Transcription
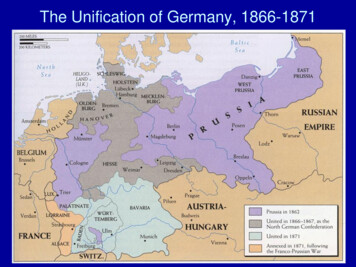
The Unification of Germany, 1866-1871
Definition of a Nation A group of people with a common cultureoccupying a particular territory with thefollowing shared bonds.– A sense of ethnocentrism – one’s own peopleis the most important to you.– Language.– History.– Religion.– Traditional homeland.– A sense of a common destiny.
The Poles are a nation of people in the late 1800sWhere are they?3
State & Nation-State Definition of a state – a political unit thatforms a federal government, boundaries &has sovereignty over a territory. (a country) Definition of a nation-state – a state whoseterritory coincides with that occupied by adistinct nation of people.– An independent govt. with a capital.– National boundaries.– Sovereignty.
What do the Poles have today?Nation-State
Nationalism Definition of nationalism:– A strong feeling of pride in & devotion toyour nation of people.– A national consciousness.– Primary allegiance to one nation-stateabove all others. Nationalism was the most powerful idea ofthe 1800s. Nationalism unified the German kingdomsinto a German Empire by 1871.
Wilhelm I, King of Prussia from 1861-18881st German emperor (Kaiser) from 1871-1888Bad hairdayHohenzollern Dynasty7
Hohenzollern Dynasty’s ancestral castle8
Otto von Bismarck Prussian. Conservative, monarchist, &nationalist. Skillful diplomat. Prime Minister for KingWilhelm I of Prussia, 18621888. Later Chancellor for theGerman Empire, 1871-1890. Believed Prussia shouldunite the different German9kingdoms.
German Unification The Deutschlandlied, 1841edition. Verses are an appeal for thecreation of a Greater Germany.A “Großdeutschland” “Deutschland, Deutschland,über alles, über alles en derWelt.” Bismarck did not want Austriaincluded. He wanted a“Kleindeutschland.”
Deutschlandlied, 1841 version(German national anthem, and, Deutschland über alles,Germany, Germany above all,Über alles in der Welt,Above everything in the world,Wenn es stets zu Schutz und TrutzeWhen always, for protection,Brüderlich zusammenhält,We stand together as brothers.Von der Maas bis an die Memel,From the Maas to the MemelVon der Etsch bis an den Belt -From the Etsch to the Belt -Deutschland, Deutschland über alles,Germany, Germany above allÜber alles in der Welt.Above all in the world.The modern verses to Germany’snational anthem are different. Why?
Geographic limits of the German language – by riversMemelBeltMaasEtschUnify all the German-speaking populations of Europe in asingle nation-state
“über alles” – “before/over all”Call to abandon former allegiances & simply be German
Frankfurt Assembly,1848 First elected parliament withreps. from the differentGerman states. Proposed a unified Germannation-state. Proposed a tri-color flag. Proposed a constitutionalmonarchy & kaiser. Friedrich Wilhelm IV ofPrussia refused the offerbecause of “divine right.”
Bismarck’s “Blood and Iron” SpeechSept. 30, 1862“Prussia's boundaries . . .arenot favorable to a healthystate life. The great questionof the time will not beresolved by speeches andmajority decisions . . . but by“iron and blood.”17
Carl von Clausewitz Prussian general &strategist of theNapoleonic War, A military theorist whowrote On War, 1832. "War is thecontinuation of politicsby other means."18
Otto von Bismarck & “Realpolitik” Politics or diplomacybased primarily onpower & practicalfactors, not on morality. Bismarck manipulatedindividuals & situationsto achieve Germanunification underPrussian leadership.19
Any similarities in their beliefs?MachiavelliClausewitzBismarck20
Bismarck set up three wars to achieve hispolitical aim - the unification of Germany.21
First two wars of German unification Prussia & Austria vs. Denmark – 1864.– Temporary allies annex parts of Denmark.– Dress rehearsal for Prussian army. Prussia vs. Austria & German allies – 1866.– Prussia wins in 7 weeks.– Prussia annexes lands ofAustria’s German allies.– Prussia became the leader ofGerman unification.22
Military factors in Prussia’s victories Universal conscription –three years of activeservice.– Larger army.– Better trained army. Prussian army reservesbased on local corps.– Faster to mobilize. More extensive railroadnetwork.– Rapid movement oftroops & supplies.Helmuth von Moltke theElder, Chief of Staff of thePrussian Army23
Military factor in Prussia’s victories Prussians equipped with single-shot breech-loadingrifles, while their enemies in the first two wars werestill using muzzle-loading rifles.24
German Railroads, 1861Do they play a role in Prussia’s war plans?25
Impact of Industrial Revolution on War26
Prussia moved 285,000 men over five railway lines &concentrated them in 25 days . Austria has only one railwayline & it will take her 45 days to assemble 200,000 men27
Austria’s German allies in war against Prussia28
The North German Confederation, 1866-18713 southern Germankingdoms not in theConfederation (yet)29
Emperor Napoleon III of FranceI wantto belike Louis-NapoléonBonaparte. Nephew of Napoleon I. President of the FrenchSecond Republic,1848-1851 (74% ofpop. vote). Coup d'état, 1851. Emperor of the SecondFrench Empire, 1851301870.
