Transcription
Managed Care BillingThe Claim Submission And Adjudication ProcessHow does it impact you?Page 1
Bonadio Receivable Solutions, LLC hasbeen a division of The Bonadio Groupsince 2008The Bonadio Group is the only independentaccounting firm with a division that specializes inaccounts receivable managementPage 2
Average Costs of Electronic TransactionsElectronic Transaction Savings Opportunities for PhysicianPractices, Milliman USAHIPAA StandardTransactionsPaper ClaimElectronic ClaimClaims * 6.63 2.90Eligibility Verification 3.70 0.74Preauthorization 10.78 2.07Payment Posting 2.96 1.48Claim Status 3.70 0.37*Includes the cost of administrative overhead to produce, submit and process, aswell as a 12-month amortization of electronic set-up costsPage 3
HIPAA Standard TransactionsHIPAA Standard TransactionsASC X 12 IdentifierTransaction270 / 271Eligibility Inquiry / Response276 / 277Claim status inquiry / Response835Payment and Remittance Advice837 P and IClaim (P professional, I institutional)Page 4
Typical Payer Workflow1.Receive claim in administrative system2.Determine patients’ eligibility/benefit level and validate provider data3.Review for prior authorization4.Apply claim edits5.Apply pricing claim edits6.Complete adjudication7.Generate EOB/RA8.Send paymentPage 5
Typical Payer Workflow1. Receive claim in administrative system Electronic claims – Data extraction/verification occurs, accept/”receive”claim and send acknowledgement report Paper claims – date stamp and scans into document managementsystem that assigns a claim routing number. May then route to specificclaims processor who manually enters it into the administrative system.Data extraction/verification then occurs. Many payers now use software thatcombines scanning, image processing andrecognition technologies (data captureworkflow) which reads/interprets the claimsdata and analyzes, corrects and validatesthe data which reduces the need for manualerror corrections.Page 6
Claims Submission Methodologies Paper Electronic claims via a direct connection between billingsystem and payer Electronic claims via a clearinghouse Payer offers a direct data entry (DDE) methodology Medicare – FISS (OmniPro) Medicaid – ePACES Wellcare – DDE Portal Others?Page 7
What Is a Clearinghouse? Vendor that serves as a middleman between facility andpayers for claims submission Rather than facility sending electronic claims to each payer asa separate transmission the clearinghouse is a central portalto submit transmissions to multiple payers Clearinghouse forwards each claim to the appropriate payer Often provides other valuable billing-related servicesPage 8
Benefits Of A Clearinghouse Payers require test claim transmissions before they issue youa submitter number – clearinghouse handles this Claims submission software (may be the facility depending onbilling system) must stay up to date and adjust when a payerchanges rules – clearinghouse handles this If a payer doesn’t accept electronic claims a clearinghouseconverts the electronic file to paper claims and forwards them Should run claim edits to verify that all fields are completed –helps ensure a “clean claim” 10-digit NPI, valid ICD-9, valid CPT, valid date formats, etc. Quickly generates report of errors for timely resubmissionPage 9
Benefits Of A Clearinghouse (continued) Electronic eligibility verification Claim status checks Secondary payer billing services Patient statement printing and mailing Patient payment portalPage 10
Selecting a Clearinghouse Cost versus benefit analysis Evaluate clearinghouse to ensure that it supports the majorityof the payers you bill Can it accommodate the output from your billing system? Can it submit claims in the required format – professional,institutional, proprietary modifications? If you have an old system that can’t create a HIPAA 837(electronic claim) the clearinghouse must be able to accept aprint image (electronic flat file format) Requires billing system to generate a claims submission batchfile and transmit the print image of its claims- This is inefficient – get a new systemPage 11
Typical Payer Workflow2. Determine patients’ eligibility/benefit level and validprovider data Determines if patient is a “match” intheir administrative system Determines if patient is eligible toreceive benefits for the date ofservice- If eligible, determines whetherservices are covered servicesaccording to the patient’s benefitplan Verify NPI, tax ID, participating provider, etc.Page 12
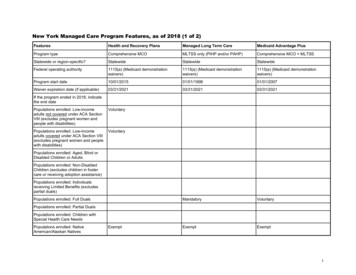
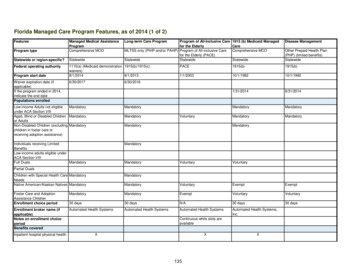
