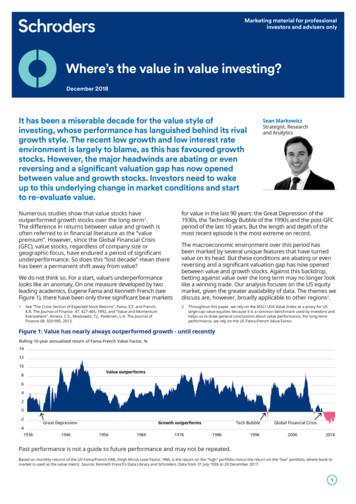
Transcription
The Value ofVulnerabilityManagement**ISACA/IIA DallasPresented by:Robert Buchheit, DirectorAdvisory Practice, DallasRicky Allen, ManagerAdvisory Practice, Houston*connectedthinkingPwC
AgendaThe need for Vulnerability ManagementCommon VulnerabilitiesVulnerability Management DefinedFive Step Vulnerability Management ProcessVulnerability Management BenefitsClosingThe Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersJanuary 2006Slide 2
The Problem:IT costs are spiraling out of control and are among the top 5corporate expenditures. On average, 15-25% of IT spending iswasted* and budgets are increased by only 5% per year.Information Security expenses are rising due to an alarmingnumber of new vulnerabilities and compliance requirements(source: Aberdeen, The Strategic IT Budget Report RealitiesBenchmark Report, Bill Malik, Oct 2004)U.S. Companies spent an estimated 15.5B in 2005 oncompliance and will spend 80B in 2005 through 2009 to ensurecompliance with regulatory requirements (source: AMR)The Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersJanuary 2006Slide 3
What is the cost of an incident? ChoicePoint granted unauthorizedaccess to 145,000 customeraccounts and spent 11.4 million ininternal costs to remediate. Marketcapitalization dropped by 720millionIdentity Theft Protection Act 11k – 11 million fine per incident21 States currently requiredcustomers to be notified when theirpersonal data has been lostCustomer data compromise costeach company between 14 and 50 millionThe Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopers Average total recovery costs were 140 per lost customer record- Lost Customer Information:What Does a Data Breach CostCompanies, Ponemon InstituteFBI/CSI Survey showed anaverage loss of proprietaryinformation to be 355,552.95% of successful attacks are fromknown vulnerabilities according toCERTCERT reported that 5,990 newvulnerabilities were discovered in2005, a 158% increase over 2004.January 2006Slide 4
What is a vulnerability?“A weakness of an asset or group of assets that can be exploitedby one or more threats” (source: ISO 17799:2005)Common vulnerabilities:Un-patched or out of date softwareDefault or weak system passwordsUntrained users (lack of security awareness)Weaknesses in facilities or infrastructureA vulnerability is more than just a technical issue, it can be a weakness inANY asset, process, or a policy violation which can be exploited tocompromise security.The Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersJanuary 2006Slide 5
Traditional Vulnerability AssessmentVulnerability assessments has been a key part of mostinformation security programs. Traditionally, vulnerabilityassessment has been a pure technical solution withoutremediation processes and business unit involvement.Standard Issues Include: Technology driven program Expert technical knowledge required Tried to remediate ALL identified vulnerabilities Difficult to track the never ending process Limited by capabilities of assessment toolsThe Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersJanuary 2006Slide 6
What is Vulnerability Management?The people, processes, and technology used to reduce the exposure ofcorporate assets. Vulnerability management addresses the entire lifecyclefrom identification to remediation. Many issues point to the need forvulnerability management:Audit ReportsRegulatoryRequirementsPolicy ViolationsAssessment ineVarianceVendor PatchesSecurityIntelligenceThe Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersJanuary 2006Slide 7
Five Step Vulnerability Management ProcessAssessAnalyze Determinecurrentsecurityinitiatives CollectInformationfrom variousfeeds StaffCapabilities Identifyvulnerabilities LeverageAssetManagement Determineroot causesThe Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersStrategize Develop anaction plan forremediation Develop aneffective riskweightingsystem forvulnerabilities Utilizebusinessunderstandingto prioritizevulnerabilitiesAlign Alignpriorities withIT to reducevulnerabilitieson criticalsystems Align withother ITprocesses toreduce theeffort ofremediationCommunicate Communicatethe value ofremediationefforts Difficultiescommunicatingtechnicalissues to abusinessaudienceJanuary 2006Slide 8
AssessXYZ[\AnalyzeStrategizeAlignCommunicateAssess the environment by collecting information through interviews, scanning,diagrams and documentation. Determine what regulatory, compliance and industryrequirements are involved with managing vulnerabilities.Determine if assets have been classified for business criticality and are trackedthrough an asset management database. Discover rogue systems and devices andbegin efforts to identify owners for the business need for unmanaged technologies.Assess the existing infrastructure to identify security policies and risk managementmodels. Translate policies to technical checks such as the enforcement of an 8character password or the use of default system passwords.Understand the resources that belong to your organization and which do not. Areliable asset management process is necessary for the success of anyvulnerability management program. The asset management solution should beable to tie into the help desk and trouble ticket system for centralized tracking.Identify and understand current business and technology objectives that requiresecurity involvement. Identify business drivers and how IT and security can drive theresults.The Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersJanuary 2006Slide 9
