 , Sr2 , Ba2 .7. All carbonates (CO32-), phosphates (PO43-), sulfides (S2-) and sulfites (SO32-) are insoluble,with the exception of the alkali metals and ammonium.Gold Standard MCAT General Chemistry Review: Acids & BaseslAcidslBasesKa [H ][A-]/[HA]STRONGWEAKPerchloric HClO4Hydrocyanic HCNChloric HClO3Hypochlorous HClONitric HNO3Nitrous HNO2Hydrochloric HClHydrofluoric HFSulfuric H2SO4Sulfurous H2SO3Hydrobromic HBrHydrogen Sulfide H2SHydriodic HIHydronium Ion H3OPhosphoric H3PO4 Kb [HB ][OH-]/[B]mmlStrong bases include any hydroxideof the group 1A metalsThe most common weak bases areammonia and any organic amine.Conjugate Acid-Base PairsmThe acid, HA, and the baseproduced when it ionizes, A-, arecalled a conjugate acid-base pair.Benzoic, Acetic andother Carboxylic AcidsMCAT-Prep.com The Only Prep You Need Page 7 of 12
MCAT-Prep.com General Chemistry SummarylWater DissociationlThe pH ScalepH -log10[H ]Kw [H ][OH-] 1.0 10-14lSalts of Weak Acids and BasespOH -log10[OH-]Ka Kb Kwlat 25 C, pH pOH 14.0BufferslProperties of Logarithms1.2.3.4.5.pH pKa log([salt]/[acid])pOH pKb log ([salt]/[base])logaa 1logaMk k logaMloga(MN) logaM logaNloga(M/N) logaM - logaN10log10(M) MGold Standard MCAT General Chemistry Review: ThermodynamicslThe First Law of ThermodynamicsΔE Q - Wmmmmlheat absorbed by the system: Q 0heat released by the system: Q 0work done by the system on its surroundings: W 0work done by the surroundings on the system: W 0Temperature Scales0 K -273.13 C.(X F - 32) 5/9 Y ClState FunctionsmW can be determined experimentally by calculating the area under a pressure-volume curvePage 8 of 12WorkHeatChanges in internalenergy1st tranf.w0-w2nd transf.W w qq-wMCAT GENERAL CHEMISTRY SUMMARY
MCAT-Prep.com General Chemistry SummaryGold Standard MCAT General Chemistry Review: Enthalpy & ThermochemistrylHeat of Reaction: Basic PrinciplesmA reaction during which heat is released is said to be exothermic (ΔH is negative).mIf a reaction requires the supply of a certain amount of heat it is endothermic (ΔH ispositive).ΔHOVERALL ΔH1 ΔH2ΔH reaction ΔHf (products) - ΔHf (reactants)lBond Dissociation Energies and Heats of FormationΔH (reaction) ΔH(bonds broken) ΔH(bonds formed) BE(reactants) - BE(products)lCalorimetryQ mC(T2 -T1)Q mLllThe Second Law of ThermodynamicsmFor any spontaneous process, the entropy of the universe increases which results in agreater dispersal or randomization of the energy (ΔS 0).EntropyΔS reaction ΔS products - ΔS reactantslFree EnergyΔG ΔH - T ΔSmmmA reaction carried out at constant pressure is spontaneous if: ΔG 0It is not spontaneous if: ΔG 0It is in a state of equilibrium (reaction spontaneous in both directions) if: ΔG 0Gold Standard MCAT General Chemistry Review: Rate Processes in ChemicalReactionslDependence of Reaction Rates on Concentration of Reactantsrate k [A]m [B]nmmmmm[ ] is the concentration of the corresponding reactant in moles per literk is referred to as the rate constantm is the order of the reaction with respect to An is the order of the reaction with respect to Bm n is the overall reaction orderMCAT-Prep.com The Only Prep You Need Page 9 of 12
MCAT-Prep.com General Chemistry SummarylDependence of Reaction Rates upon Temperaturek A e-Ea/RTPotential Energy Diagrams: Exothermic vs. Endothermic ReactionslCatalysisEaEaEaEaEaPotential Energy Diagrams: Without and With a CatalystSaturation KineticsPage 10 of 12MCAT GENERAL CHEMISTRY SUMMARYEa
MCAT-Prep.com General Chemistry SummarylEquilibrium in Reversible Chemical ReactionsaA bBmlcC dD{Note: Catalysts speed up the rate of reaction without affecting Keq}Le Chatelier’s PrinciplemLe Chatelier’s principle states that whenever a perturbation is applied to a systemat equilibrium, the system evolves in such a way as to compensate for the appliedperturbation.mRelationship between the Equilibrium Constant and the Change in the Gibbs FreeEnergyΔG -R T ln KeqGold Standard MCAT General Chemistry Review: ElectrochemistrylllGeneralitiesmThe more positive the E value, the more likely the reaction will occur spontaneously aswritten.mThe strongest reducing agents have large negative E values.mThe strongest oxidizing agents have large positive E values.mThe oxidizing agent is reduced; the reducing agent is oxidized.Galvanic CellsmMnemonic: LEO is A GERCnLose Electrons Oxidation is AnodenGain Electrons Reduction at CathodeConcentration CellmNernst equationEcell E cell - (RT/nF)(ln Q)lFaraday’s LawmFaraday’s law relates the amount of elements deposited or gas liberated at an electrodedue to current.mOne mole ( Avogadro’s number) of electrons is called a faraday ( ).mA faraday is equivalent to 96 500 coulombs.mA coulomb is the amount of electricity that is transferred when a current of one ampereflows for one second (1C 1A . S).MCAT-Prep.com The Only Prep You Need Page 11 of 12
MCAT-prep.comThe Only Prep You Need Increase your chances of getting into the medical school of your choice with theseMCAT preparation resources.MCAT Prep Courses and Practice sesmcat-prep.com/mcat-practice-testsFree MCAT Practice Tests and Sample -prep.com/mcat-sample-questionsScience cat-prep.com/mcat-biochemistry-review-summaryMCAT com/mcat-study-schedule
Page 4 of 12 MCAT GENERAL CHEMISTRY SUMMARY MCAT-Prep.com General Chemistry Summary Gold Standard MCAT General Chemistry Review: Phases & Phase Equilibria l Standard Temperature and Pressure, Standard Molar Volume m 0 C (273.15 K) and 1.00 atm (101.33 kPa 760 mmHg 760 torr);