Enrollment – CB-LTC MLTC for dual eligible if in mandatory county & CB-LTC for 120 days Current recipients of Medicaid CB-LTC Services (Personal Care, CHHA,Adult Day Care, Private Nursing, Lombardi) Transition to MLTC through mandatory enrollment process Receive series of notices- Announcement letter 60-day choice letter (NY Medicaid CHOICE aka Maximus) and Managed CareGuide Choose or be auto enrolled Enroll with MLTC or Medicaid Advantage Plus or PACE-If Medicaid Advantage Plus or PACE – must enroll directly with plan New applicants to CB-LTC Services If no Medicaid, apply at local DSS and when approved enroll in MLTCPage 13
Enrollment – CB-LTC (continued) There are no Medicaid pending services in MLTC CHHA – possible if they are willing Can be dis-enrolled if sabotage care, not cooperate, not payspend-down, other reasons Note about delivery of care: 90-day Transition Period – ALL care must remain the same (not applywhen switch plans) After Transition Period – MLTC will sent client new Plan of Care, effectiveno earlier than day 91 Client may appeal by requesting an Internal Appeal with the MLTC State Fair Hearing option only when lose Internal AppealPage 14
Enrollment – Nursing Home Pending Federal Approval (postponed once already) Seniors and People with Disabilities who have Medicare have to enrollin a MLTC to get nursing home care Those with Medicaid only with no Medicare have to enroll in a“mainstream” Medicaid Managed Care plan to get nursing home care June 2014 – NYC, Long Island, Westchester December 2014 – Rest of state ALL adult Medicaid recipients age 21 who become permanentNH residents (after June/December 2014) required to enroll inManaged Care Plan MLTC for dual eligible Mainstream Medicaid Managed Care for those w/o MedicarePage 15
Enrollment – Nursing Home (continued) New Admission w/o MLTC or Mainstream Medicaid ManagedCare Plan Apply for institutional Medicaid, after approved, choose MLTC within 60 days If not select, will be assigned in a plan nursing home contracts with NY Medicaid CHOICE assists with education, selection and enrollment New Admission with Mainstream Medicaid Managed Care Plan Must enter a nursing home that participates in plan New temporary Admission with MLTC – can go to anywhere, plan can’trestrict Probably will be under Medicare coverage and plan will pay coinsurance if noMedigap coverage Current resident with Medicaid – grandfathered but will have eventualvoluntary enrollment in MLTCPage 16
Enrollment NY Medicaid CHOICE assists with education, selection andenrollment for MLTC plans NY Medicaid CHOICE does NOT assist with MedicaidAdvantage Plan or PACE enrollment 2 transactions: 1st Medicare Advantage and then a connectedMedicaid plan Client can switch MLTC plans at any time in the month Change effective date: 1st of next month or the following monthPage 17
Enrollment (continued) How will you track initialenrollment? How will you track dis-enrollments and changes? Who? Schedule? Develop P&P Failure to track will result inthe in-ability to bill correct payerPage 18
Eligibility/Insurance Verification Medicare, Medicare Advantage Plan, Medicare Part D,Supplemental Plans, Medigap, Commercial Plans, Medicaid,Medicaid Managed Care, Medicaid Long Term CareExample Scenarios: Dual Eligible with original Medicare, Medicare Part D, Medigap andMLTC will have 5 insurance cards Medicare, Medicare Part D, Medigap, Medicaid and MLTC Dual Eligible with Medicare Advantage and MLTC will have 3 cards Medicare Advantage, Medicaid, MLTC Dual eligible with Medicaid Advantage Plus will have one cardPage 19
Eligibility/Insurance Verification (cont’d) ePACES Carefully look at eligibility codes (institutional Medicaid, spend down, etc.) Follow up as needed Medicare Common Working File Need to check for each patient – not just Medicare admissions CWF isn’t always correct – follow up on inconsistencies Clearinghouse Contact/verify each insurance Document every call/contact in your billingsystem Verification completed before admissionPage 20
Participating Providers Contracts will likely require credentialing MMCP will credential NH but will “minimize additional NHrequirements” Is CAQH UPD (Council for Affordable Quality HealthcareUniversal Provider Datasource) utilized by payer? What types of providers will have to be credentialed? MD, NP/PA, CNM, LCSW, LMHC, LMFT, PT/OT/SP, AuD Will billing office complete forms and monitor credentialingprogress? Time consuming Already overworked billing staffPage 21
CredentialingPayer and PlanCredentialing(on-line Provider Manuals April 2014)Fidelis Care (All Plans)CAQH other required documentsMD/DO, NP, PA, PT, OT, CNMWellCareCAQH not indicatedMD/DO, Allied Health Professionals (AHP), homehealth agencies, SNF, other ancillaryfacilities/health care delivery organizations.AHP includes but not limited to (NP, PA, CNM,LCSW, LMHC, LMFT, PT, OT, SP, Audiologist)VNSNY CHOICE (All Plans)CAQH not indicatedMD/DO and all other health professionals andfacilities who are permitted to practiceindependently under State lawPage 22
Typical Payer Workflow3. Review for prior authorization Was prior authorization required? Is prior authorization number on claim? Validate prior authorization numberPage 23