Emperor Napoleon III of France, 1851-1870 Aggressive leader whowanted his uncle’sglory. Feared Prussiagrowing power.Europe. Wanted a war withPrussia.31
32
Bismarck & The Franco-Prussian War, 1870-71 Knew southernGerman kingdomsfeared a Frenchinvasion. If France started a war,the southern Germankingdoms wouldprobably join Prussia.33
A Problem in Spainearly 1870 Spain offered itsvacant throne to theHohenzollern PrinceLeopold. Napoleon III objectedto threat of beingsurrounded byHohenzollerns. July 1870 Leopolddeclined the offer.34
Napoleon III was suffering from gallstones35
Napoleon III was suffering from gallstones36
Bad Ems – a German spa37
The Ems Telegram, July 1870 The Frenchambassador deliveredmessage to Wilhelm Iat Bad Ems. Napoleon IIIdemanded assurancethere would be nomore attempts to put aHohenzollern prince inSpain. Wilhelm I refused; senta telegram to38Bismarck.
Bismarck releasedan edited telegram-read like Wilhelm Iinsulted France. Napoleon IIIdeclared war onPrussia, July 1870.39
The Franco-Prussian War, July 1870 –May 187142
North German Confederation 3 southernGerman kingdoms vs. France.What thesouthernkingdomsfeared43
44
Prussia & other German allies easily defeatedFrance Battle of Sedan,Aug.-Sept. 1870 French army of104,000encircled byPrussia & allies. French armysurrendered. Napoleon IIIcaptured, wentinto exile inGreat Britain.45
Napoleon III surrendered to Wilhelm ISeptember 1870 after French defeat at Sedan.46
Brandenberg Gate, Berlin, Sept. 1870"What a change through God's guidance"47
German artillery at Sedan48
Mitrailleuse – early French machine gun49
French Chassepot bolt-action rifle50
Prussia & other German allies easily defeated France Second French army of 180,000 surrendered atBattle of Metz, Oct. 1870. Paris revolted & overthrew Napoleon III'sSecond Empire. Third Republic declared.– Paris under siege for 130 days.– French govt. surrendered Jan. 1871. Prussian army occupied Paris; victory paradethrough Arch of Triumph.51
52
Siege of Paris, 187153
Krupp siege artillery bombarded Paris54
Prussian Victory Parade, Paris, 187155
2nd German victory march in Paris, Aug. 194056
German Empire was Proclaimed, Jan. 18, 1871 Ceremony in the Hall ofMirrors at Versailles. Wilhelm I crownedemperor - "Kaiser" ofthe Second “Reich”(empire). Germany – now themajor land power inEurope. France humiliated &wanted revenge.It’s a good timeto be German!57
“The Proclamation of Wilhelm as Kaiser of the newGerman Reich, in the Hall of Mirrors at Versailles”58
59
Treaty of Frankfurt, May 1871 France lostAlsace &Lorraine. France paid 5billion francs inwar reparations.61
Area ofFranceoccupieduntil the warreparationswere paid62
French statue personifying the loss ofAlsace-Lorraine Bismarck opposedthe transfer ofAlsace-Lorraine tothe German Empire. Knew it would createa French hatred ofGermany. Prussian generalsconvinced Wilhelm Iit was necessary fordefense.63
The Germania statue - overlooks the Rhine River64
Germania“In memory of theunanimousvictorious uprising ofthe German Peopleand the creation ofthe German Empire1870-1871.”65
Kulturkampf - "culture struggle"Bismarck’s policy to make Prussia secular & reduce thepower of the Catholic Church in Prussia, 1871 - 1880.
Otto von Bismarck quotationsA generation that has taken a beating isalways followed by a generation that dealsone.I am bored. The great things are done.The German Reich is made.Some damned foolish thing in the Balkanswill provoke the next war.
Largest ancestry in U.S. counties is German (light blue)About 50 million claim German ancestry – 17% of U.S. pop.
Napoleon III, wife & son granted exile inGreat Britain70
Napoleon III & family buried in the crypt ofSt. Michael’s Abbey in the UK71
Napoléon Eugène LouisJean Joseph(Napoleon IV), PrinceImperial, 1856-187972
The Prince Imperial was a cadet at theRoyal Military Academy in the U.K.73
Zulu War, 1879, southern AfricaPrince Imperial’s mother petitioned Queen Victoriato allow her son to go with the British army74
75
While on a reconnaissance mission, he wasambushed and killed by Zulus76
The tomb of thePrince Imperial By his father andmother77
First two wars of German unification Prussia & Austria vs. Denmark –1864. –Temporary allies annex parts of Denmark. –Dress rehearsal for Prussian army. Prussia vs. Austria & German allies –1866. –Prussia wins in 7 weeks. –Prussia a