Transcription
3/13/2019ComplianceChallenges forAdvancedPractice Providers Kim Huey, MJ, CHC, CPC, CCS-P,PCS, CPCO, COC Sandy Giangreco Brown, BS, RHIT,CCS, CCS-P, CHC, CPC, COC, CPC-I,COBGC HCCA Compliance Institute 2019DefinitionsAdvancedPracticeProviderCoding andBillingMedicareIncident-toSplit/SharedOther PayersCompliance IssuesOther Thoughts1
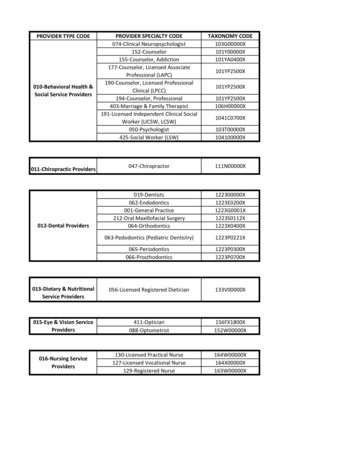
3/13/2019Advanced Practice ProvidersNon-Physician Practitioners Nurse Practitioner (APN, APRN,CRNP, etc.) Clinical Nurse Specialist Certified Nurse Midwife Physician AssistantDifferent rules for different insurers –Must pay attention to the patient’sinsurance when deciding how toutilize these providers in yourpractice.MedicareBilling options NPP’s own provider number Incident-to physician’s service Shared visitNurse Practitioners must have Master’s or Doctorate in Nursing (orcredentialed prior to 1/1/2003)Nurse Practitioners can be paid directly, but PA payment must go to theemployer.2
3/13/2019 Any services allowed by theAPP’s state scope of practiceAPP’sProviderNumber Reimbursed at 85% of thephysician fee schedule 100% for nurse midwives,beginning 1/1/2011 – previously65%“Incident-to” aMedicare termIncident-toAPP must beeligibleBilled under the physician’snumberPaid at 100% of the physician’sfee schedule3
3/13/2019Incident to a physician’sprofessional serviceIn the physician’s officeUnder the physician’sdirect supervisionFurnished by anindividual who qualifiesas an employee – eitherW-2 employee orcontracted employeeIncident-toRulesIncident-to a physician’s professional service An integral, though incidental part of the physician’s professionalservice– Following a plan of care established by the physician– Physician must perform initial service and be involved in subsequentservices of a “frequency which reflect active participation andmanagement”– Some MACs give more specific requirements – Cahaba, for example,requires cosignature Furnished in the physician’s office or clinic4
3/13/2019Under the physician’s direct supervision In the office suite and immediately available– What constitutes an office suite?– How do you prove immediately available? Supervision can be provided by another physician in thegroup practice– Service billed under supervising physician– Ordering physician’s name and NPI entered in box 17Employee of the Physician W-2 employee of the physician, group practice or legal entitythat employs the physician 1099 contracted/leased employee Under the control of the physician Must represent an expense to the physician, group practice, orlegal entity5
3/13/2019ServicesIncident-to anAPPServices performed by auxiliarypersonnel supervised by APP andfollowing plan of care establishedby APP.Billed under the provider whoordered the service and who issupervising – the APP, not thecollaborating physicianKGG Coding and Reimbursement Consulting, LLC - kimthecoder.comIncident-toBilling – CMSFinal Rule2016Appears to be clarification rather than new regs Must be billed under supervising physician (theone who is actually in the office at the time ofservice) Provider cannot be excluded from any federalprogram Provider can’t have had Medicare enrollmentrevoked In compliance with state law6
3/13/2019Shared VisitsInternet Only Manual section 30.6.1.B“When a hospital inpatient/hospital outpatient or emergency department E/M is sharedbetween a physician and an NPP from the same group practice and the physicianprovides any face-to-face portion of the E/M encounter with the patient, the servicemay be billed under either the physician’s or the NPP’s UPIN/PIN number. However,if there was no face-to-face encounter between the patient and the physician (e.g.,even if the physician participated in the service by only reviewing the patient’smedical record) then the service may only be billed under the NPP’s UPIN/PIN.Payment will be made at the appropriate physician fee schedule rate based on theUPIN/PIN entered on the claim.”Shared Visit DocumentationPer Terrence Kay, Director of the Division of Practitioner andAmbulatory Care in the Center for Medicare Management,CMS –“ any face-to-face portion of an E/M encounter (i.e., history,physical exam, or medical decision-making in whole or inpart). A social salutation alone does not constitute a face-toface portion or “physician work” of an E/M service.”7
3/13/2019DocumentationExamplesSharedServices A separate visit by thephysician detailing someportion of the E&M service Notations within the APP’snote – adding to or verifyingelements of the history orexam As long as there is evidence of a faceto-face service by both the MD andAPP, the work is combined and billedunder the MD – both must see thepatient in the hospital setting Must be clear what portions of theservice each performed “Seen and agree” not sufficient Expect to see documentation ofphysician repeating some portion ofthe examination or discussion withpatient Some MACs audit for “substantive”involvement of physician8