Vulnerability Identification Capability CurveNo vulnerability identificationAd hoc vulnerability identificationPeriodic vulnerability assessmentsRiskTargetManaged assessment programCurrentRogue technology identification programAutomated compliance testingCentralized vulnerability detectionFutureStateFundamentalTacticalThe Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersStrategicJanuary 2006Slide 10
ty Intelligence information can significantly decrease the time required to applyand deploy patches in the organization. A database is maintained with yourtechnologies and Alerts will only be sent when you are affected.Analyze existing audit and security reports to identify existing security weaknesses.Review Sarbanes Oxley IT or SAS70 Controls to identify critical systems in theenvironment.Vulnerability scan output should be analyzed to remove false positives andinsignificant findings. Track the new, reoccurring and corrected vulnerabilities.Identify change control windows allowed for scanning across the organization.Work with IT management to obtained an agreed upon time and intensity ofscanning. Regardless to the tool or methodology, a risk exists to crash theserver.Analyze the identified vulnerabilities to make sense of the information. Combine orremove vulnerabilities and identify root causes.The Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersJanuary 2006Slide 11
s strategy to evaluate identified vulnerabilities and determine false positives,criticality and feasibility. Determine the acceptable limit of false positives allowed ineach report. Work with the vulnerability assessment tool vendor to reduce the numberof false positives.Prioritization and validation of vulnerabilities is one of the most time consuming butimportant steps. Work within configuration baselines for each technology to identifyand document the remediation steps required.Develop an effective risk weighting system for vulnerabilities which takes businessprocesses, asset value and likelihood to determine risk ratings. See the vulnerabilityevaluation checklist*Focus on the high risk areas for the company first to protect perimeters and criticalbusiness applications. All of the identified vulnerabilities (potentially 10,000 ) donot need to be corrected immediately.Combine reports from various tools and processes to obtain a holistic understanding ofthe risk to the applicable applications, technology, processes and personnel.The Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersJanuary 2006Slide 12
Vulnerability Evaluation Checklist Does the vulnerability affect systems within the organization’s network? Are critical business systems impacted by the vulnerability? Do hosts run the vulnerable version of software? Can the vulnerability be exploited remotely? Is a patch available for the identified vulnerability? What is the relative ranking provided by the vendor or assessment tool? How prevalent is the vulnerable application on the network? Can the vulnerability be mitigated? Are there exploits available for this vulnerability? Has a propagating worm been developed? Do security policies and standards need to be updated in response to thisvulnerability?The Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersJanuary 2006Slide 13
AssessXYZ[\AnalyzeStrategizeAlignCommunicateAlign priority vulnerabilities with asset classification to remediate the highest risksystems first. Leverage deployment and configuration management technology forspeedy remediation.Change control and testing processes are important when deploying and trackingsecurity remediation changes. Many vulnerability management products will integratewith existing trouble ticket systems, to effectively track time and resources.Significant cost savings can be realized by integrating software to automate thedeployment of remediation patches, changes and updates. Remediation is the mostimportant step of the entire process.Vulnerability management is dependent on other processes such asautomated patch management, change control and incident responseto effectively operate.Perform compliance monitoring through continued scans to verify the vulnerability iscorrected. System restores and new patches may reintroduce the vulnerability.The Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersJanuary 2006Slide 14
Vulnerability Remediation Capability CurveNo remediation processRiskAd hoc remediationprocessTargetCurrentDocumented remediation processAutomated remediation processIntegrated remediation processFundamental TacticalThe Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersStrategicFuture StateJanuary 2006Slide 15