Prior-Authorization Can be very time consuming ALWAYS verify if an authorization is needed and for what services Payer requirements change and payers often require prior-auths for some plansbut not others Fax, phone, on-line portal, specific form? Document contact and telephone numbersfor future authorization extensions Document every call/contact Coordinate between billing and prior auth staff When/how/does billing get authorization number? Don’t just write off claims denied for noauthorization Attempt to obtain a retroactive authorizationPage 24
Prior Authorization (continued)Payer and PlanPrior Authorization(on-line Provider Manuals April 2014)Fidelis CarePre-authorization obtained by QualityHealth Care Management (QHCM)Department. Request should be sent atleast 5 days before DOS.Fidelis Care at Home (FCAH)All non-emergency services must beauthorized by Nurse Care ManagerFidelis Medicare Advantage (4 plansoffered)No prior-authorization. Out of networkservices have higher out of pocket cost.Fidelis Medicare Advantage – DualAdvantage PlansNo prior-authorization. All care (excludingemergent/urgent) must be in-network.Fidelis Medicaid Advantage PlusAll services must be coordinated by NurseCare ManagerWellCareRequired for elective and non-urgentservicesPage 25
Prior Authorization (continued)Payer and PlanPrior Authorization(on-line Provider Manuals April 2014)VNSNY CHOICE Medicare AdvantageAll elective admissions, outpatientsurgery outpatient treatment/testing ifdone out of network. Specific list for innetwork.VNSNY CHOICE SelectHealthSpecific list availableVNSNY CHOICE MLTCAdult Day Services, Audiology, Choreand Housekeeping, Home Care, HomeDelivered Meals, Home SafetyModification, Med/Surg Supplies/Equip,Nursing Home Care, NutritionalSupplements, OP Rehab, PERS, Podiatry(if non-Medicare covered), TransportationPage 26
Ongoing Authorization Considerations Ongoing Authorizations When updated? What forms are used? What triggers a reassessment? Is there a portal or other electronic method used? What department oversees the authorizations? Does/when/how billing department get/need/use theauthorization?Page 27
Typical Payer Workflow4. Apply claim edits Determines whether specific codes and combinations of codesare eligible for paymentPage 28
Typical Payer Workflow4. Apply claim edits (continued) Payers use CPT, NCCI (National Correct Coding Initiative) and CMSpayment rules Other common proprietary claim edits Correct claim format – UB04 or 1500 Billed contracted rate Specific revenue codes and modifiers used Missing condition/value/occurrence/CPT Itemized or room/board line Non-covered services Timely filing Duplicate claim Missing NPI, member ID Incorrect payerPage 29
Claim Edits Common claim edits (CPT, NCCI, CMS, etc.) Medicare Billing Error Rate: 11% 34.3 Billion Use editing software Build into your billing system Possible to achieve denial rates less than 1% (benchmark 3%) Claims editing software Substantially lowers administrative costs associated with billing Improved compliance with reimbursement guidelines Improved revenue cycle from a reduction in inaccurate claims andsubmissions Reduced audit risks Rapid return on investmentPage 30
Claim Edits Common claim edits (CPT, NCCI, CMS, etc.) (cont’d) Clearinghouse editingPage 31
Timely Filing Timely Filing Considerations Know timely filing requirements Easiest way to file timely - Bill Monthly! Claims should be sent by the 15th of thefollowing month Keep claims alive through follow up Document every submission, mailing, phone call, letter, etc.in the billing system Make sure claim is received – fax, registered mail, deliver inperson, clearinghouse acknowledgement reports Appeal before write off if claim denied for timely filing andclaim has been kept alivePage 32
Timely Filing (continued)Payer and PlanTimely Filing(on-line Provider Manuals April 2014)Fidelis Care at Home (FCAH)90 daysFidelis Medicare Advantage (4 plansoffered plus 2 Fidelis Dual Advantageplans)Not indicatedFidelis Medicaid Advantage Plus90 daysWellCare180 days, 90 days after primary paymentwhen WellCare is secondary payerVNSNY CHOICEPer contractVNSNY CHOICE MLTC – Nursing Home90 days after end of month servicesrenderedVNSNY CHOICE MLTC – TransportationNot indicatedPage 33
Typical Payer Workflow5. Apply pricing claim edits Paper claims: Claims processor manually enters each line into its administrativesystem and in some cases the claims processor manually reviews theline items during data entry to make the non-fee determinations(covered services, down-coded, bundled) Electronic claims: System adjudicates using complex series of claim edits thatdetermines fee schedule, allowed amount, contracted rate and thenadjusts rate to reflect additional adjustmentsPage 34