3/13/2019ProceduresNOT SharedVisitsWelcome toMedicareCritical CareMust still meet incident-toguidelinesIf visit dominated by andcoded based on counselingand coordination of care,can combine NPP andphysician timeShared Visits in the Office9
3/13/2019Take care not to confuse shared visit ruleswith Teaching Physician guidelines!Scribes CMS silent on scribes, other than that scribesdo NOT have to sign the record Some MACs have policies on scribes “Human Dictaphone” – cannot add anyobservations of their own (other than ROS andPFSH as allowed by DocumentationGuidelines) Must sign as “Scribed by --- for Dr. ---” Opinion: Suspicion of use of employee at thelevel of NPP as clerical staff10
3/13/2019CIGNA on Scribes If a nurse or mid-level provider (PA, NP, CNS) acts as a scribe for thephysician, the individual writing the note (or history or dischargesummary, or any entry in the record) should note "written by xxxx, actingas scribe for Dr. yyy." Then, Dr. yyyy should co-sign, indicating that thenote accurately reflects work and decisions made by him/her. Note: Thescribe is functioning as a “living recorder,” recording in real time theactions and words of the physician as they are done. If this is done inany other way, it is inappropriate. This should be clearly documented asnoted, by both the scribe and the physician. Failure to comply with theseinstructions may result in denial of claims. Always bill under APP’s number Always bill under MD’s number Documentation for visit determineshow to bill – may vary from patient-to-patient,visit-to-visitScenarios for MedicarePatients11
3/13/2019Limitation onLevel ofService? Officially no limitation on level ofservice billed Some consultants consider higher levelsof medical decision-making “what itmeans to be a physician” Some payers limit the levels of servicepayable to APPsOther Payers Some allow billing under the MD regardless of incident-toguidelines or physician presence Some credential separately and allow independent billing12
3/13/2019Other Payers ExampleDefinition of “incident-to” is not the same asMedicare– Physician must also see the patient on thedate of service– Not specified which portions of the serviceeach can perform– Billed under the physician and paid at thephysician fee scheduleOther Payers ExampleFor some payers, APPs can be credentialed andbilled under their own NPI– Payment may be based on patient’s contractbenefits– Only certain CPT codes (E&M codes andsome minor surgery – some exclude hospitalvisits)– Payment usually at 70-80% of physician feeschedule and may vary by CPT code)– Must be billed this way when the MD doesnot see the patient on the same date ofservice13
3/13/2019Other Payers ExampleAlabama Medicaid In order to bill under the physician, he/she mustalso see the patient on DOS APPs can bill under their own numbers only forcodes on the approved list– E&M codes paid at CRNP/PA fee schedule(but not hospital visits)– Laboratory codes paid at physician feeschedule– Injectables paid at physician fee schedule APPs can bill as assistant-at-surgery for certaincodes (orthopedic codes)Other Payers ExampleBCBS of Alabama –– Visit must be billed under the provider whodocuments the History of Present Illness14
3/13/2019 High number of visits billedunder physician’s providernumberComplianceIssues/RedFlags Physician did not knowhe/she was “supervisingphysician” Patient dissatisfactionAuditing Considerations - MedicareOffice Service – Need entire medical record - not just one DOS– Are incident-to requirements met? Established patient – established problem Previous visit to establish plan to treat this problem Visits by physician addressing this problem – does your MAC/payer establishfrequency requirements? Established patient – “minor” problem If requirements met, and more than 50% of the visit is counseling, can combineMD and NPP time– If requirements not met, must bill under APP’s own provider number15
3/13/2019Auditing Considerations - MedicareHospital Service– Admission, Subsequent Visit or Discharge Is there a face-to-face visit by the MD? Combine documentation from both MD and APP to determine level of service– Consultation Cannot combine documentation – must bill under either the MD or the NPP basedon each individual’s documentationNursing Facility Service– Must bill under APP’s own numberIncome distribution - forAPP and supervisingOtherIssues/ThoughtsNot just what income theAPP brings in, but whatthis provider frees up thephysician to do16
3/13/2019Resources Nurse Practitioner Scope of ?pageid 3465 American Academy of Physician Assistantshttp://www.aapa.org/ Medicare Benefit Policy Manual, chapter 15, section 60 df Medicare Claims Processing Manual, chapter 12, clm104c12.pdfKim Huey, MJ, CHC, CPC, CCS-P, PCS,CPCO, thecoderSandy Giangreco Brown, BS, RHIT, CCS,CCS-P, CHC, CPC, COC, CPC-I, COBGC970/581-5144giangrecosandy@gmail.com orsandy.giangrecobrown@claconnect.com17
Advanced Practice Provider Coding and Billing Definitions Medicare Incident-to Split/Shared Other Payers Compliance Issues Other Thoughts. 3/13/2019 2 Advanced Practice Providers Non-Physician Practitioners Nurse Practitioner (APN, APRN, .