icate the current status of the vulnerability management program tomanagement on monthly intervals. Define the key issues and challenges for yourorganizations security program and the progress you have made to achieve the goals.Integrate the vulnerability management progress with your other security initiatives.Map protection efforts against business applications and not just physical servers.Reporting should also created based on the existing organizational chart, usually bybusiness unit or geographic region.Identify the metrics that show creditable change in the organization. Traditionalmetrics such as; 40,375 vulnerabilities were identified should be replaced with; internalsecurity incidents are down 84% and system uptime is 99%.Identify efficiencies that can be gained by improving the process andcommunicate them to the vulnerability management team.While it may be difficult to show impact to corporations earnings, profitability andshareholder value, show how much you can save by reducing risk to the organizationand by being prepared for an incident to limit overall impact.The Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersJanuary 2006Slide 16
How to get resultsStrategizeParticipants Business unit and/or processAnalyzeAlignarea representatives Project Teams Information Security Information TechnologyAssess Risk / e Prioritized Remediation Roadmap Training requirements identified Maintenance organization identified Ongoing monitoring requirements identified Roles / responsibilities Effectiveness metrics Hardening Procedures Policies and procedures identified Enabling technology requirements identified Reduced Vulnerability Signature Response procedures Compliance programThe Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersJanuary 2006Slide 17
Where savings occurX Have a well defined process workflowY Reliable asset management processZ Efficient scanning and identification[ Drawing vulnerabilities from multiple processes and not just a technology\ Security intelligence services can reduce research time significantly] Integration with trouble ticket system to track compliance and cost Use of automated configuration management remediation toolsStandard platform baselines help define the gap and reduces vulnerabilities Reduce wasted time chasing down the system owner and location ofunmanaged systems.a Show executives that action is being taken and that the process is workingThe Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersJanuary 2006Slide 18
The Value of Vulnerability mgmtReactive measures are not enough to deal with currentvulnerabilities. Zero day attacks are here and worms canpropagate faster than we can deploy patches. The value of avulnerability management program: Increases compliance with regulatory issues (e.g., SOX,HIPAA, PCI) by enhancing the control network Creates increased transparency with management bycollecting and automating reports for executive dashboards Improves management of IT assets and processes Reduces risk by more effectively allocating controlsThe Value of Vulnerability ManagementPricewaterhouseCoopersJanuary 2006Slide 19
CISO Forum“There is still a tendency within security organizations to focus on reactivesecurity rather than taking a proactive approach. Reactive security appears,at first hand, to be less resource-consuming, with faster results and moreflexibility, but this is a misconception. In the medium to long term, reactivesecurity provides no scope for growth or adaptation and amounts to little morethan expensive firefighting.”“Proactive security requires early identification of the business and technicalrequirements that can give a security chief the necessary edge to build anorganization flexible and adaptable enough to provide holistic services,meeting both immediate need and providing structure for future growth.Taking the time to get it right in the early stages reaps huge benefits in thelong term.”Craig Thomas, Global CISO, PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
Questions?For more information and to download our latestWhitepaper: “How to align security with your strategicbusiness objectives”, please visit:www.pwc.com/techspotlightOther Questions:Robert y Allenrichard.allen@us.pwc.com713-356-5155 2006 PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP. All rights reserved. "PricewaterhouseCoopers" refers toPricewaterhouseCoopers LLP (a Delaware limited liability partnership) or, as the context requires, other memberfirms of PricewaterhouseCoopers International Ltd., each of which is a separate and independent legal entity.*connectedthinking is a trademark of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP.PwC
The Value of Vulnerability Management PricewaterhouseCoopers January 2006 What is Vulnerability Management? The people, processes, and technology used to reduce the exposure of corporate assets. Vulnerability management addresses the entire lifecycle from identification to remediation. Ma