Payment AccuracyContracted Fee Schedule Match Rate2013 National Health Insurer Report Card hemCignaHCSCHumanaRegenceUHCMedicarePage 35
Payment Accuracy (continued) Underpayment concerns 2.5% error rate on 3M 75,000 Know what you should be paid Establish process to ensurepayments are correct Store rate in billing system andperform automatic cross checks Review payment exceptionreports and follow up onunderpaid claims Review how each staff handles- w/o as contractual?Page 36
Typical Payer Workflow6. Complete adjudication Determines the level at which the claim will be paid Issue denial Issue paymentPage 37
How To Handle Denials Know each payer’s appeal process Time limits Specific forms Internal Process Who gathers necessary documents? Who submits? Who monitors progress? Report final decision to interestedparties? What can be learned from denials?Page 38
Claim AppealsPayer and PlanAppeals/Disputes/Reconsiderations(on-line Provide Manuals April 2014)Fidelis CareMedical necessity appeal - Submit within 60 daysAdministrative denial reconsideration (timely filing, co-insurance, eligibility,lacking pre-auth, other errors on claim, underpayments) – Submit within 60daysTimely filing – penalty of up to 25% may be imposedWellCareTimely filing, incidental procedures, bundling, unlisted procedure codes, noncovered, etc. – Submit within 6 years of the date of denialVNSNY CHOICE –MCare and MCaidAdvantage PlansDisputes resulting from claim adjustments or denials:Standard reconsideration request - denial of payment or medical necessity –per contractVNSNY CHOICE –Medicaid MLTCDisputes resulting from claim adjustments or denials:Standard reconsideration request – denial of payment or medical necessity per contractRequest for denial of payment due to claim coding – Submit within 90 daysRequest for denial of payment due to no authorization – Submit within 90 daysPage 39
Typical Payer Workflow6.Complete adjudication (continued) Approves payment Queued into a payment register or “topay” system Places claim in the cycle for the nextcheck run During check run payer cuts checkand mails or processes EFT With electronic remittances: processesthe 835 EOB/RA and sends it tofacility or clearinghouse Paper or electronic EOB/RA may ormay not accompany paper check orEFTPage 40
Typical Payer Workflow7. Generate EOB/RA (explanation of benefits/remittanceadvice) Sends a paper or an electronic 835 to you and the patient thatdetails the allowed amount, contracted adjustment amount, thepaid amount and the patient responsibilityPage 41
Review EOB/RA Use the information to process and post payments andadjustments to billing system Make sure to reconcile against payment Evaluate EOB/RA for accuracy to detect processing errors(inappropriate CPT changes, inaccurate reimbursementrates, quantity of services not recognized, etc.) Standard remittance advice remark codes? Know how to handle each codePage 42
Typical Payer Workflow8. Send Payment Payment transmission or EFT Review payment and the remittance information for consistency withthe information on the EOB/RA as well as the information from theoriginal claim submitted EOB/RA should show reasons (remark codes) for partial payments Denied claims will appear as a zero remittance EOB/RAPage 43
Communication With Payer Communication Tips Training provided? Billing, Prior Authorization, etc. Online access to provider and billing manuals? Billing department needs contract, providerand billing manuals that are easily accessible Develop a summary page of key points foreach contract and keep updated Ask questions Don’t assume you know the answers Don’t assume payer always knows the right answer either-Follow up on inconsistenciesPage 44
Communication With Payer Communication Tips (continued) Provider representatives: Make sure you are assigned a provider representative Develop a partnership with each payer via their representative Request and hold regular meetings with representatives Realize that representatives would much rather help up front thandeal with you when you are frustratedPage 45
Provider Manuals Fidelis Medicare/Medicaid/FHP/CHP/MLTC (numerous versions/dates) Section 22A – Fidelis Medicare Advantage (V11-1/1/11) Section 22B – Fidelis Care At Home (V13.0-12/9/13) Section 22c – Medicaid Advantage Plus (V13.0-12/9/13) WellCare (June 17, 2013) VNSNY Choice (12/27/13) Many sections broken into sub-sections for VNSNY CHOICE Medicare Advantage Plans VNSNY CHOICE Select Health VNSNY CHOICE Managed Long Term Care PlanPage 46
Page 47
Andrea Hagen, ManagerBonadio Receivable Solutions, LLC171 Sully’s TrailPittsford, NY 14534Office (585) 249-2814 Cell (585) 967-3716ahagen@bonadio.comwww.bonadio.com
VNSNY CHOICE MLTC . Adult Day Services, Audiology, Chore and Housekeeping, Home Care, Home Delivered Meals, Home Safety Modification, Med/Surg Supplies/Equip, Nursing Home Care, Nutritional Supplements, OP Rehab, PER